Unraveling the Tapestry of American Soil: A Comprehensive Guide to the Soil Map of the United States
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of American Soil: A Comprehensive Guide to the Soil Map of the United States
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of American Soil: A Comprehensive Guide to the Soil Map of the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of American Soil: A Comprehensive Guide to the Soil Map of the United States
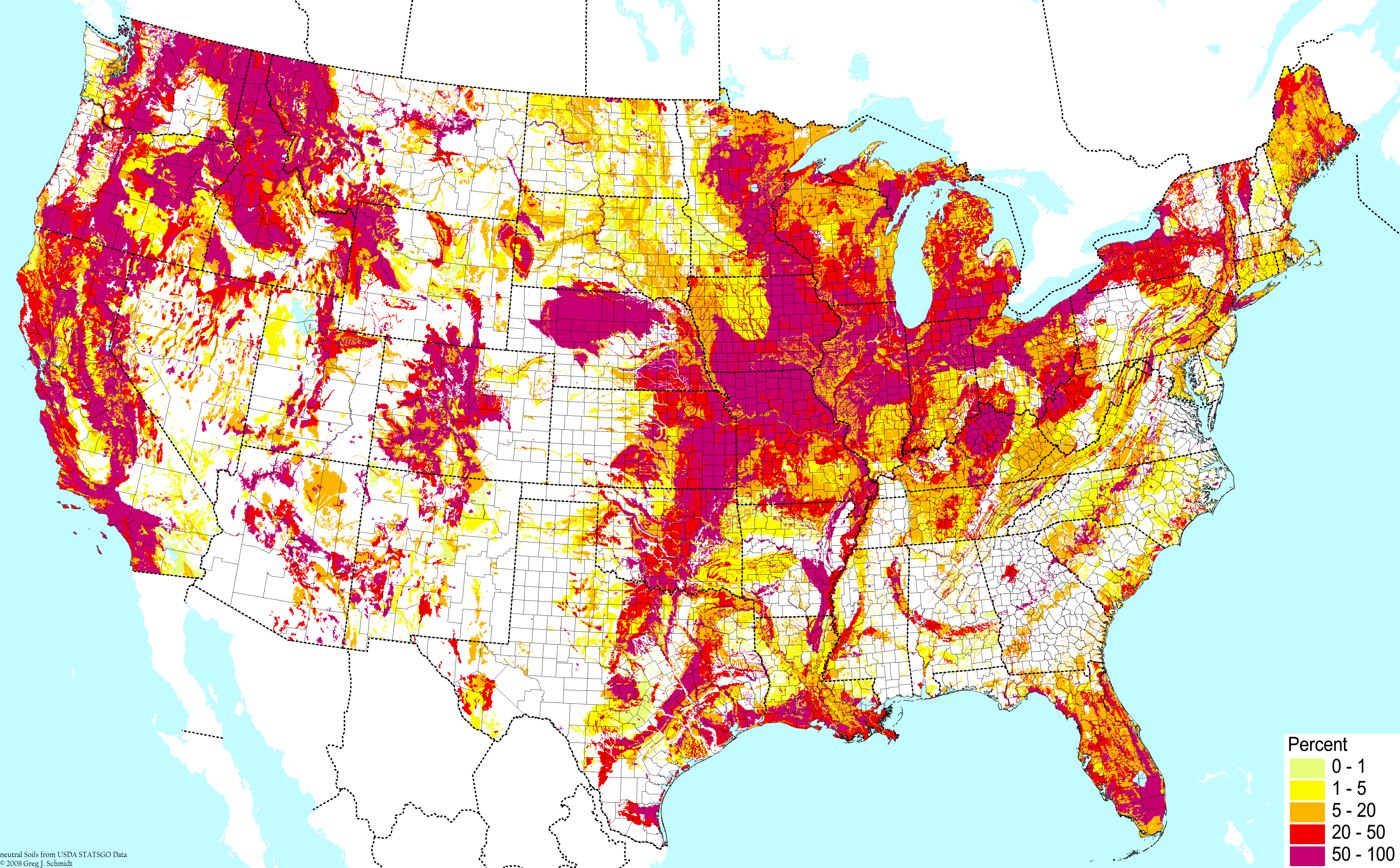
The United States, a land of diverse landscapes and ecosystems, boasts a rich tapestry of soils. Understanding this intricate mosaic is crucial for various endeavors, from agriculture and land management to environmental protection and urban planning. The Soil Map of the United States, a monumental collaborative effort, serves as an invaluable tool for navigating this complex landscape.
