Understanding California’s Seismic Landscape: A Guide to Earthquake Maps
Related Articles: Understanding California’s Seismic Landscape: A Guide to Earthquake Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding California’s Seismic Landscape: A Guide to Earthquake Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding California’s Seismic Landscape: A Guide to Earthquake Maps
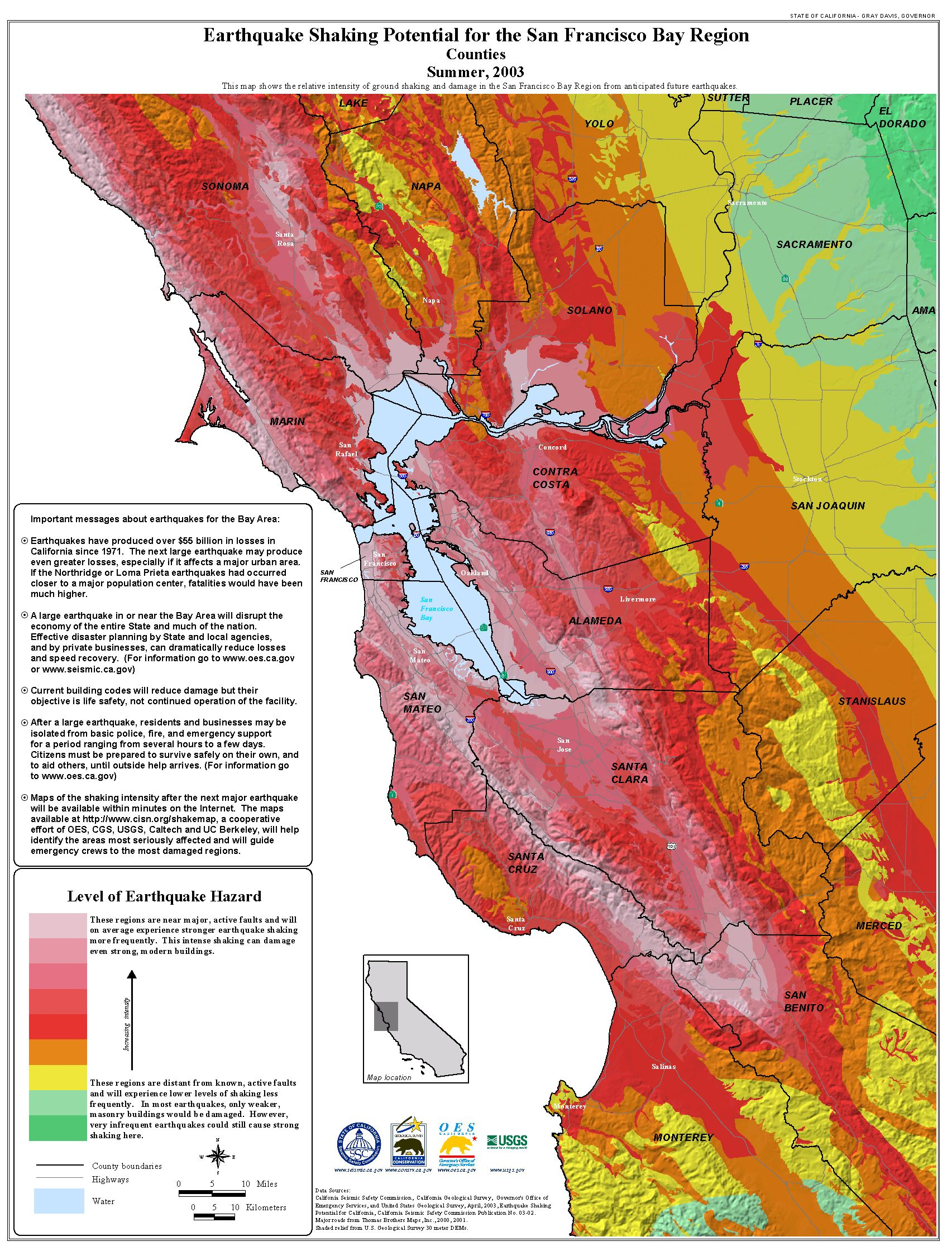
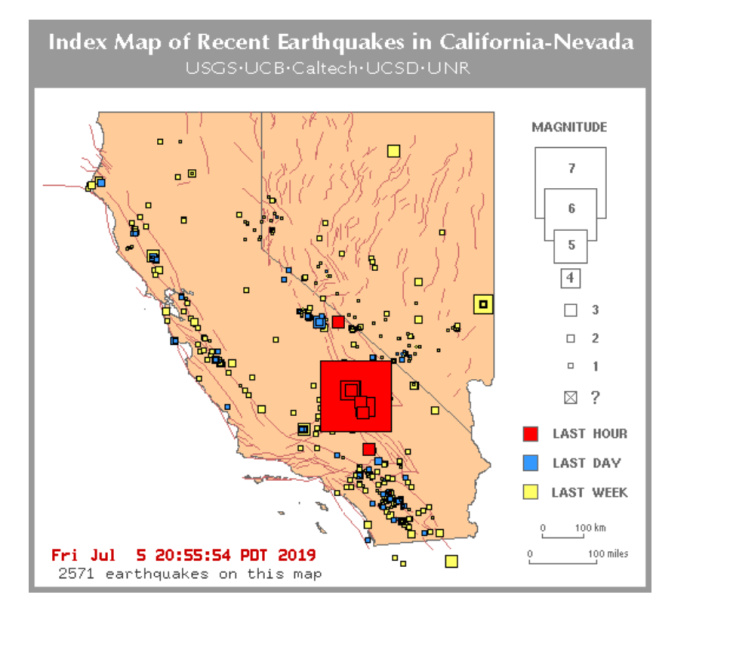
California, a state renowned for its diverse landscapes and vibrant culture, is also known for its dynamic geological history. This dynamism manifests in the form of frequent seismic activity, a reality that underscores the importance of understanding earthquake hazards and preparedness. A key tool in this endeavor is the California Earthquake Maps, which provide invaluable insights into the state’s seismic landscape.
Deciphering the Language of Earthquake Maps:
