Tibet on the World Map: A Land of High Altitudes and Deep Significance
Related Articles: Tibet on the World Map: A Land of High Altitudes and Deep Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Tibet on the World Map: A Land of High Altitudes and Deep Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Tibet on the World Map: A Land of High Altitudes and Deep Significance
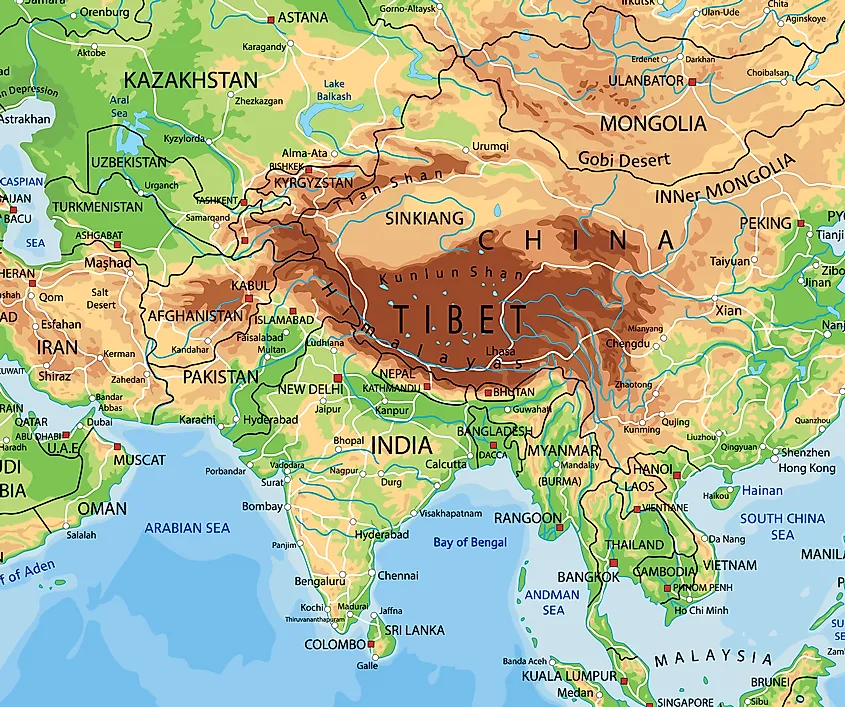
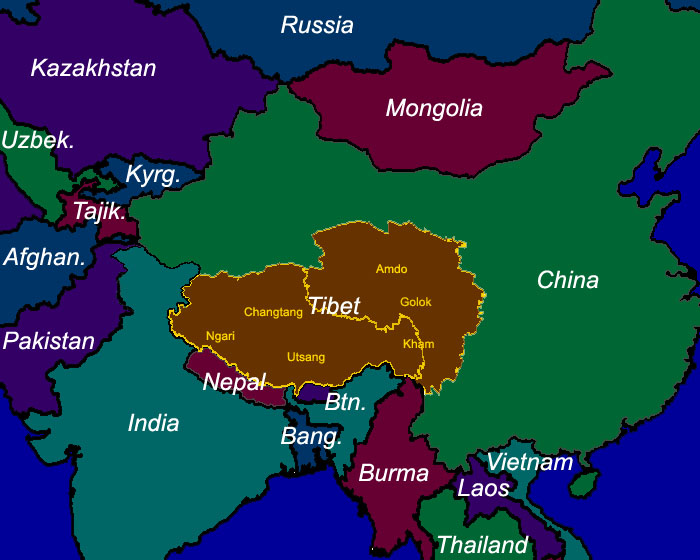
Tibet, often referred to as the "Roof of the World," occupies a prominent position on the world map, nestled in the heart of Asia. Its geographical location, spanning a vast plateau stretching across the southwestern portion of China, makes it a region of immense cultural, historical, and environmental significance.
