Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Map Elevations
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Map Elevations
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Map Elevations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Map Elevations
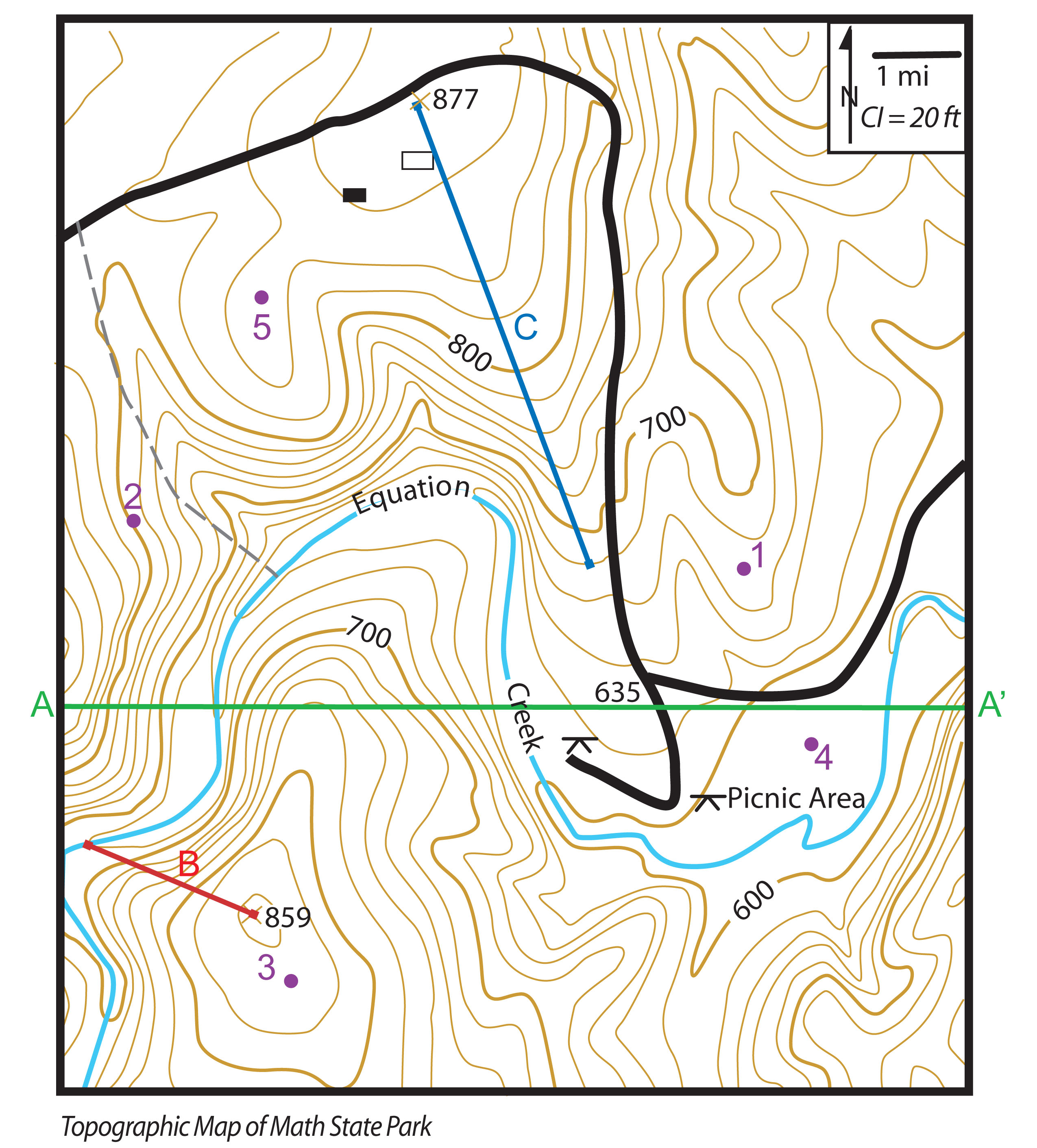
Topographic maps are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, capturing not just the location of features like roads, rivers, and buildings, but also the shape and elevation of the terrain. This critical aspect, the representation of elevation, is the foundation upon which these maps provide invaluable insights for diverse applications.
The Language of Elevation: Contour Lines and Spot Elevations
Topographic maps use two primary methods to depict elevation: contour lines and spot elevations.
