Visualizing the Rising Tide: Understanding Water Level Rise Maps
Related Articles: Visualizing the Rising Tide: Understanding Water Level Rise Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Visualizing the Rising Tide: Understanding Water Level Rise Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Visualizing the Rising Tide: Understanding Water Level Rise Maps
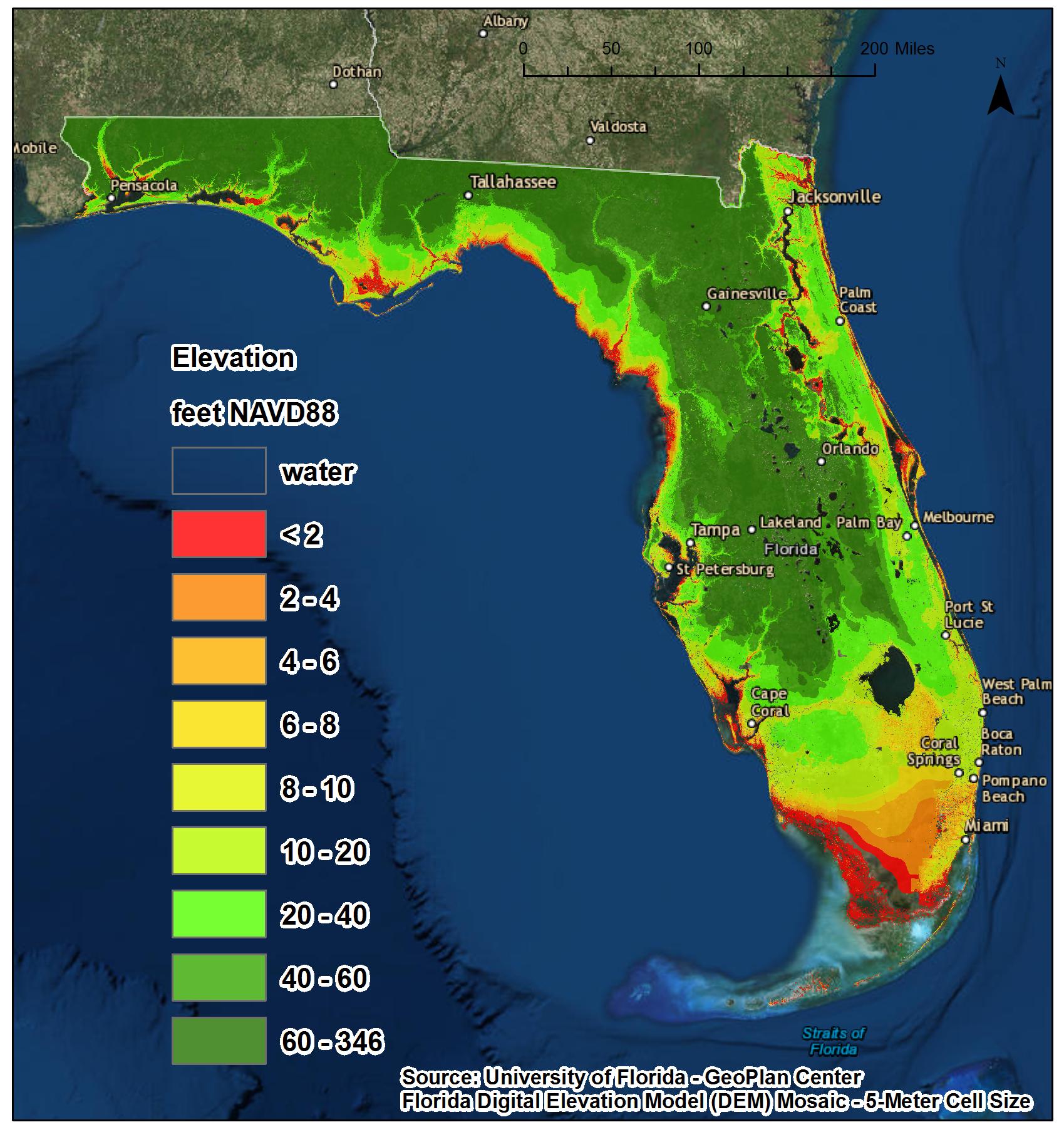
The Earth’s oceans are rising, a consequence of climate change and its associated melting glaciers and ice sheets. This phenomenon, known as sea level rise, poses a significant threat to coastal communities worldwide, impacting infrastructure, ecosystems, and human lives. To understand the scope and potential impact of this rising tide, scientists and policymakers rely on crucial tools: water level rise maps.
