Unveiling the Mysteries of Ancient Etruria: A Journey Through Maps and History
Related Articles: Unveiling the Mysteries of Ancient Etruria: A Journey Through Maps and History
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Mysteries of Ancient Etruria: A Journey Through Maps and History. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Mysteries of Ancient Etruria: A Journey Through Maps and History

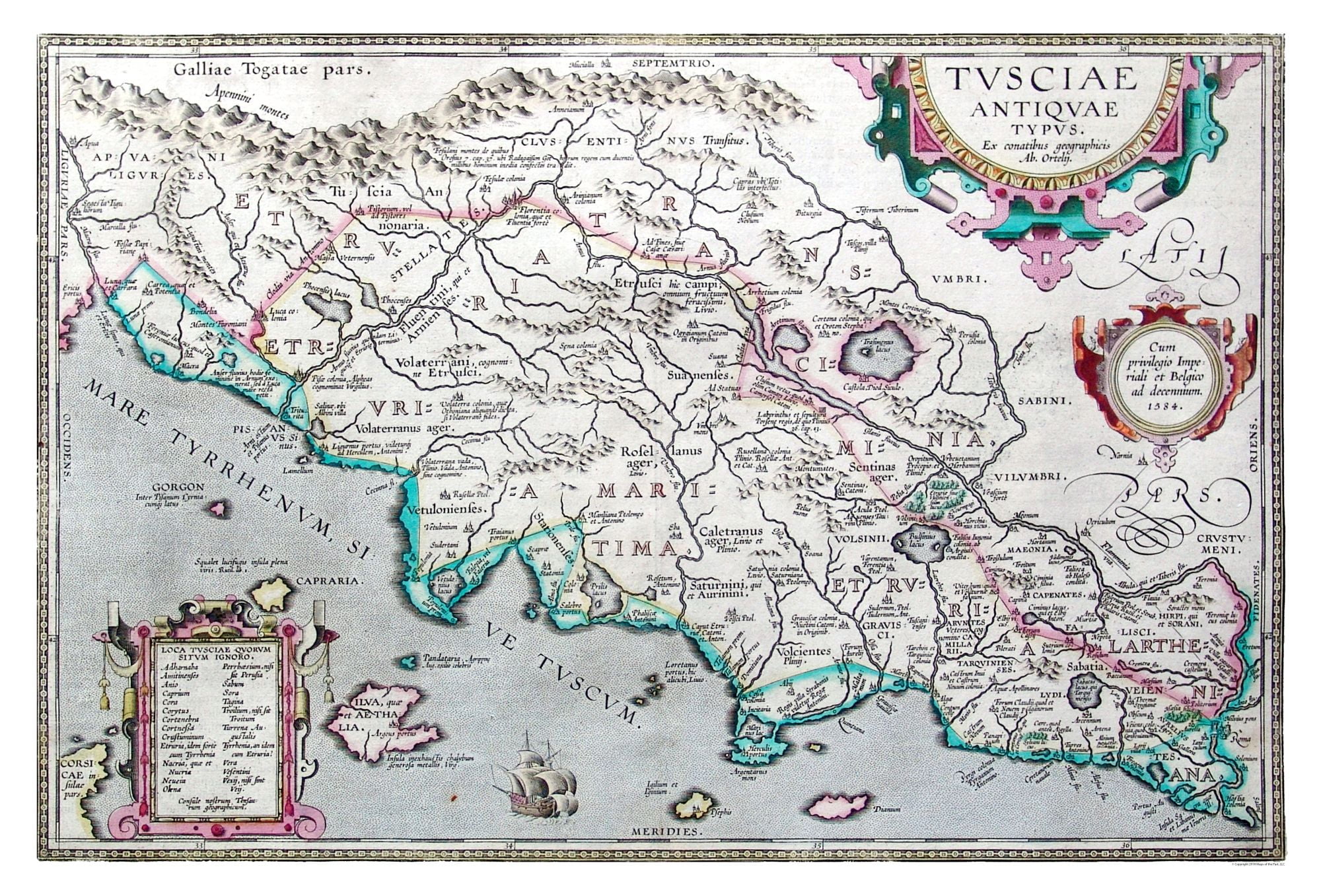
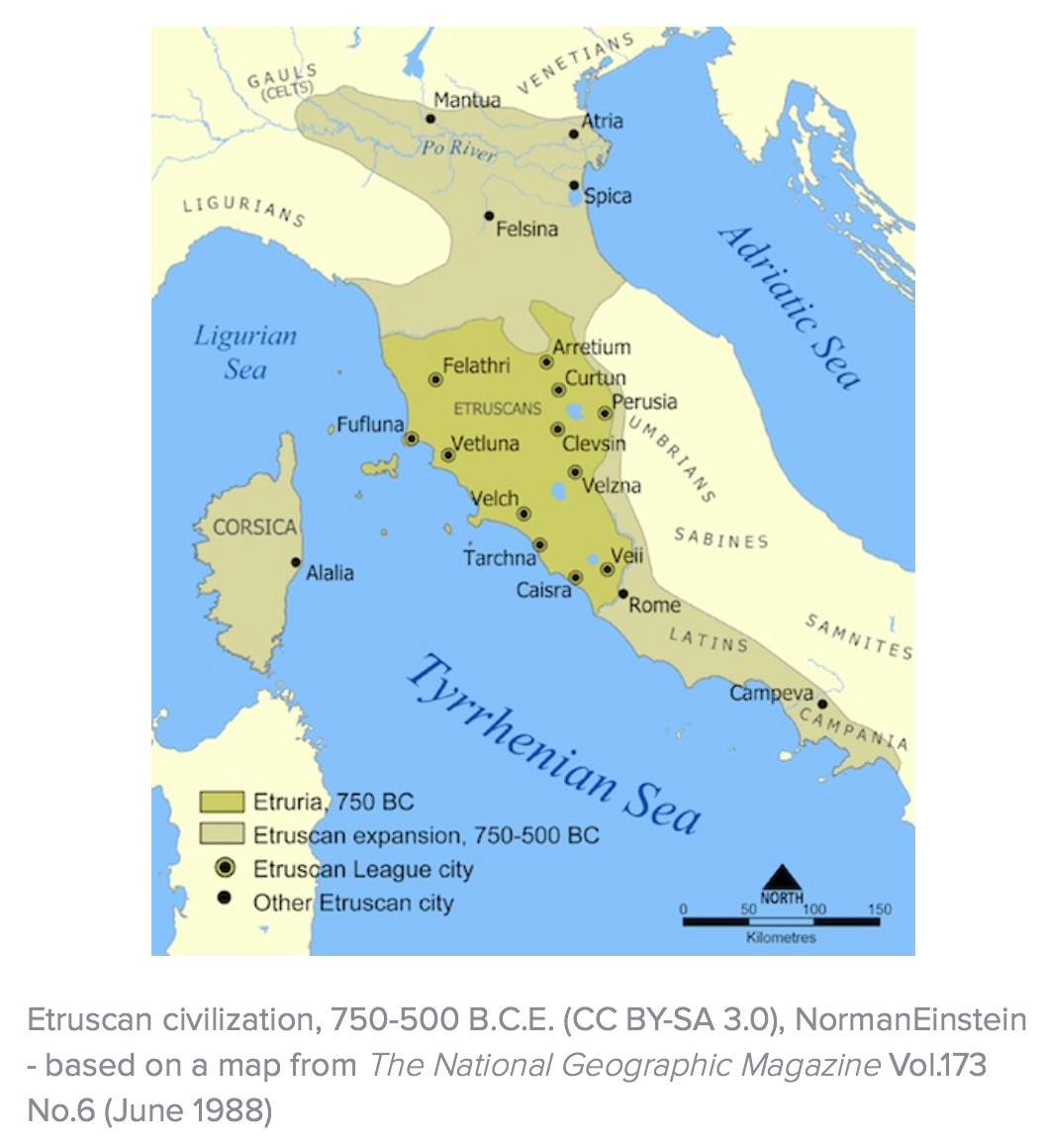
The Etruscan civilization, a vibrant and enigmatic culture that flourished in ancient Italy from the 8th to the 1st century BCE, has left an enduring legacy on the world. While their language, customs, and art continue to intrigue scholars, the geographical extent of their influence remains a fascinating area of study. Etruscan maps, though scarce, offer a unique window into the understanding of this lost civilization. They provide invaluable insights into the political, social, and economic landscape of ancient Etruria, allowing us to piece together the intricate tapestry of their existence.
