Unlocking the Potential of Indiana: A Deep Dive into Geographic Information Systems
Related Articles: Unlocking the Potential of Indiana: A Deep Dive into Geographic Information Systems
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Potential of Indiana: A Deep Dive into Geographic Information Systems. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Potential of Indiana: A Deep Dive into Geographic Information Systems

Indiana, a state rich in history, culture, and diverse landscapes, benefits immensely from the application of Geographic Information Systems (GIS). GIS, a powerful tool that integrates spatial data with other information, offers a comprehensive understanding of the state’s environment, infrastructure, and population dynamics. By visualizing and analyzing geographically referenced data, GIS provides a valuable platform for informed decision-making across various sectors in Indiana.
Understanding the Foundation: What is GIS?
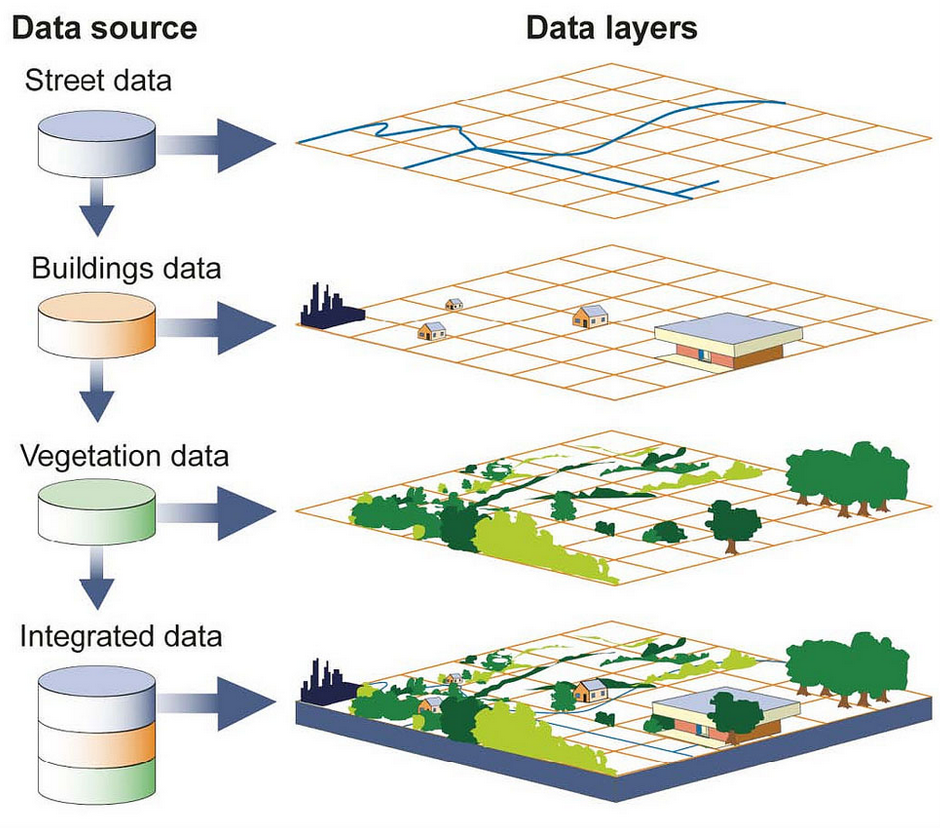
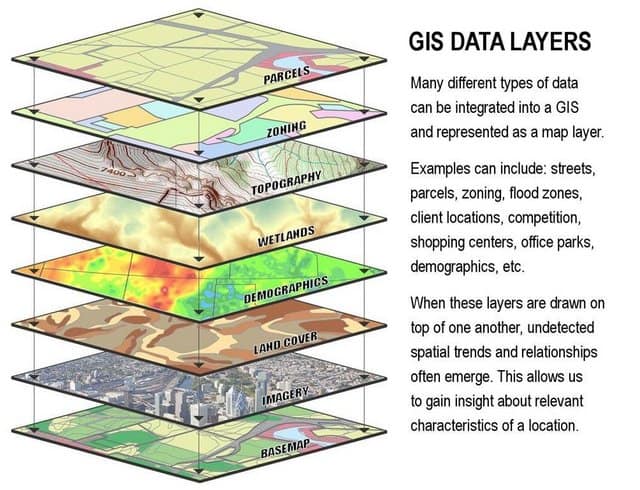
At its core, GIS is a system for capturing, storing, analyzing, managing, and presenting geographically referenced data. This data, often referred to as geospatial data, can encompass a wide range of information, including:
- Environmental Data: Elevation, soil type, vegetation cover, water bodies, and climate patterns.
- Infrastructure Data: Roads, bridges, power lines, pipelines, and communication networks.
- Population Data: Demographics, housing, social services, and healthcare facilities.
- Economic Data: Business locations, employment rates, and industry clusters.
GIS utilizes specialized software to integrate this diverse data, creating interactive maps and visualizations. These maps are not merely static representations; they are dynamic tools for analysis and decision-making.