A Visual Representation of Soil Diversity
The Soil Map of the United States, developed and maintained by the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), presents a comprehensive overview of soil types across the nation. This map, available in various formats, including digital and print, utilizes a standardized system of soil classification, known as the Soil Taxonomy. This system categorizes soils based on their physical and chemical properties, including texture, structure, color, mineral content, and organic matter content.
Beyond Color-Coded Regions: Delving Deeper into Soil Properties
The map itself is a visual representation of the diverse soil types found across the country. Each color represents a distinct soil series, signifying a unique combination of soil properties. However, the map is merely a starting point. Detailed soil surveys, often available at county or even smaller scales, provide a more in-depth analysis of specific locations, outlining:
- Soil horizons: The distinct layers within the soil profile, each with unique characteristics.
- Soil texture: The proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles, influencing water holding capacity and drainage.
- Soil structure: The arrangement of soil particles, impacting aeration and root penetration.
- Soil fertility: The availability of essential nutrients for plant growth.
- Soil drainage: The rate at which water moves through the soil, impacting plant growth and potential for flooding.
- Soil limitations: Factors such as salinity, acidity, or rockiness that might restrict plant growth or agricultural practices.
Navigating the Soil Map: A User-Friendly Interface
The Soil Map of the United States is readily accessible through various platforms. The NRCS Web Soil Survey provides an interactive online tool, allowing users to explore soil data at different scales, from national to local. Users can:
- Locate specific areas: Enter an address, zip code, or geographic coordinates to view soil information for a particular location.
- Visualize soil data: Access interactive maps displaying soil types, properties, and limitations.
- Download reports: Generate detailed reports containing soil descriptions, interpretations, and recommendations for land use.
- Access additional resources: Explore supporting information, including soil survey reports, technical manuals, and educational materials.
The Significance of Soil Mapping: A Foundation for Informed Decisions
The Soil Map of the United States serves as a cornerstone for numerous applications, underpinning crucial decisions across various sectors:
Agriculture: Farmers and ranchers utilize soil information to optimize crop selection, manage irrigation, and apply fertilizers effectively. Understanding soil properties allows them to maximize yields, minimize environmental impacts, and ensure sustainable agricultural practices.
Land Management: Land managers rely on soil data to assess land suitability for various uses, including forestry, grazing, and urban development. This information helps minimize soil degradation, protect water resources, and promote responsible land use.
Environmental Protection: Soil mapping plays a vital role in understanding and mitigating environmental risks. It helps identify areas susceptible to erosion, flooding, and pollution, guiding conservation efforts and land management practices.
Urban Planning: Soil information is crucial for urban planning and development. It helps determine suitable locations for infrastructure projects, assess potential for soil contamination, and guide strategies for sustainable urban growth.
Research and Education: The Soil Map of the United States serves as a valuable resource for researchers and educators, providing a foundation for understanding soil science, conducting environmental studies, and developing educational materials.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Soil Mapping
Q: How often is the Soil Map of the United States updated?
A: The Soil Map of the United States is a dynamic resource, constantly evolving as new data becomes available and scientific understanding advances. The NRCS conducts ongoing soil surveys and updates the map accordingly, ensuring its accuracy and relevance.
Q: What is the difference between a soil series and a soil map unit?
A: A soil series represents a group of soils with similar characteristics, while a soil map unit represents a specific area on the map where a particular soil series is dominant. A map unit may contain multiple soil series, each with varying proportions.
