Unraveling the Layers of History: A Guide to the Map of Ancient Troy
Related Articles: Unraveling the Layers of History: A Guide to the Map of Ancient Troy
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Layers of History: A Guide to the Map of Ancient Troy. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Layers of History: A Guide to the Map of Ancient Troy

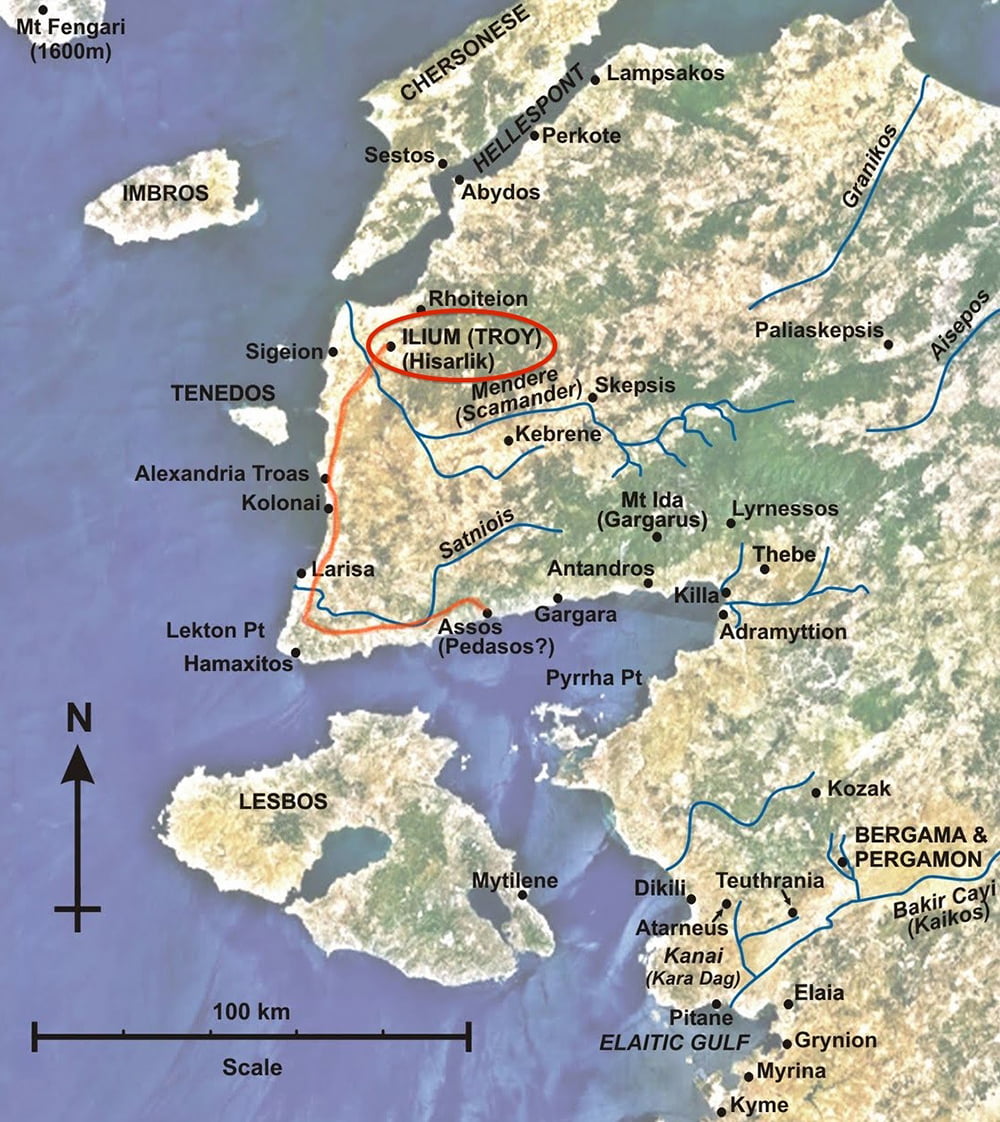
The city of Troy, immortalized by Homer’s epic poem The Iliad, has captivated the imagination of humankind for millennia. Its location, nestled on the northwest coast of Turkey, has been the subject of intense archaeological investigation, revealing a complex and layered history spanning centuries. Understanding the layout of ancient Troy, as depicted on maps, offers invaluable insights into the city’s development, its societal structure, and its strategic importance in the ancient world.
A Tapestry of Eras: Delving into the Layers of Troy
The map of ancient Troy is not a singular entity, but rather a collection of superimposed layers representing different phases of the city’s existence. Excavations have unearthed nine distinct layers, each representing a different settlement period, from the Early Bronze Age to the Roman era. These layers, designated as Troy I to Troy IX, provide a chronological framework for understanding the city’s evolution.