Earthquake maps, often referred to as seismic hazard maps, are visual representations of the potential for ground shaking and other earthquake-related hazards. They are not predictions of when an earthquake will occur, but rather, they depict the probability of experiencing strong ground shaking in a specific area. These maps use a variety of colors and symbols to illustrate different levels of seismic risk, helping to visualize the potential impact of earthquakes on communities.
Key Components of California Earthquake Maps:
California’s earthquake maps incorporate various data sources and analytical methods to provide a comprehensive picture of seismic hazards. Some of the key components include:
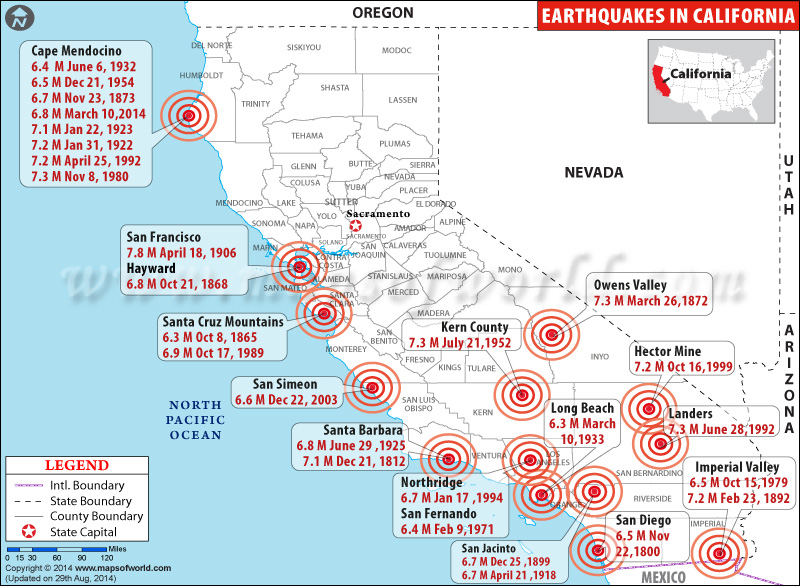
- Fault Lines: These are fractures in the Earth’s crust where tectonic plates move past each other. California is crisscrossed by numerous fault lines, including the infamous San Andreas Fault, which is responsible for some of the state’s most significant earthquakes.