A Land of Extremes:
Tibet’s landscape is characterized by towering Himalayan peaks, including Mount Everest, the world’s highest mountain, and vast, windswept plains. The region is also home to numerous glaciers, alpine lakes, and deep canyons, creating a breathtaking tapestry of natural beauty. This harsh environment, with its thin atmosphere and extreme temperatures, has shaped the unique culture and traditions of the Tibetan people.
A Historical Crossroads:
Tibet’s strategic location at the crossroads of major trade routes connecting India, China, and Central Asia has played a crucial role in its history. Ancient civilizations, including the Yarlung Dynasty, flourished in Tibet, establishing a unique cultural and religious identity. The introduction of Buddhism in the 7th century CE transformed Tibetan society, shaping its art, literature, and philosophy.
The Tibetan Plateau: A Global Environmental Hotspot:
The Tibetan Plateau, the largest and highest plateau on Earth, is a vital source of water for major rivers like the Yangtze, Yellow, Indus, and Ganges. Its glaciers act as natural reservoirs, providing water for billions of people downstream. The plateau’s unique ecosystem, with its diverse flora and fauna, also plays a critical role in regulating global climate patterns.
A Cultural Tapestry:
Tibet’s rich cultural heritage is deeply intertwined with Buddhism. The region is home to numerous monasteries, temples, and sacred sites, attracting pilgrims and visitors from around the world. Traditional Tibetan art, music, and dance reflect the spiritual and philosophical values of the people. The iconic Tibetan prayer wheels, spinning mantras and prayers, are a testament to the enduring influence of Buddhism in everyday life.
A Complex Political Landscape:
Tibet’s political status has been a source of ongoing international debate. The region was historically an independent kingdom before being incorporated into China in the 1950s. The Dalai Lama, the spiritual leader of Tibetan Buddhism, advocates for autonomy for Tibet, while the Chinese government maintains its sovereignty over the region. This complex political situation has implications for Tibet’s cultural preservation, environmental sustainability, and economic development.
The Importance of Tibet on the World Map:
Tibet’s geographical, cultural, and environmental significance makes it a vital part of the global landscape. The region’s unique ecosystem plays a crucial role in regulating global climate patterns, while its cultural heritage contributes to the diversity and richness of human civilization. The Tibetan Plateau’s vast water resources are essential for the well-being of billions of people in Asia.
FAQs about Tibet on the World Map:
Q: Where is Tibet located on the world map?
A: Tibet is located in the southwestern part of China, occupying a vast plateau in the Himalayas.
Q: What is the significance of Tibet’s location?
A: Tibet’s location at the crossroads of major trade routes has historically connected it to India, China, and Central Asia.
Q: What are the main environmental concerns in Tibet?
A: The Tibetan Plateau’s fragile ecosystem is threatened by climate change, pollution, and overgrazing.
Q: What is the political status of Tibet?
A: Tibet is currently an autonomous region of China, but there are ongoing debates about its political status.
Q: What are some of the cultural highlights of Tibet?
A: Tibet is renowned for its rich Buddhist heritage, including monasteries, temples, and sacred sites.
Tips for Exploring Tibet:
- Plan your trip well in advance: Obtain the necessary permits and visas, and book accommodations and tours.
- Respect local customs and traditions: Dress modestly and avoid taking photos of people without permission.
- Be prepared for altitude sickness: Acclimatize gradually and drink plenty of fluids.
- Support local businesses and communities: Patronize Tibetan-owned businesses and participate in cultural events.
- Learn about Tibetan history and culture: Read books and articles, watch documentaries, and visit museums.
Conclusion:
Tibet’s position on the world map reflects its unique and complex history, culture, and environment. The region’s significance extends beyond its geographical boundaries, influencing global climate patterns, cultural diversity, and political dynamics. Understanding Tibet’s place in the world is crucial for appreciating its importance and the challenges it faces. By engaging with the Tibetan people, their culture, and their land, we can contribute to the preservation of this remarkable region for future generations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Tibet on the World Map: A Land of High Altitudes and Deep Significance. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!