-
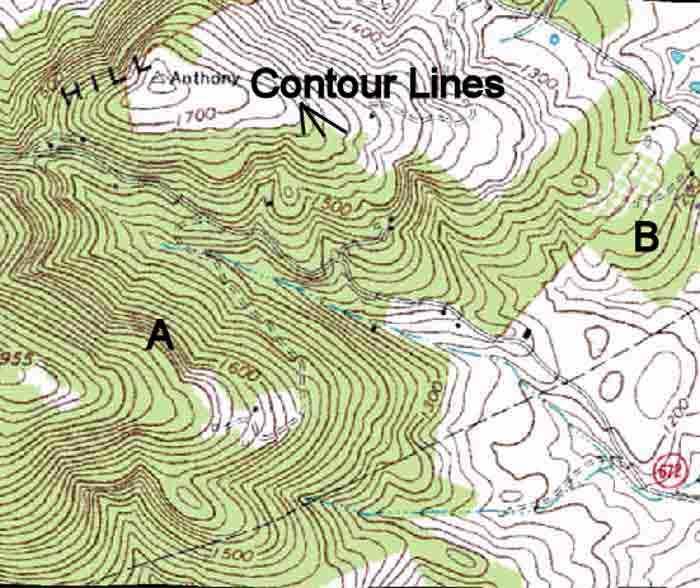
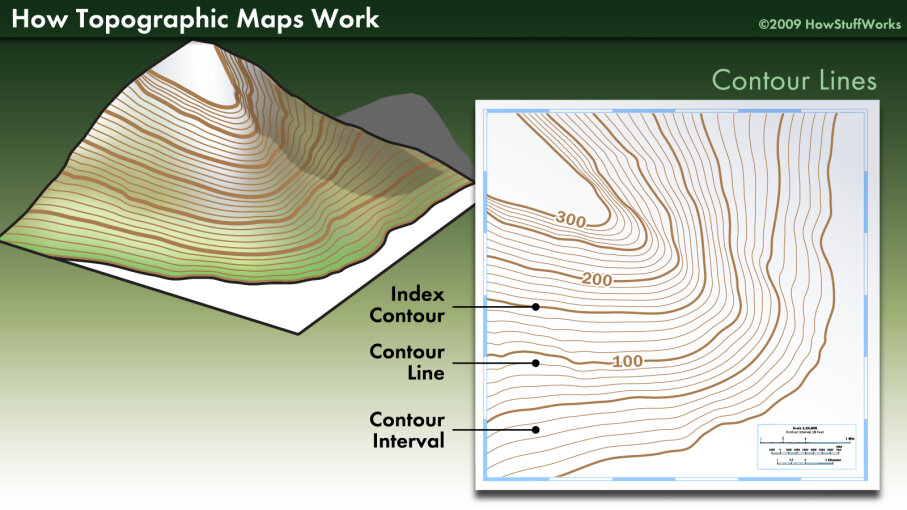
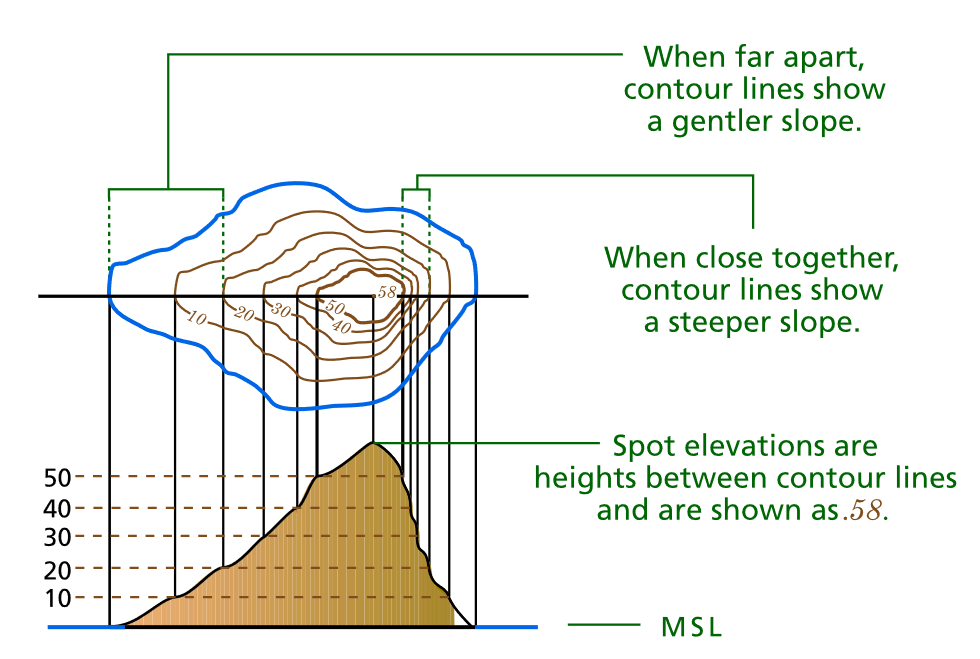
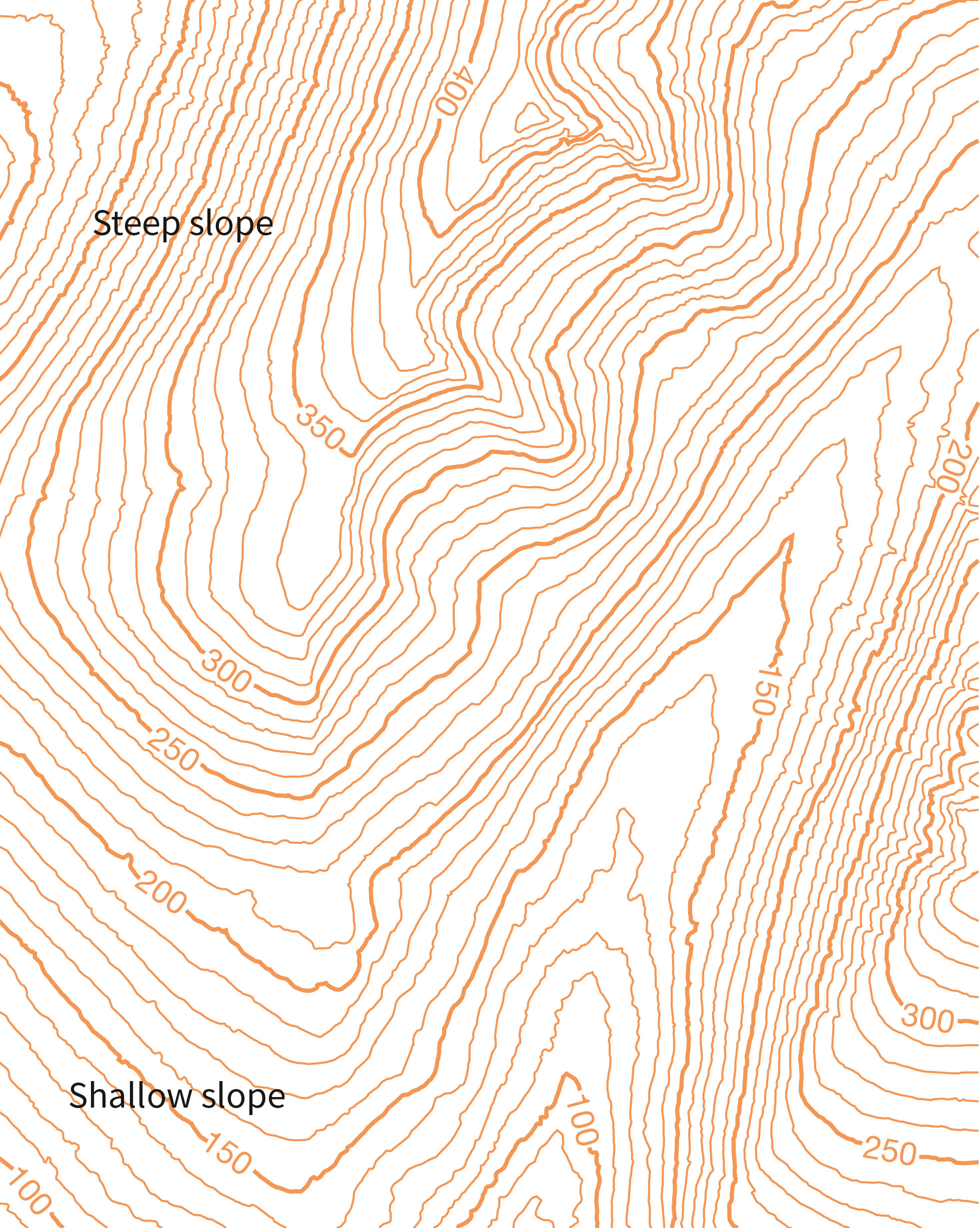
Contour lines are lines connecting points of equal elevation. They are like slices through the landscape, revealing the shape of hills, valleys, and other features. The closer the contour lines, the steeper the slope; the farther apart they are, the gentler the incline.
-
Spot elevations are numerical values indicating the precise altitude of specific points on the map. These points are often located at significant features like peaks, saddles, or along roads.
