Unlocking the Past: Understanding North America’s Ice Age Map
Related Articles: Unlocking the Past: Understanding North America’s Ice Age Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Past: Understanding North America’s Ice Age Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Past: Understanding North America’s Ice Age Map

The North American landscape, a tapestry of diverse ecosystems, harbors a fascinating history etched in glacial ice and sculpted by its retreat. The Ice Age, a period spanning from approximately 2.6 million years ago to 11,700 years ago, dramatically reshaped the continent, leaving behind a legacy of geological wonders and a profound impact on the evolution of life. Understanding the Ice Age, particularly through the lens of a North American Ice Age map, offers a window into the past, illuminating the forces that shaped the present and informing our understanding of the future.
A Visual Journey Through Time:
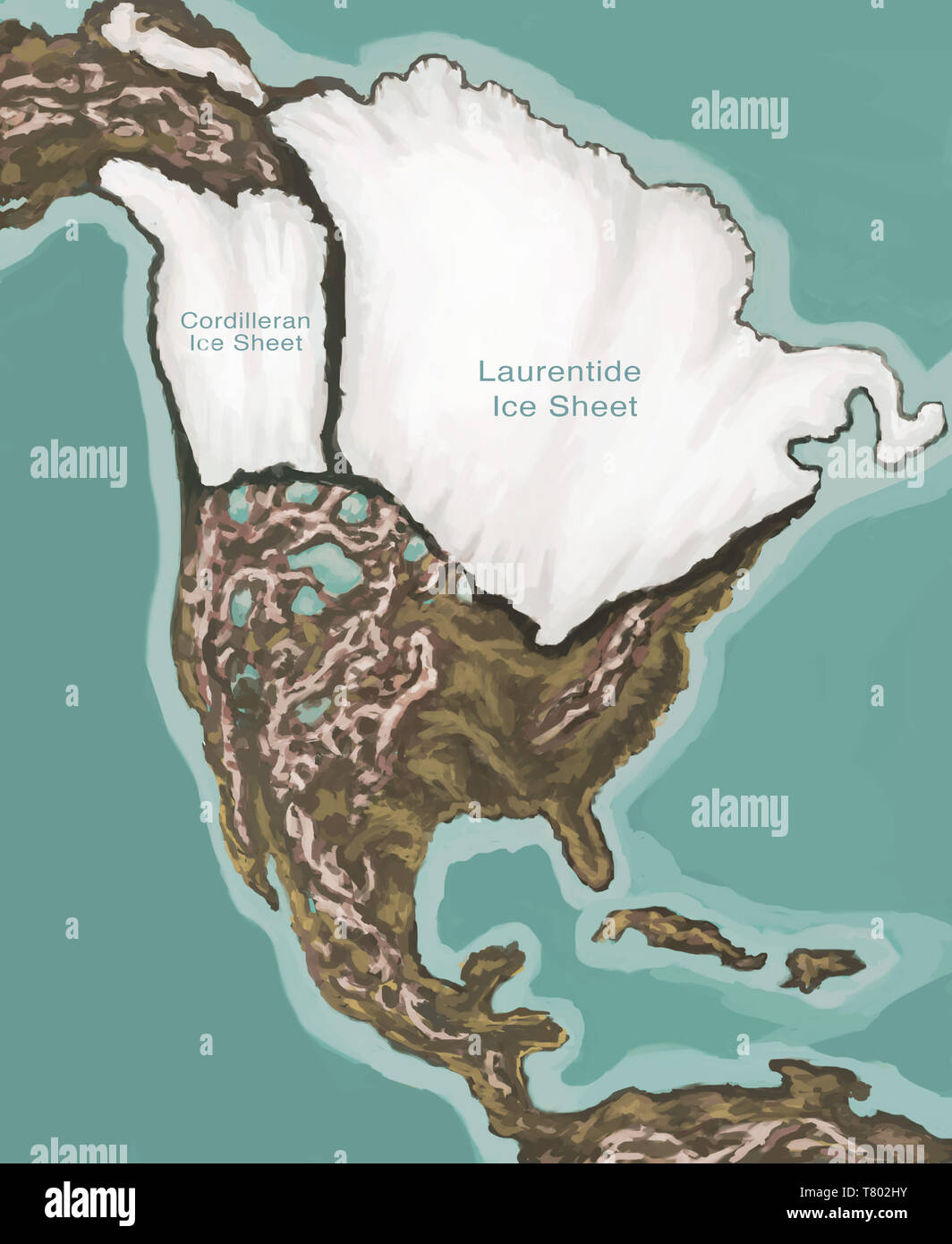
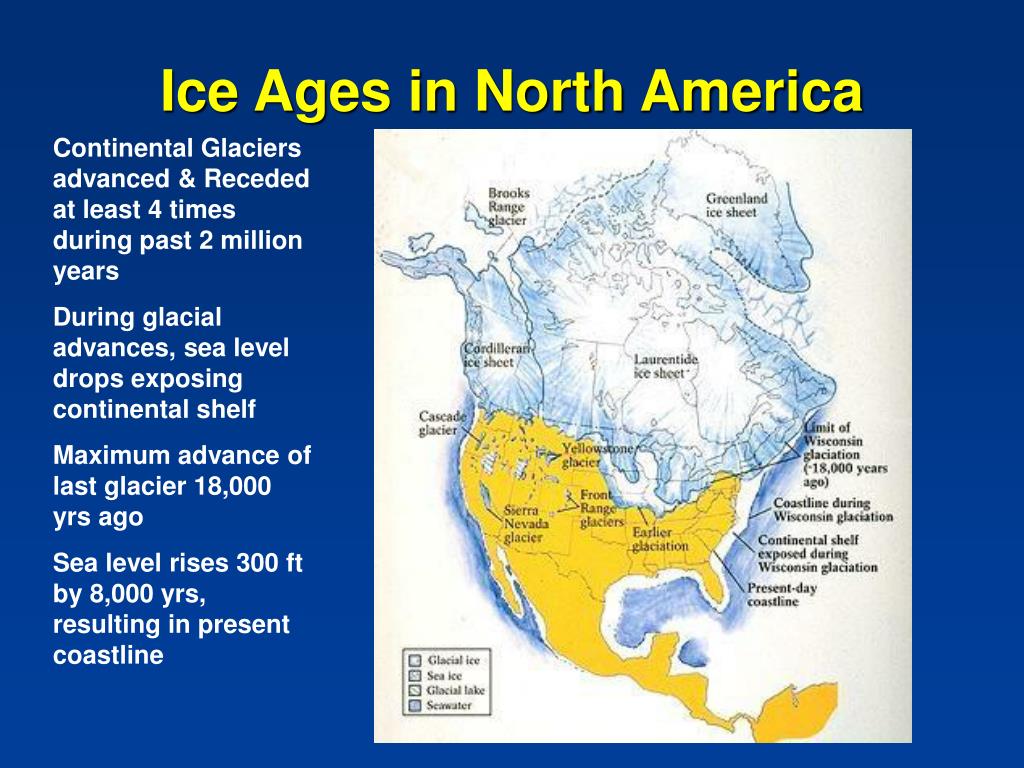
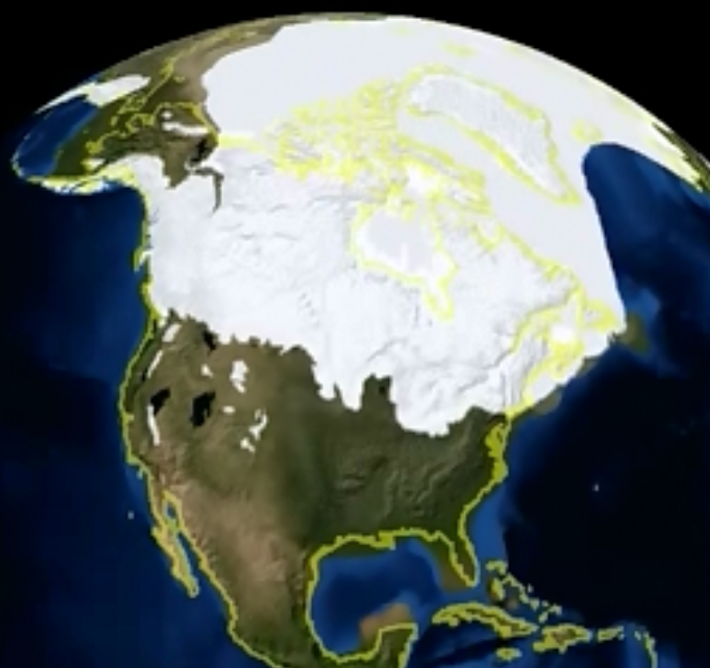
A North American Ice Age map is a powerful tool for visualizing the glacial cycles that swept across the continent. It reveals the extent and movement of massive ice sheets, their advances and retreats, and the dramatic changes in geography they wrought. These maps typically depict the maximum glacial extent, often referred to as the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), which occurred approximately 20,000 years ago. During this period, vast ice sheets, originating in the Canadian Shield and the Rocky Mountains, covered much of North America, reaching as far south as the Ohio River Valley and the Missouri River Valley.
The Power of Ice:
The ice sheets, colossal masses of frozen water, possessed immense power. Their sheer weight pressed down on the land, causing the Earth’s crust to sink. This phenomenon, known as isostatic depression, led to the formation of large basins that later filled with water as the ice melted, forming the Great Lakes and other prominent geographical features. The movement of the ice sheets, driven by gravity and the force of their own weight, carved out valleys, sculpted mountains, and deposited vast quantities of sediment, leaving behind the distinctive landscapes we see today.
