Unveiling the Depths: A Journey Through Oceanic Trench Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Depths: A Journey Through Oceanic Trench Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Depths: A Journey Through Oceanic Trench Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Depths: A Journey Through Oceanic Trench Maps
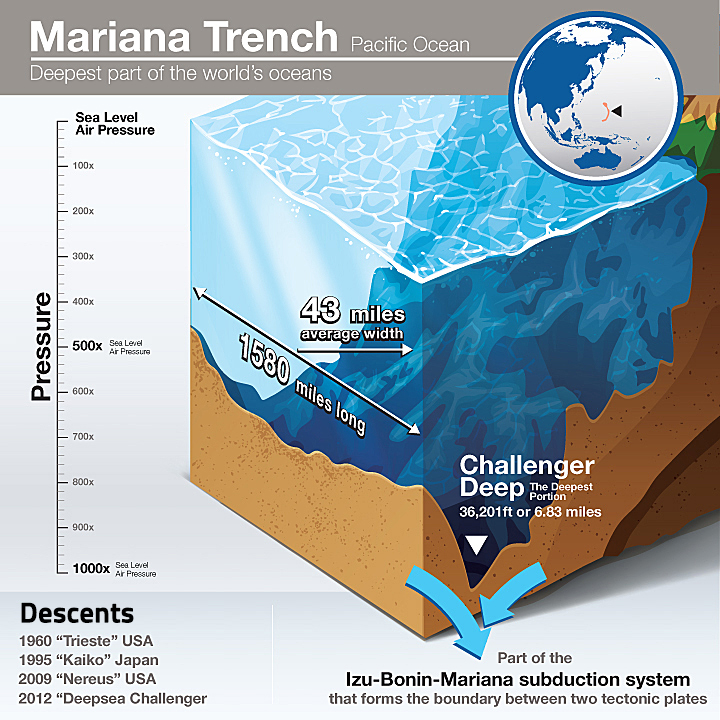
Oceanic trenches, the deepest and most enigmatic features on Earth’s surface, are often referred to as the "Grand Canyon of the Sea." These vast, elongated depressions in the ocean floor are formed at convergent plate boundaries where one tectonic plate subducts, or slides beneath, another. Understanding the intricate web of these trenches is paramount for comprehending the planet’s geological history, understanding the dynamics of plate tectonics, and exploring the potential for valuable resources and scientific discoveries.