Q: Can I access soil information for my specific property?
A: Yes, the NRCS Web Soil Survey allows users to access soil information for specific locations, including properties. You can enter an address, zip code, or geographic coordinates to view detailed soil data for your property.
Q: How can I learn more about soil science and soil mapping?
A: The NRCS offers a wealth of educational resources, including online courses, publications, and workshops. Additionally, numerous universities and research institutions conduct soil science research and offer educational programs.
Tips for Utilizing the Soil Map of the United States
- Start with the national map: Gain a general understanding of soil types across the country.
- Explore local soil surveys: Access more detailed information about specific areas.
- Consult with experts: Reach out to soil scientists or land management professionals for assistance in interpreting soil data and making informed decisions.
- Stay updated: The Soil Map of the United States is constantly evolving. Stay informed about the latest updates and resources.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Soil Knowledge
The Soil Map of the United States stands as a testament to the dedication of soil scientists and the importance of understanding our nation’s soil resources. This invaluable tool provides a foundation for informed decisions, promoting sustainable land use, protecting our environment, and ensuring the well-being of future generations. By harnessing the knowledge embedded within this map, we can cultivate a future where soil resources are cherished, protected, and utilized to their fullest potential.
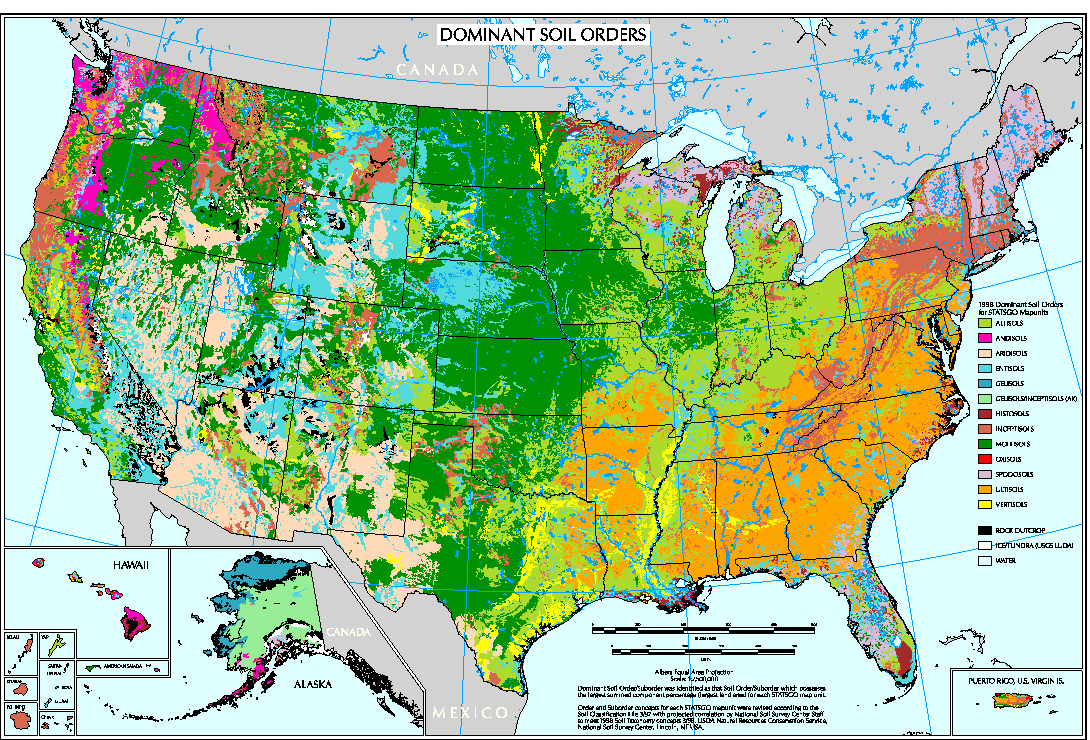

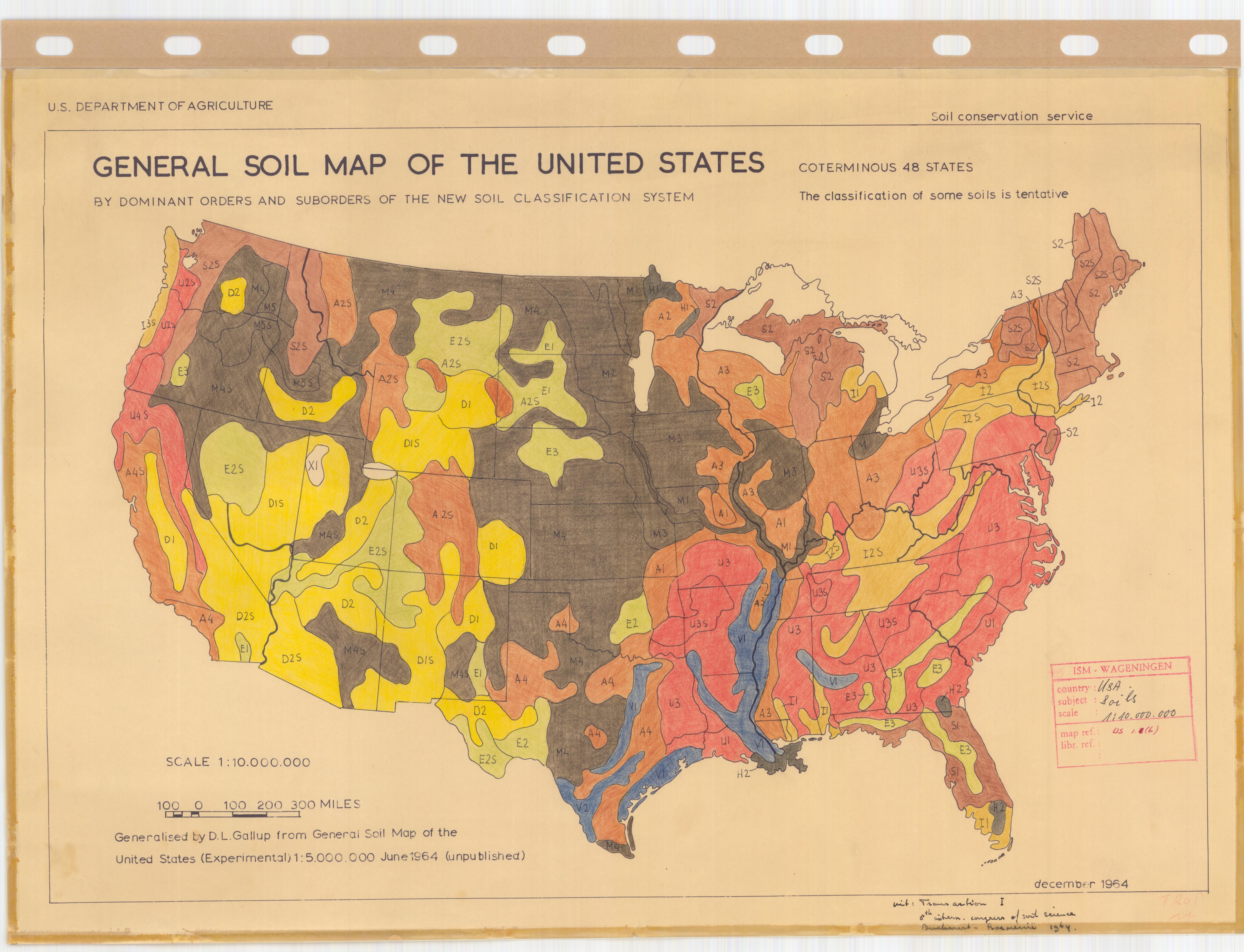





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of American Soil: A Comprehensive Guide to the Soil Map of the United States. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!