Troy I – III (c. 3000 – 2500 BCE): The Dawn of Civilization
The earliest settlements at Troy, Troy I to III, date back to the Early Bronze Age. These were small, fortified settlements with rudimentary structures, likely inhabited by agricultural communities. The presence of pottery and tools indicates early forms of craftsmanship and trade.
Troy IV – VI (c. 2500 – 1900 BCE): The Rise of a Powerhouse
The period between Troy IV and VI marks a significant transformation. The city expanded considerably, developing a more sophisticated urban layout. Fortifications became more elaborate, and the presence of monumental structures suggests the emergence of a ruling elite. This period also witnessed the introduction of metalworking, indicating technological advancement and economic prosperity.
Troy VIIa (c. 1300 – 1250 BCE): The City of Homer’s Iliad
Troy VIIa, often referred to as the "Homeric Troy," is the most well-known layer due to its association with the Trojan War described in The Iliad. This period saw the construction of the iconic "Trojan Wall," a formidable defensive structure that played a pivotal role in the epic poem. The layout of Troy VIIa reveals a city with a well-defined urban plan, a complex system of streets, and a central citadel.
Troy VIIb (c. 1250 – 1180 BCE): The Aftermath of War
Following the Trojan War, Troy VIIb witnessed a period of decline and reconstruction. The city’s fortifications were rebuilt, but evidence suggests a significant population decrease. This period may reflect the aftermath of the war and the subsequent instability.
Troy VIII – IX (c. 1180 – 400 BCE): A New Chapter
Troy VIII and IX mark a revival of the city, though on a smaller scale than its previous peak. The city continued to exist as a trading center, but its influence diminished compared to its earlier prominence. The Roman period (Troy IX) saw the city integrated into the Roman Empire, eventually becoming a small provincial town.
Unraveling the Secrets of Troy: The Importance of the Map
The map of ancient Troy serves as a vital tool for understanding the city’s historical trajectory. It allows archaeologists and historians to:
- Reconstruct the physical layout of the city at different periods. By analyzing the placement of buildings, streets, and fortifications, researchers can piece together a detailed picture of how the city functioned and evolved over time.
- Identify key areas of activity and importance. The map reveals the location of public spaces, religious structures, residential areas, and defensive features, providing insights into the city’s social, religious, and political organization.
- Understand the city’s strategic significance. The map’s depiction of fortifications and its location on a strategic trade route highlight the city’s importance as a military and economic hub in the ancient world.
- Trace the impact of historical events. The map helps to visualize the changes brought about by events like the Trojan War, demonstrating the city’s resilience and adaptation to periods of both prosperity and decline.
FAQs about the Map of Ancient Troy:
Q: How accurate are the maps of ancient Troy?
A: The maps of ancient Troy are based on archaeological excavations and are constantly being refined as new discoveries are made. While they provide a general overview, it’s important to note that they are reconstructions based on available evidence, and some details may remain uncertain.
Q: What are the main features depicted on the map of ancient Troy?
A: The map typically shows the city walls, gates, streets, key buildings (such as temples, palaces, and houses), and the location of significant archaeological finds.
Q: What are the most important archaeological sites in Troy?
A: Some of the most notable archaeological sites in Troy include the Trojan Wall, the Scaean Gate, the Citadel, the Temple of Athena, and the "House of Priam" (the presumed palace of the Trojan king).
Q: How can I access the map of ancient Troy?
A: You can find maps of ancient Troy in archaeological publications, textbooks, and online resources. Many museums and archaeological sites also provide maps as part of their exhibits.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Ancient Troy:
- Study the different layers of the city. Understand the chronological sequence of the various Troy periods to grasp the city’s evolution over time.
- Pay attention to the key features. Focus on the location of fortifications, gates, major buildings, and streets to understand the city’s layout and organization.
- Use other resources. Combine the map with historical texts, archaeological reports, and photographs to gain a more comprehensive understanding of ancient Troy.
- Visit the site if possible. Seeing the ruins firsthand can provide an invaluable perspective and enhance your understanding of the city’s history.
Conclusion: A Legacy Engraved in Stone
The map of ancient Troy serves as a powerful testament to the enduring legacy of this legendary city. By visualizing its layout, we gain a deeper appreciation for the city’s rich history, its complex social structure, and its strategic importance in the ancient world. The map not only guides us through the ruins of a bygone era but also connects us to the epic tales and enduring myths that have shaped human civilization for centuries.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Layers of History: A Guide to the Map of Ancient Troy. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!