Unveiling the Benefits: How GIS Transforms Indiana
The impact of GIS on Indiana is multifaceted, extending across various sectors, including:
1. Environmental Management:
- Natural Resource Management: GIS enables efficient monitoring and management of Indiana’s natural resources, including forests, wetlands, and water bodies. Analyzing spatial patterns of land use and environmental stressors allows for targeted conservation efforts and sustainable resource utilization.
- Disaster Preparedness: GIS plays a crucial role in disaster preparedness by providing real-time information on flood zones, evacuation routes, and critical infrastructure. This data empowers emergency responders to make informed decisions and mitigate the impact of natural disasters.
- Pollution Monitoring: GIS aids in tracking and analyzing air and water pollution levels, identifying pollution sources, and implementing effective mitigation strategies.
2. Infrastructure Planning and Development:
- Transportation Planning: GIS helps optimize transportation networks, planning new roads and public transit systems, and analyzing traffic flow patterns. This data-driven approach leads to efficient infrastructure development and reduced congestion.
- Utility Management: GIS assists in managing utility networks, including water, electricity, and gas distribution. This includes locating infrastructure assets, identifying potential hazards, and optimizing maintenance schedules.
- Land Use Planning: GIS enables informed land use planning, balancing development with environmental protection, and ensuring sustainable urban growth.
3. Public Safety and Emergency Response:
- Crime Mapping: GIS tools allow law enforcement agencies to analyze crime patterns, identify high-risk areas, and deploy resources effectively. This data-driven approach helps prevent crime and improve public safety.
- Emergency Response: GIS provides crucial information during emergencies, such as fire outbreaks or hazardous material spills, facilitating rapid deployment of emergency services and improving response efficiency.
- Search and Rescue: GIS assists search and rescue teams in locating missing persons, leveraging terrain data, weather information, and historical data to guide search efforts.
4. Economic Development and Business:
- Site Selection: GIS aids businesses in finding ideal locations for new facilities, considering factors such as proximity to transportation networks, workforce availability, and market access.
- Market Analysis: GIS helps businesses analyze market trends, identify target demographics, and understand customer behavior. This data-driven approach optimizes marketing strategies and business operations.
- Tourism and Recreation: GIS supports the tourism industry by providing interactive maps of attractions, hiking trails, and other recreational activities, enhancing visitor experiences and promoting tourism development.
5. Education and Research:
- Spatial Analysis: GIS empowers researchers and educators to analyze spatial data, identify patterns, and explore relationships between different variables. This facilitates scientific research and enhances educational resources.
- Remote Sensing: GIS integrates with remote sensing data, such as satellite imagery, allowing for detailed analysis of land cover changes, environmental monitoring, and resource management.
- Geographic Education: GIS introduces students to spatial thinking and data analysis, fostering a deeper understanding of geography and its applications in various fields.
FAQs about Indiana GIS
1. What are the key resources for accessing GIS data in Indiana?
Indiana offers various resources for accessing geospatial data. The Indiana Geographic Information Council (IGIC) serves as a central hub for sharing and promoting GIS data. The Indiana Department of Natural Resources (IDNR) provides a wide range of environmental data, including land cover, elevation, and water bodies. The Indiana Department of Transportation (INDOT) offers road network data and traffic information. Other agencies, including the Indiana Department of Health and the Indiana Department of Education, also contribute to the state’s GIS data repository.
2. How can I learn more about GIS and its applications in Indiana?
Several institutions in Indiana offer GIS education and training programs. Purdue University, Indiana University, and Ball State University have strong GIS departments, offering undergraduate and graduate degrees. The Indiana GIS Association (IGISA) provides networking opportunities and professional development resources for GIS professionals. Online platforms like Coursera and edX also offer GIS courses and certifications.
3. What are the challenges associated with using GIS in Indiana?
Despite its numerous benefits, GIS implementation in Indiana faces certain challenges. Data availability and standardization can be a concern, with different agencies using varying data formats and collection methods. Ensuring data accuracy and reliability is crucial for effective GIS applications. Additionally, funding and technical expertise are essential for maintaining and updating GIS systems.
Tips for Utilizing GIS in Indiana
1. Data Quality and Standardization: Prioritize data quality by adhering to established standards and ensuring data accuracy. This involves consistent data collection methods, data validation procedures, and regular updates.
2. Collaboration and Data Sharing: Foster collaboration between different agencies and organizations to facilitate data sharing and resource pooling. This enhances the comprehensiveness and value of GIS data.
3. Education and Training: Invest in GIS education and training programs to equip professionals with the necessary skills to effectively utilize GIS tools and data.
4. Public Engagement: Engage the public in GIS initiatives to raise awareness about its applications and benefits. This can involve interactive mapping tools, citizen science projects, and community workshops.
5. Technological Advancement: Stay abreast of technological advancements in GIS, including cloud-based platforms, mobile applications, and artificial intelligence. These innovations can enhance GIS capabilities and expand its potential applications.
Conclusion
GIS is an invaluable tool for understanding and managing Indiana’s complex environment, infrastructure, and population dynamics. By leveraging its power, the state can optimize resource management, enhance public safety, promote economic development, and improve decision-making across various sectors. As Indiana continues to embrace GIS, its potential to drive progress and improve the lives of its citizens will continue to grow.
![]()



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Potential of Indiana: A Deep Dive into Geographic Information Systems. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!