Interpreting the Terrain: Reading Contour Lines
Understanding contour lines is crucial for deciphering the topography represented on a map. Here are key aspects to consider:
-
Contour Interval: The difference in elevation between consecutive contour lines is known as the contour interval. This value is typically indicated on the map’s legend and determines the scale of elevation changes depicted. A smaller contour interval reveals finer details of the terrain, while a larger interval provides a more generalized view.
-
Contour Line Direction: The direction of the contour lines indicates the direction of the slope. Lines that curve inward (forming a "U" shape) represent a depression or valley, while those curving outward (forming an "O" shape) represent a hill or ridge.
-
Closed Contours: When contour lines form closed loops, they indicate a hill or depression. If the numbers within the closed contour increase, it represents a hill; if they decrease, it represents a depression.
-
Contour Line Spacing: The spacing between contour lines reveals the steepness of the slope. Closely spaced lines indicate a steep slope, while widely spaced lines indicate a gentle slope.
The Importance of Elevation: Applications Across Disciplines
Topographic maps, with their elevation information, are essential tools across various disciplines, including:
-
Navigation and Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts rely on topographic maps to plan routes, assess difficulty, and navigate safely through challenging terrain. Elevation information helps them determine the altitude changes they will encounter, identify potential hazards, and plan for appropriate gear.
-
Engineering and Construction: Civil engineers use topographic maps to design roads, bridges, and buildings, ensuring that structures are built on stable ground and account for the natural contours of the landscape. This information is critical for calculating earthwork volumes, determining drainage patterns, and mitigating potential environmental impacts.
-
Environmental Management: Environmental scientists and resource managers use topographic maps to study landforms, analyze soil erosion patterns, and assess the impact of development on sensitive ecosystems. Elevation data helps them understand water flow patterns, identify areas prone to flooding, and plan for sustainable land use practices.
-
Military Operations: Military planners utilize topographic maps to assess terrain features, identify potential ambush points, and plan troop movements. Elevation information is critical for understanding lines of sight, determining firing positions, and planning for safe and effective operations.
-
Urban Planning and Development: Urban planners use topographic maps to evaluate the suitability of land for development, assess potential risks from flooding, and plan for infrastructure projects. Elevation data helps them understand the natural drainage patterns of the area, identify potential hazards, and optimize land use for the benefit of the community.
FAQs on Topographic Map Elevations:
Q: What is the difference between a topographic map and a regular map?
A: A topographic map differs from a regular map by including elevation information, which allows it to depict the shape and contours of the terrain. Regular maps focus primarily on geographical features like roads, rivers, and cities without detailing the elevation changes.
Q: How can I determine the elevation of a specific point on a topographic map?
A: You can determine the elevation of a specific point using either contour lines or spot elevations. If contour lines are present, locate the line passing through the point and refer to the contour interval provided in the map’s legend. Alternatively, if a spot elevation is marked near the point, the numerical value represents the elevation at that location.
Q: How accurate are topographic map elevations?
A: The accuracy of topographic map elevations depends on the map’s scale and the methods used to collect the data. Modern maps utilize sophisticated surveying techniques and GPS data to ensure high levels of precision. However, older maps may have lower accuracy due to limitations in the technology available at the time of their creation.
Q: What are some common uses of topographic map elevations in daily life?
A: Topographic map elevations are used in various everyday applications, such as:
- Hiking and outdoor activities: Planning routes, assessing trail difficulty, and determining potential hazards.
- Urban planning and development: Assessing land suitability, planning infrastructure projects, and mitigating flooding risks.
- Navigation and transportation: Planning routes, identifying elevation changes, and navigating challenging terrain.
- Environmental monitoring: Analyzing landform changes, assessing soil erosion patterns, and managing natural resources.
Tips for Using Topographic Map Elevations:
- Understand the map’s scale and contour interval: This information is crucial for interpreting the elevation changes represented on the map.
- Pay attention to the direction of contour lines: This helps you visualize the slope of the terrain and identify potential hazards.
- Use a compass and protractor: These tools can aid in accurately measuring distances and angles, which is essential for navigation and planning.
- Practice reading contour lines: Familiarity with contour lines and their interpretation is key to understanding the topography represented on a map.
- Consult multiple sources: Cross-referencing information from different maps and sources can help ensure accuracy and provide a comprehensive understanding of the terrain.
Conclusion:
Topographic map elevations are essential for understanding the shape and contours of the Earth’s surface. They provide valuable insights for navigation, planning, environmental management, and numerous other applications. By understanding the principles of contour lines and spot elevations, individuals can unlock the wealth of information contained within these maps, gaining a deeper appreciation for the complexities of the natural world and making informed decisions based on the terrain’s unique characteristics.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: Understanding Topographic Map Elevations. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!