- Ground Shaking Intensity: This refers to the strength of shaking that is expected during an earthquake. It is often measured using the Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale, which ranges from I (not felt) to XII (extreme).
- Liquefaction Potential: This refers to the likelihood of soil turning into a fluid-like substance during an earthquake, which can cause significant damage to buildings and infrastructure.
- Tsunami Risk: Some areas along the California coast are at risk of being impacted by tsunamis, giant waves generated by earthquakes in the ocean.
The Significance of Earthquake Maps:
Earthquake maps serve as essential tools for a variety of stakeholders, including:
- Government Agencies: These maps help agencies like the California Geological Survey (CGS) and the California Office of Emergency Services (OES) to develop and implement earthquake preparedness plans.
- Emergency Responders: Firefighters, police officers, and paramedics use these maps to assess potential risks and develop strategies for responding to earthquake events.
- Engineers and Architects: These professionals rely on earthquake maps to design and build structures that can withstand seismic forces.
- Land Use Planners: These individuals use earthquake maps to guide development decisions and ensure that communities are located in areas with minimal seismic risk.
- Individuals and Families: Understanding earthquake maps empowers individuals and families to take proactive steps to prepare for earthquakes, such as securing furniture, creating emergency kits, and developing evacuation plans.
Exploring the Benefits of Earthquake Maps:
The benefits of utilizing earthquake maps extend beyond simply understanding the potential for seismic events. They provide a framework for:
- Informed Decision-Making: By visualizing the potential for ground shaking and other earthquake-related hazards, these maps allow individuals, communities, and organizations to make informed decisions about land use, infrastructure development, and emergency preparedness.
- Risk Mitigation: Understanding the seismic hazards in a particular area enables the implementation of mitigation strategies, such as building codes that incorporate earthquake-resistant design principles, and the development of early warning systems to provide advance notice of impending earthquakes.
- Community Resilience: By fostering awareness and preparedness, earthquake maps contribute to building community resilience, enabling individuals, families, and communities to better cope with the challenges of earthquakes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about California Earthquake Maps:
Q: How often are California earthquake maps updated?
A: Earthquake maps are constantly being updated as new data becomes available. The California Geological Survey (CGS) periodically revises its maps based on advances in scientific understanding, new geological data, and the occurrence of significant earthquakes.
Q: What is the difference between a seismic hazard map and a risk map?
A: A seismic hazard map depicts the potential for ground shaking and other earthquake-related hazards, while a risk map takes into account the potential consequences of these hazards, such as the potential for damage to buildings, infrastructure, and human life.
Q: How can I access California earthquake maps?
A: You can access California earthquake maps online through the California Geological Survey (CGS) website, the United States Geological Survey (USGS) website, and various other sources.
Q: What are some tips for preparing for an earthquake in California?
A: Here are some tips for earthquake preparedness:
- Secure heavy objects: Secure heavy furniture, appliances, and other objects that could fall and cause injury.
- Create an emergency kit: Prepare an emergency kit that includes food, water, first-aid supplies, a flashlight, a radio, and other essential items.
- Develop an evacuation plan: Develop an evacuation plan for your family and practice it regularly.
- Know your earthquake safety procedures: Familiarize yourself with the earthquake safety procedures for your workplace, school, or other places you frequent.
Conclusion:
Understanding California’s seismic landscape is crucial for ensuring the safety and well-being of its residents. California earthquake maps provide a vital tool for visualizing the potential for ground shaking and other earthquake-related hazards. By utilizing these maps, individuals, communities, and organizations can make informed decisions about land use, infrastructure development, and emergency preparedness, ultimately contributing to a more resilient and earthquake-safe California.