A Legacy of Change:
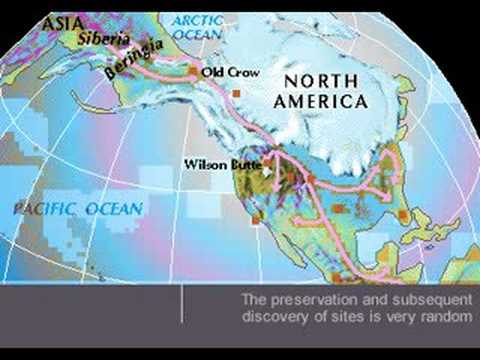
The retreat of the ice sheets, a gradual process that spanned millennia, left behind a landscape transformed. The melting ice released enormous volumes of water, contributing to rising sea levels and inundating coastal areas. The deposited sediments formed fertile soils, providing the foundation for diverse ecosystems and shaping the distribution of plant and animal life. The Ice Age also played a crucial role in shaping the course of human migration, influencing the routes and patterns of early human settlements.
Unveiling the Past, Understanding the Future:
The study of the North American Ice Age map is not merely a historical exercise. It holds significant implications for our understanding of climate change and its potential impact on the future. By analyzing past glacial cycles, scientists can gain insights into the dynamics of ice sheets, their response to changing temperatures, and the potential consequences of future warming. These insights are critical for developing strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change and adapt to the challenges it presents.
Exploring the Map’s Significance:
1. Geological Formation: The North American Ice Age map is a testament to the transformative power of glacial processes. It reveals how the landscape was sculpted by the advance and retreat of ice sheets, highlighting the formation of valleys, mountains, and vast deposits of sediment.
2. Geographical Evolution: The map demonstrates the dynamic nature of the Earth’s surface, showcasing how the movement of ice sheets altered coastlines, created lakes, and shaped the distribution of landforms.
3. Biological Diversity: The retreat of the ice sheets facilitated the migration of plants and animals, leading to the development of diverse ecosystems and the establishment of unique flora and fauna.
4. Human History: The map provides insights into the routes and patterns of human migration, revealing how early human settlements were influenced by the availability of resources and the changing landscape.
5. Climate Change Insights: By studying past glacial cycles, scientists can gain valuable information about the dynamics of ice sheets, their response to changing temperatures, and the potential consequences of future warming.
FAQs about the North American Ice Age Map:
Q: What is the significance of the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM)?
A: The LGM represents the peak of the most recent glacial period, marking the maximum extent of ice sheets covering North America. Understanding the LGM is crucial for analyzing the impact of glacial processes and their influence on the landscape.
Q: How did the ice sheets contribute to the formation of the Great Lakes?
A: The weight of the ice sheets caused the Earth’s crust to sink, creating large basins. As the ice melted, these basins filled with water, forming the Great Lakes.
Q: What evidence exists to support the existence of the Ice Age?
A: Evidence includes glacial striations, moraines, glacial erratics, and the presence of specific plant and animal species adapted to cold climates.
Q: How does the North American Ice Age map inform our understanding of climate change?
A: By studying past glacial cycles, scientists can gain insights into the dynamics of ice sheets and their response to changing temperatures, providing valuable information for predicting the potential consequences of future warming.
Tips for Understanding the North American Ice Age Map:
1. Explore the Map’s Key Features: Pay attention to the extent of the ice sheets, their direction of movement, and the locations of prominent glacial features.
2. Consider the Temporal Scale: Understand that the Ice Age was not a single event but a series of glacial cycles, each with its own unique characteristics.
3. Relate the Map to Present-Day Geography: Identify the areas that were once covered by ice sheets and observe how the landscape has been shaped by their retreat.
4. Explore the Interconnections: Recognize the interconnectedness of glacial processes, climate change, and the evolution of life on Earth.
5. Consult Additional Resources: Utilize online databases, scientific articles, and educational materials to deepen your understanding of the Ice Age and its impact on North America.
Conclusion:
The North American Ice Age map is a powerful tool for understanding the forces that shaped the continent, revealing a history of dramatic change, geological wonders, and the enduring impact of glacial processes. By exploring the map’s key features and considering its broader implications, we gain a deeper appreciation for the dynamic nature of the Earth’s surface, the interconnectedness of natural systems, and the importance of studying the past to inform our understanding of the future. The map serves as a reminder that the landscape we inhabit is not static but rather a product of ongoing geological and climatic forces, shaping the environment and influencing the course of life on Earth.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Past: Understanding North America’s Ice Age Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!