These maps are not merely static representations of current sea levels. They are dynamic, data-driven visualizations that project future sea level rise scenarios, offering a glimpse into the potential consequences of inaction. They provide a powerful means to communicate the urgency of addressing climate change and its associated risks.
Dissecting the Data: How Water Level Rise Maps are Created
Creating accurate water level rise maps involves a complex interplay of data and sophisticated modeling techniques. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
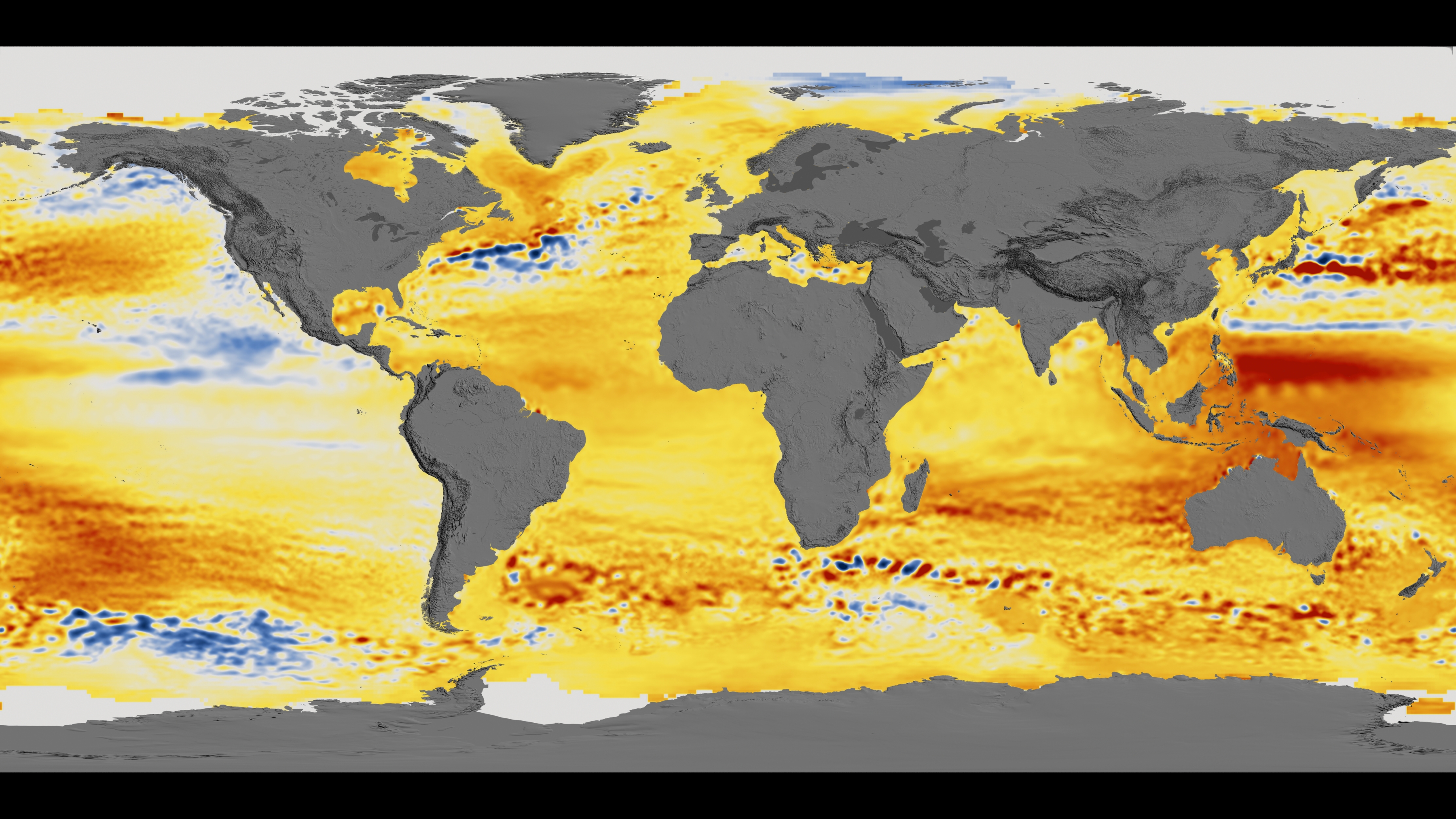
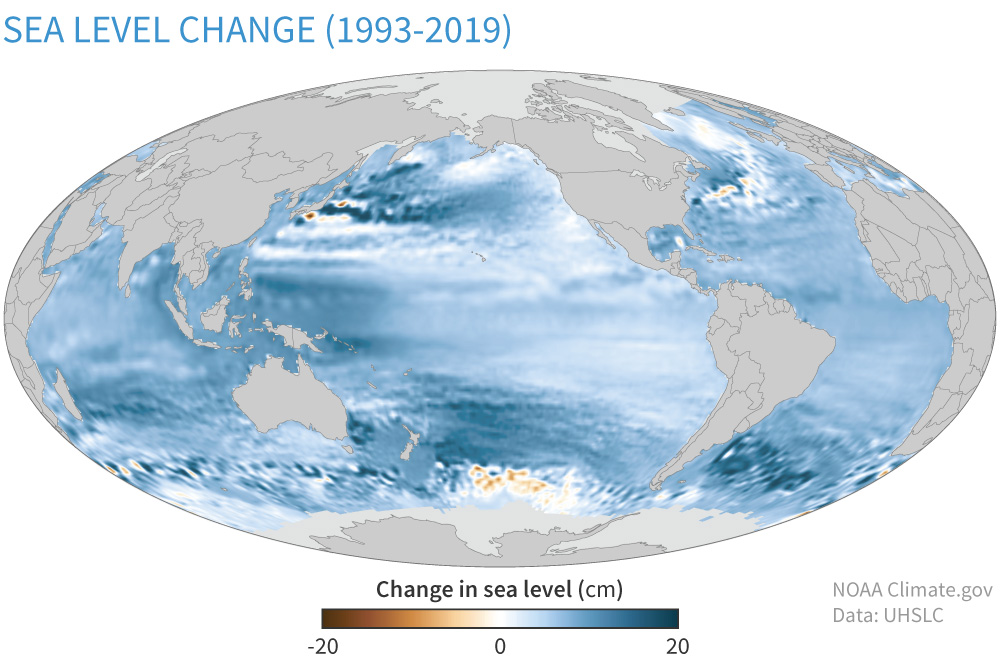
- Satellite Data: Satellites continuously monitor changes in Earth’s gravitational field and measure the height of the ocean surface. This data provides a global overview of sea level changes over time.
- Tide Gauge Data: Tide gauges, strategically placed along coastlines, record water levels at specific locations. This data provides localized information about sea level fluctuations and long-term trends.
- Climate Models: Climate models, powered by supercomputers, simulate the Earth’s climate system, incorporating factors like greenhouse gas emissions, ocean currents, and ice sheet dynamics. These models project future sea level rise scenarios based on different emission pathways.
- Geospatial Data: Geographic information systems (GIS) integrate data from various sources, including satellite imagery, topographic maps, and coastline data. This data is crucial for mapping the potential inundation zones and assessing the vulnerability of coastal areas.
Interpreting the Map: Understanding the Visual Language
Water level rise maps typically present a range of scenarios, each representing a different level of future sea level rise. These scenarios are often based on different emission pathways, reflecting varying levels of climate change mitigation efforts.