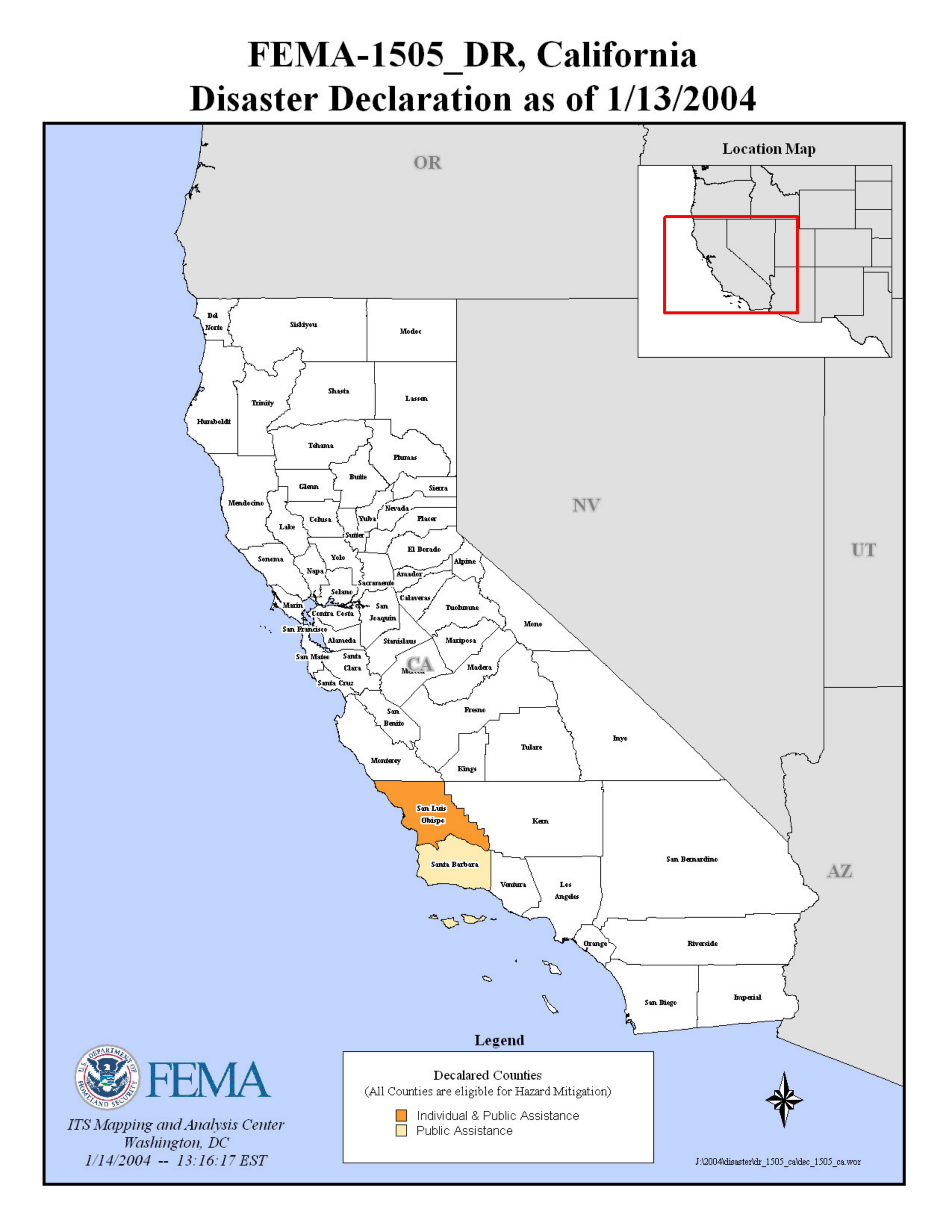
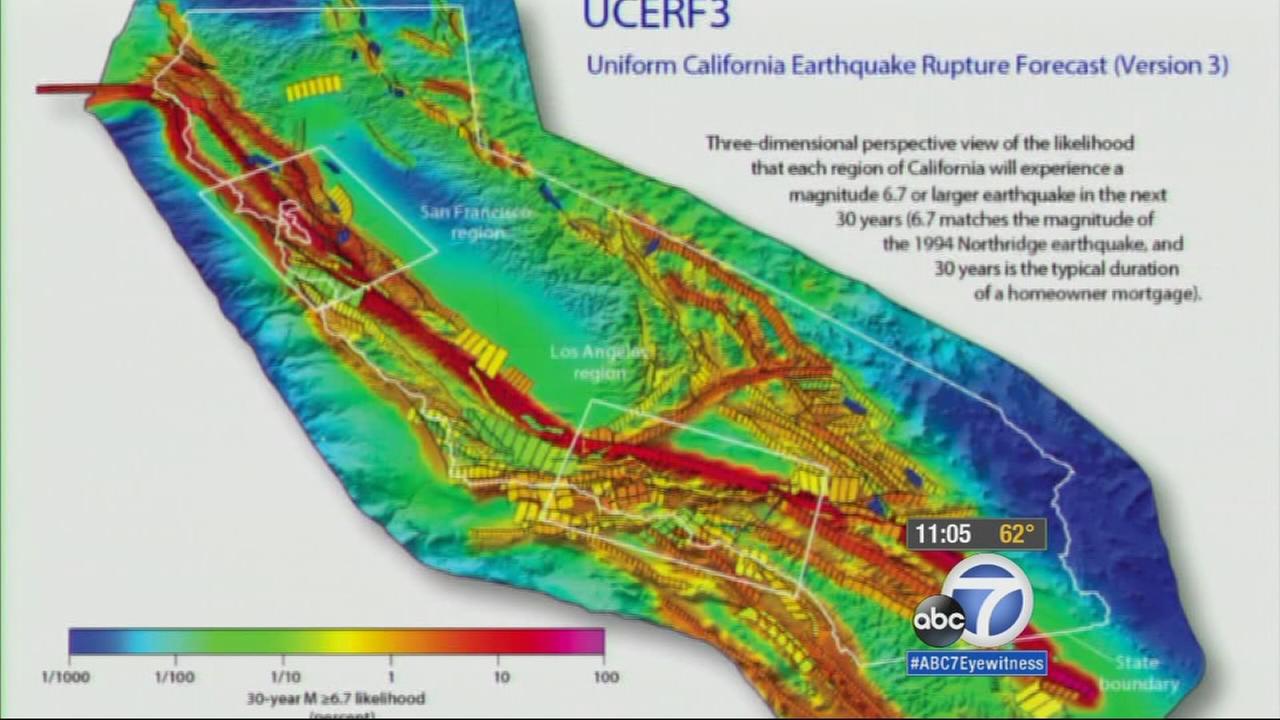
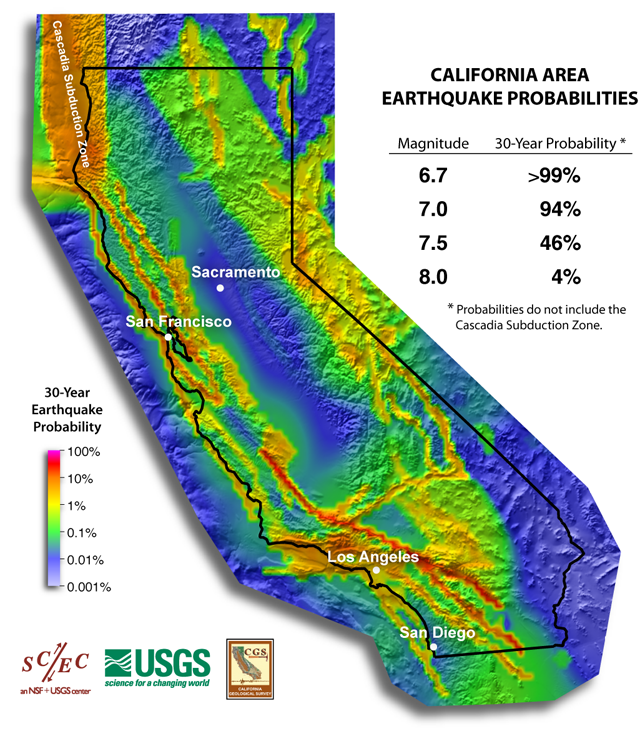

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding California’s Seismic Landscape: A Guide to Earthquake Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!