A Map of the Abyss: Deciphering the Depths
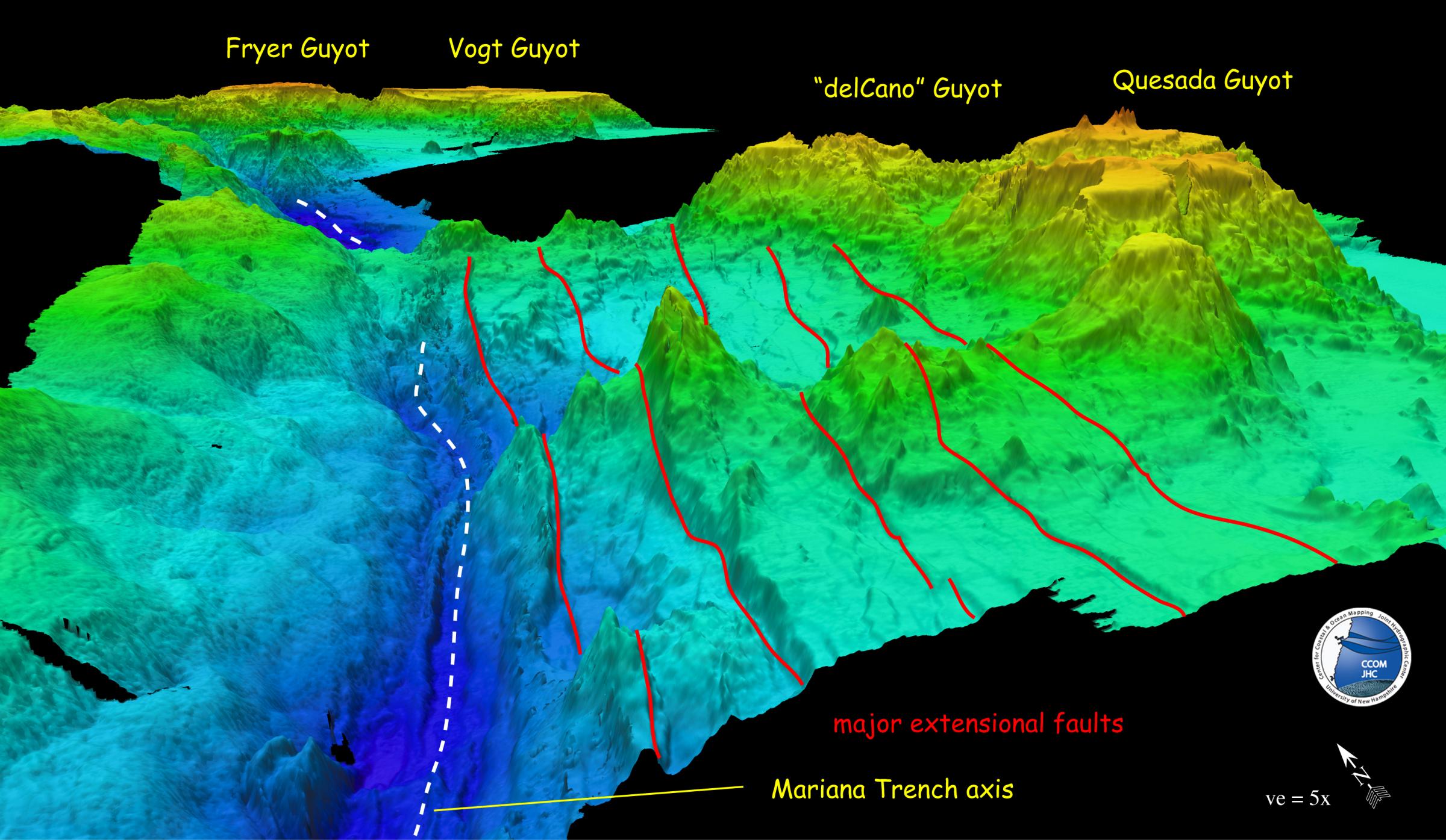
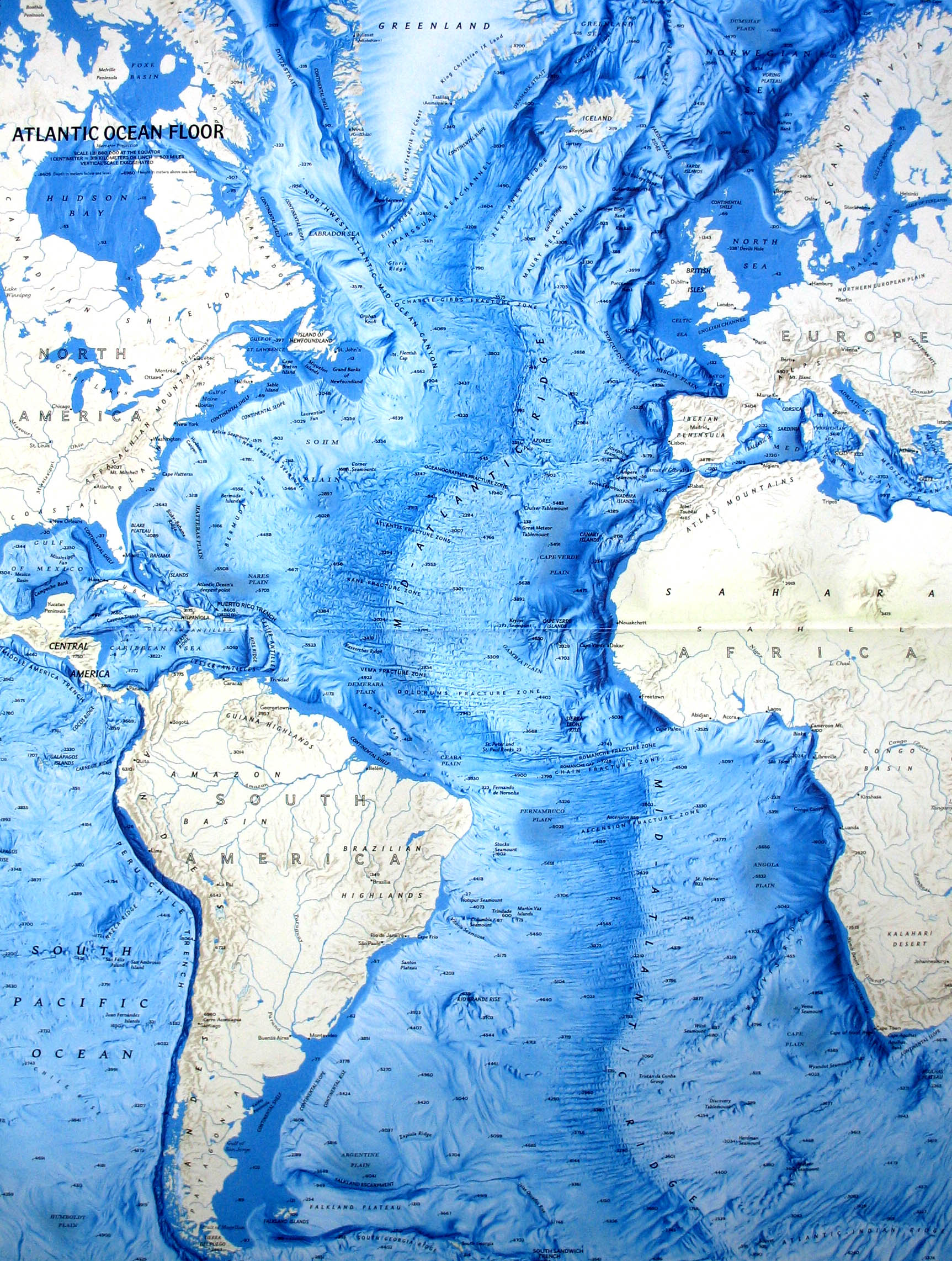
Oceanic trench maps are essential tools for visualizing and analyzing these profound geological features. These maps, often depicted as contour lines or shaded relief, reveal the morphology of the trenches, highlighting their depths, lengths, and relationships to surrounding tectonic plates. They provide a crucial visual representation of the Earth’s dynamic processes, offering insights into:
- Plate Tectonics: Oceanic trenches are key indicators of subduction zones, where denser oceanic plates plunge beneath continental or other oceanic plates. Mapping these trenches allows scientists to trace the movement of tectonic plates and understand the forces driving continental drift.