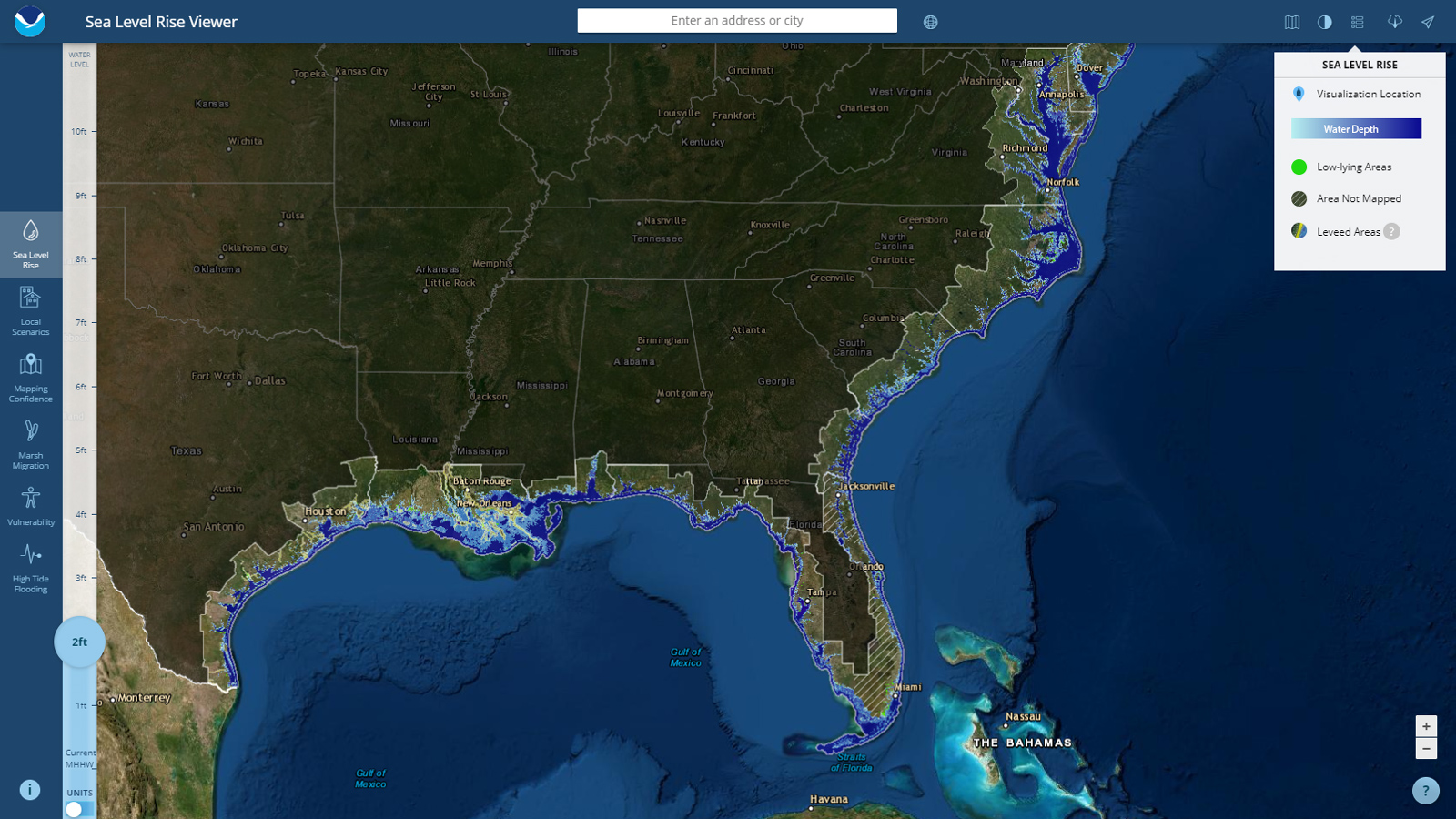
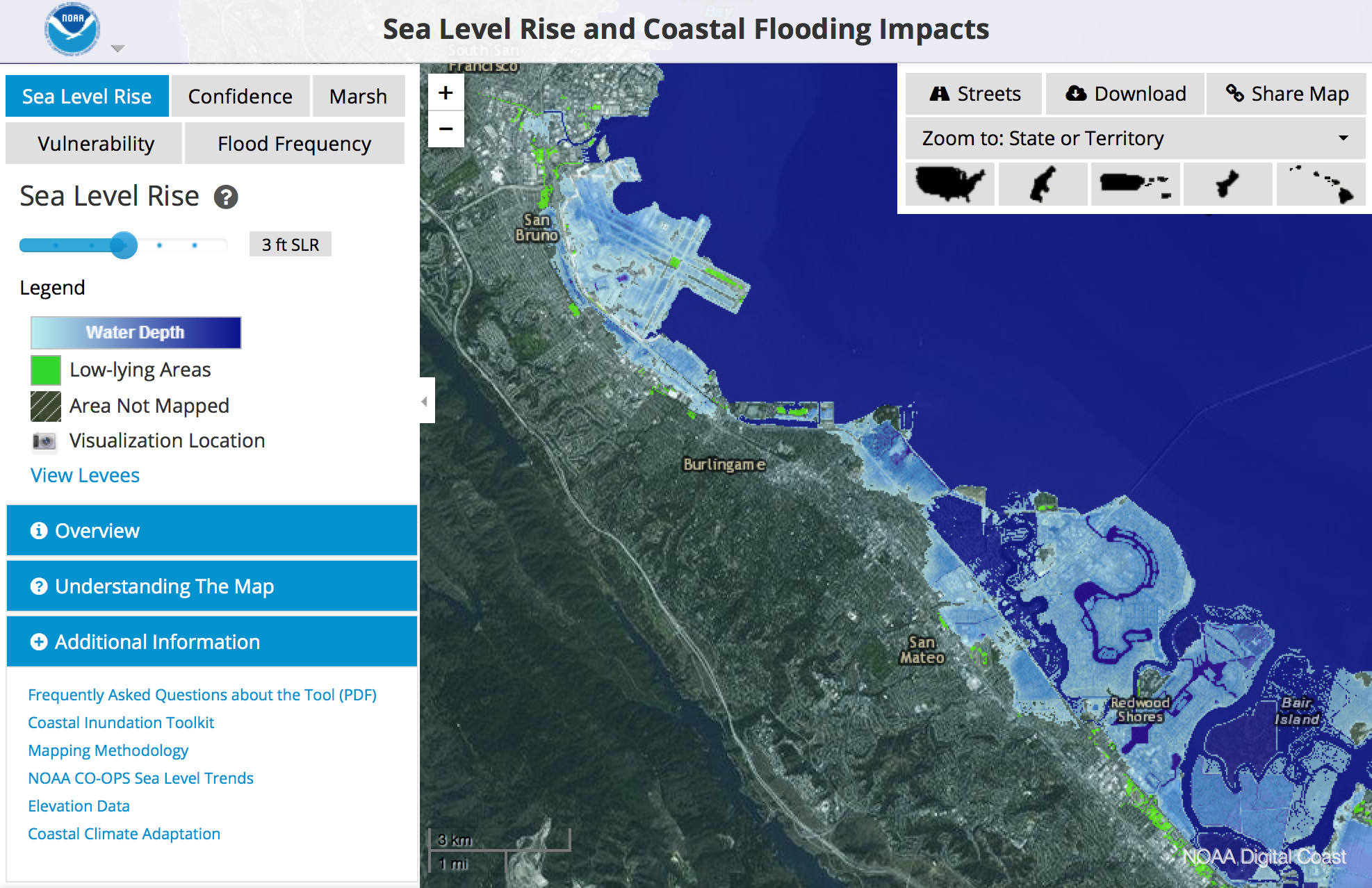
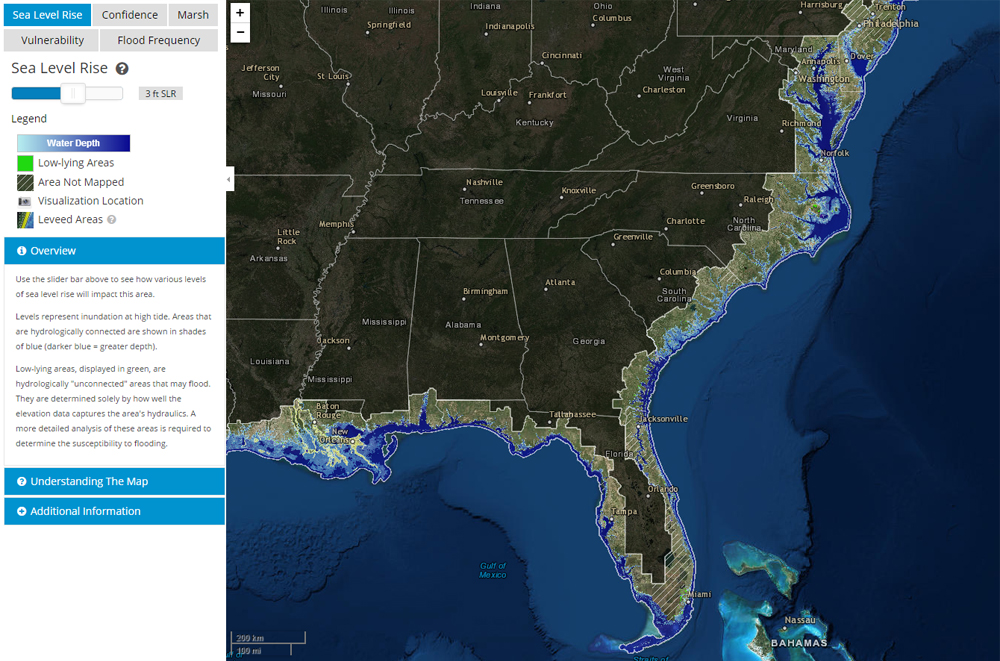
The maps use color gradients or shaded areas