The Significance of Etruscan Maps
Etruscan maps, unlike their modern counterparts, were not solely concerned with precise geographical representation. They served a multifaceted purpose, acting as tools for:
- Religious and Ritualistic Practices: Many Etruscan maps were likely associated with religious rituals and divination. They might have been used to represent the sacred landscape, depicting the locations of temples, oracles, and other significant sites.
- Political and Administrative Purposes: Etruscan cities and settlements were often organized into leagues or confederations, and maps may have been used to depict these political structures, outlining territories and boundaries.
- Trade and Economic Activities: The Etruscans were skilled traders, and maps could have been used to track trade routes, identify resource-rich areas, and facilitate economic activity.
Types of Etruscan Maps
Etruscan maps, while limited in number, come in various forms:
- Terracotta Models: These small-scale, three-dimensional models, often depicting cities or landscapes, provide valuable insights into the urban planning and architectural styles of the Etruscans.
- Painted Tombs: Tombs adorned with intricate frescoes often feature representations of landscapes, including rivers, mountains, and settlements. These depictions, though not always accurate in a modern cartographic sense, offer valuable clues about the Etruscan perception of their world.
- Bronze Mirrors: Some Etruscan bronze mirrors feature engraved maps, often depicting idealized landscapes or symbolic representations of sacred sites. These mirrors, used for personal grooming and ritualistic purposes, highlight the interconnectedness of everyday life with the sacred realm.
The Evolution of Etruscan Cartography
While the earliest Etruscan maps date back to the 7th century BCE, their development and use appear to have evolved over time. Early maps were likely rudimentary and primarily symbolic, focusing on the representation of key sites and landmarks. As the Etruscan civilization matured, their cartographic skills advanced, leading to more detailed and complex representations.
The Importance of Interpretation
Interpreting Etruscan maps requires a multidisciplinary approach, drawing upon knowledge from archaeology, art history, linguistics, and anthropology. While some maps offer straightforward depictions of landscapes, others are highly symbolic and require careful analysis to decipher their intended meaning. The study of Etruscan maps is an ongoing process, with new discoveries and interpretations constantly emerging.
FAQs about Etruscan Maps
Q: Are there any surviving Etruscan maps?
A: While Etruscan maps are rare, a few examples have survived, primarily in the form of terracotta models, tomb frescoes, and bronze mirrors.
Q: How accurate were Etruscan maps?
A: The accuracy of Etruscan maps varied depending on their purpose and the time period. While some maps were likely intended to be purely symbolic, others may have aimed for a more realistic depiction of the landscape.
Q: What are the limitations of studying Etruscan maps?
A: The scarcity of surviving maps, the ambiguity of their symbolism, and the difficulty of deciphering the Etruscan language all pose significant challenges to the study of Etruscan cartography.
Tips for Understanding Etruscan Maps
- Context is Key: Analyze Etruscan maps within the broader context of their cultural and historical setting.
- Symbolism Matters: Recognize that Etruscan maps often employed symbolic language and imagery.
- Compare and Contrast: Compare different Etruscan maps to identify patterns and variations in their depiction of landscapes and sites.
Conclusion
Etruscan maps, though scarce, offer a unique perspective on the world of this ancient civilization. Their study provides valuable insights into the Etruscan understanding of their environment, their religious beliefs, and their political and economic structures. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of Etruscan cartography, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and sophistication of this lost civilization.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Mysteries of Ancient Etruria: A Journey Through Maps and History. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!