- Earthquakes and Tsunamis: The intense pressure and friction generated at subduction zones can trigger powerful earthquakes and devastating tsunamis. Oceanic trench maps help identify high-risk areas, enabling better preparedness and mitigation strategies for these natural disasters.
- Volcanism: The subduction process often leads to the formation of volcanic arcs, chains of volcanoes that emerge along the edge of the overriding plate. Trench maps assist in understanding the spatial distribution of these volcanic zones and their potential hazards.
- Marine Life and Ecosystems: The unique conditions within trenches, including extreme pressures, low temperatures, and lack of sunlight, support specialized ecosystems teeming with unique marine life. Trench maps guide researchers in exploring these environments and understanding the biodiversity they harbor.
- Resource Exploration: Oceanic trenches hold potential for mineral resources, such as manganese nodules and hydrothermal vents, which can be valuable for various industries. Trench maps assist in identifying potential resource-rich areas and guide exploration efforts.
Beyond the Surface: Unveiling the Secrets of the Deep
Oceanic trench maps are not merely static representations of the ocean floor. They serve as stepping stones for further exploration and research. By combining these maps with data from various sources, including sonar mapping, sediment cores, and remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), scientists gain a more comprehensive understanding of the trenches’ characteristics:
- Bathymetry: Trench maps provide the foundation for detailed bathymetric surveys, which measure the depth and topography of the ocean floor. This information is crucial for understanding the shape and structure of the trenches, identifying potential hazards, and guiding navigation.
- Sedimentation: Sediments accumulating on the trench floor provide a record of past geological events and environmental changes. By analyzing sediment cores, scientists can reconstruct the history of plate movements, climate variations, and biological activity.
- Hydrothermal Vents: These unique ecosystems, often found along trenches, release hot, mineral-rich fluids from the Earth’s interior. Mapping these vents helps scientists understand their role in supporting diverse life forms and their potential for resource extraction.
- Marine Biodiversity: The extreme conditions within trenches have led to the evolution of fascinating and diverse marine life. Trench maps guide research expeditions to explore these environments and document the unique species they harbor.
Frequently Asked Questions about Oceanic Trench Maps
Q: What are the most prominent oceanic trenches on Earth?
A: The most significant trenches include the Mariana Trench (the deepest known point on Earth), the Peru-Chile Trench, the Tonga Trench, the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench, and the Puerto Rico Trench.
Q: How are oceanic trench maps created?
A: Trench maps are primarily created using sonar technology, which emits sound waves that bounce off the ocean floor and are detected by receivers. The time it takes for the sound to return provides information about the depth and topography of the seabed.
Q: What are the benefits of using oceanic trench maps?
A: Oceanic trench maps offer a wide range of benefits, including:
- Understanding plate tectonics and Earth’s geological history.
- Identifying and mitigating risks associated with earthquakes and tsunamis.
- Exploring potential for resource extraction, such as minerals and hydrothermal vents.
- Guiding research expeditions to study unique marine ecosystems and biodiversity.
Q: How do oceanic trench maps contribute to the study of marine life?
A: Trench maps help locate and characterize deep-sea environments, enabling researchers to study the unique adaptations of organisms that thrive in these extreme conditions.
Q: What are the challenges in mapping oceanic trenches?
A: Mapping trenches presents significant challenges due to their immense depths, harsh conditions, and vastness. Technological limitations, funding constraints, and environmental concerns also pose hurdles.
Tips for Using Oceanic Trench Maps
- Consider the scale and resolution of the map.
- Examine the legend and symbols to understand the data represented.
- Relate the map to other geological features, such as tectonic plates and volcanic arcs.
- Use the map in conjunction with other data sources, such as sediment cores and bathymetric surveys.
- Interpret the map within the context of Earth’s dynamic processes.
Conclusion
Oceanic trench maps are invaluable tools for understanding the Earth’s dynamic processes and exploring the mysteries of the deep. By revealing the morphology of these profound geological features, these maps provide insights into plate tectonics, earthquake and tsunami risks, volcanic activity, marine ecosystems, and potential resources. As technology advances and research progresses, oceanic trench maps will continue to play a crucial role in unraveling the secrets of the ocean floor and fostering a deeper understanding of our planet.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Depths: A Journey Through Oceanic Trench Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!