to depict the extent of projected inundation, with darker shades indicating areas most likely to be submerged. Key features on the maps include:
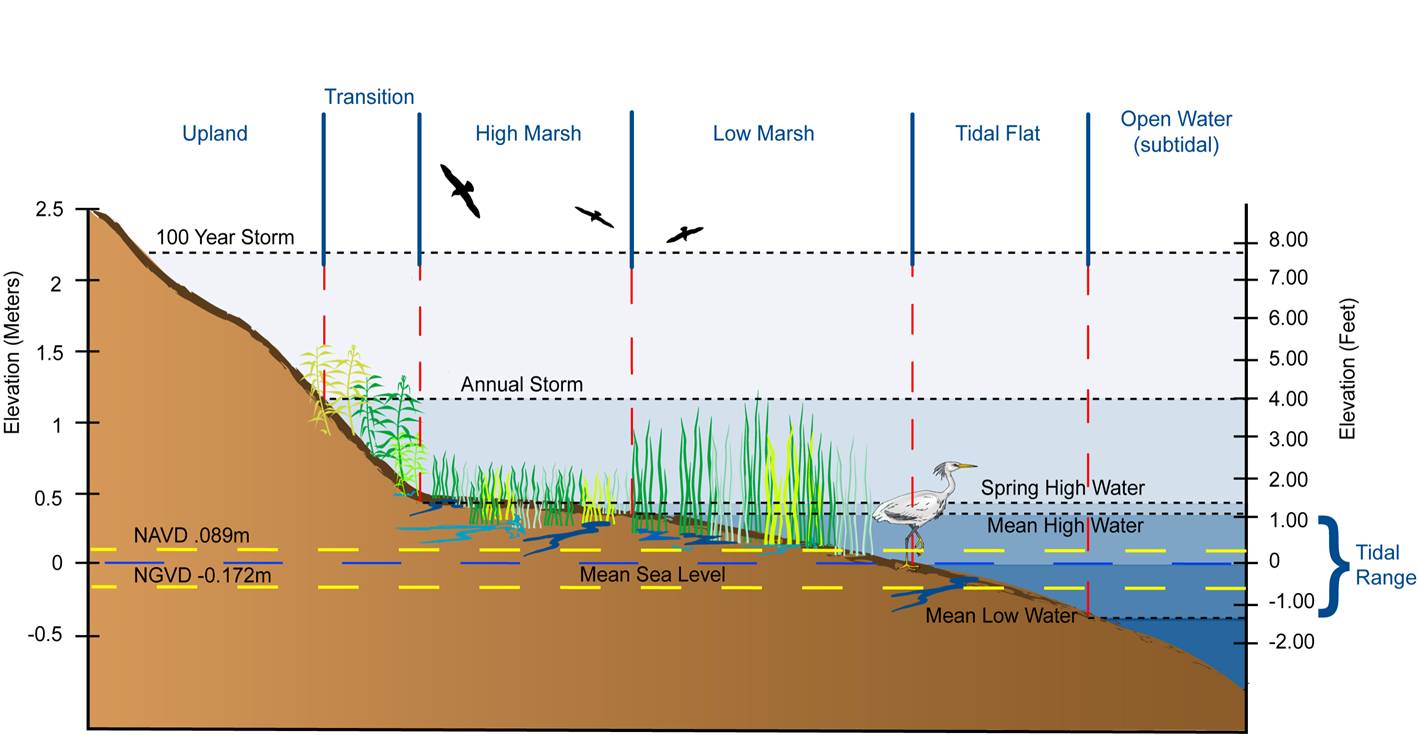
- Baselines: These lines represent current sea levels or specific elevation levels, providing a reference point for assessing future changes.
- Projected Inundation Zones: These areas are shaded to indicate regions that could be submerged under different sea level rise scenarios.
- Coastal Infrastructure: Important infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and buildings, is often highlighted on the maps to assess their vulnerability to rising sea levels.
- Population Density: Population density data can be overlaid on the maps to highlight areas where a large number of people could be affected by sea level rise.
Beyond the Visuals: The Importance of Water Level Rise Maps
These maps serve as vital tools for understanding the potential consequences of sea level rise and informing decision-making at multiple levels:
- Policy and Planning: Governments and local authorities utilize these maps to develop adaptation strategies, strengthen coastal defenses, and guide urban planning in vulnerable areas.
- Infrastructure Development: Engineers and planners can assess the vulnerability of existing infrastructure and design new projects with resilience to sea level rise in mind.
- Community Awareness: Maps can be used to educate the public about the risks of sea level rise, fostering community preparedness and engagement in climate action.
- Scientific Research: Researchers use these maps to refine climate models, assess the impact of sea level rise on ecosystems, and develop strategies for mitigating the effects of rising sea levels.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Water Level Rise Maps
1. How accurate are water level rise maps?
The accuracy of water level rise maps depends on the quality of data used, the sophistication of the climate models, and the uncertainties inherent in climate projections. While these maps provide valuable insights, they are not perfect predictions. They are best understood as probabilistic estimates of future sea level rise scenarios, reflecting the potential range of outcomes.
2. How often are these maps updated?
Water level rise maps are typically updated periodically, reflecting new data and advancements in climate modeling. The frequency of updates varies depending on the source and purpose of the map. However, ongoing research and data collection ensure that these maps remain relevant and informative.
3. What are the limitations of water level rise maps?
While water level rise maps offer valuable insights, they have certain limitations:
- Uncertainties in Climate Projections: Future greenhouse gas emissions and the response of the Earth’s climate system are inherently uncertain. This uncertainty translates into varying projections for sea level rise.
- Limited Spatial Resolution: Some maps may have limited spatial resolution, meaning they may not accurately depict localized changes in sea level rise.
- Focus on Physical Impacts: These maps primarily focus on physical impacts of sea level rise, such as inundation. They may not fully capture the social, economic, and ecological consequences of these changes.
4. What is the role of these maps in climate adaptation?
Water level rise maps are crucial for climate adaptation by providing a visual understanding of the potential risks and informing decision-making. They help governments, communities, and businesses to plan for the future, develop adaptation strategies, and invest in resilient infrastructure.
5. How can I access water level rise maps?
Numerous organizations, including government agencies, research institutions, and non-profit organizations, provide access to water level rise maps. These maps are often available online, through interactive platforms, or as downloadable data sets.
Tips for Using Water Level Rise Maps Effectively
- Consider the Source: Assess the credibility of the organization creating the map and the data sources used.
- Understand the Scenarios: Pay attention to the different sea level rise scenarios presented and the assumptions behind each scenario.
- Focus on Localized Impacts: Use the map to understand the potential impacts of sea level rise in your specific region.
- Engage with Local Authorities: Share the information from the map with local officials and advocate for adaptation measures.
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of the latest scientific findings and updates to water level rise maps.
Conclusion: A Call for Action
Water level rise maps serve as powerful tools for understanding the potential consequences of climate change and informing action. They provide a visual representation of the rising tide, highlighting the urgent need to address the issue. By using these maps effectively, we can raise awareness, inform decision-making, and work towards building a more resilient future in the face of rising sea levels. These maps are not merely visualizations; they are calls to action, urging us to prioritize climate action and safeguard the future of our coastal communities.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing the Rising Tide: Understanding Water Level Rise Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!