The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation
Related Articles: The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation

The thirteen original colonies of British North America played a pivotal role in shaping the United States of America. Their unique history, diverse populations, and shared struggle for independence laid the groundwork for a nation that would eventually become a global power.
A Geographical Tapestry:
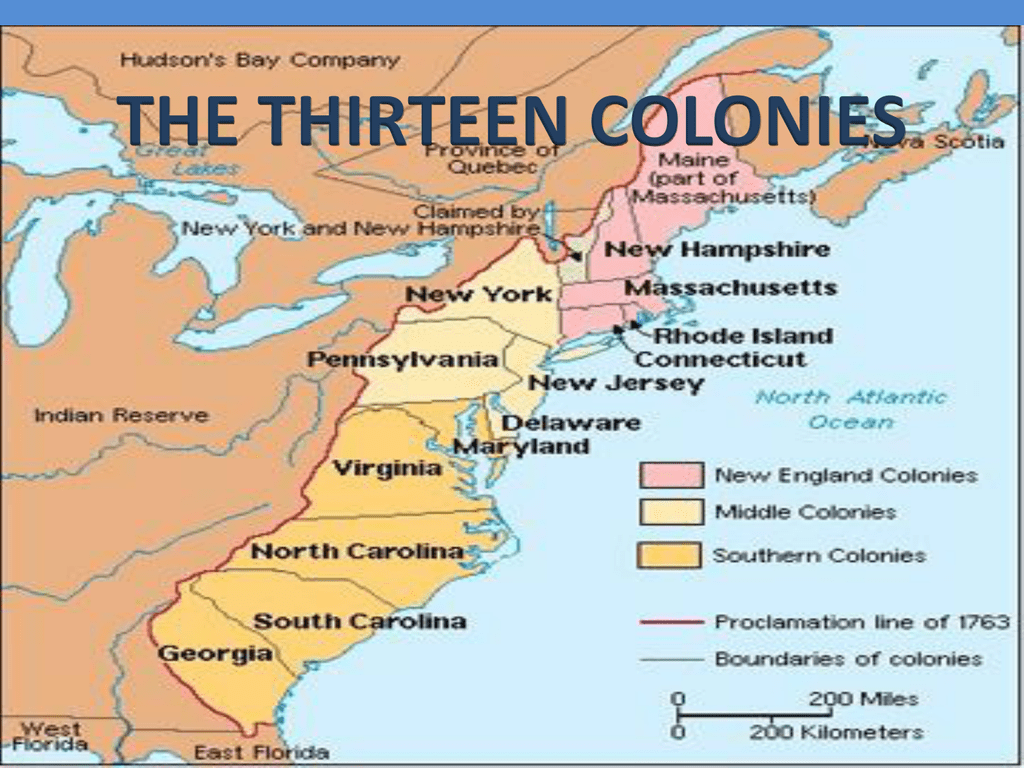
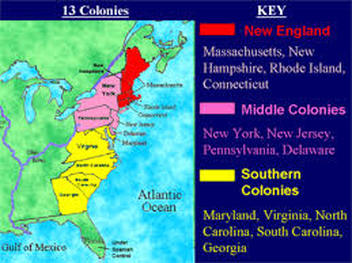
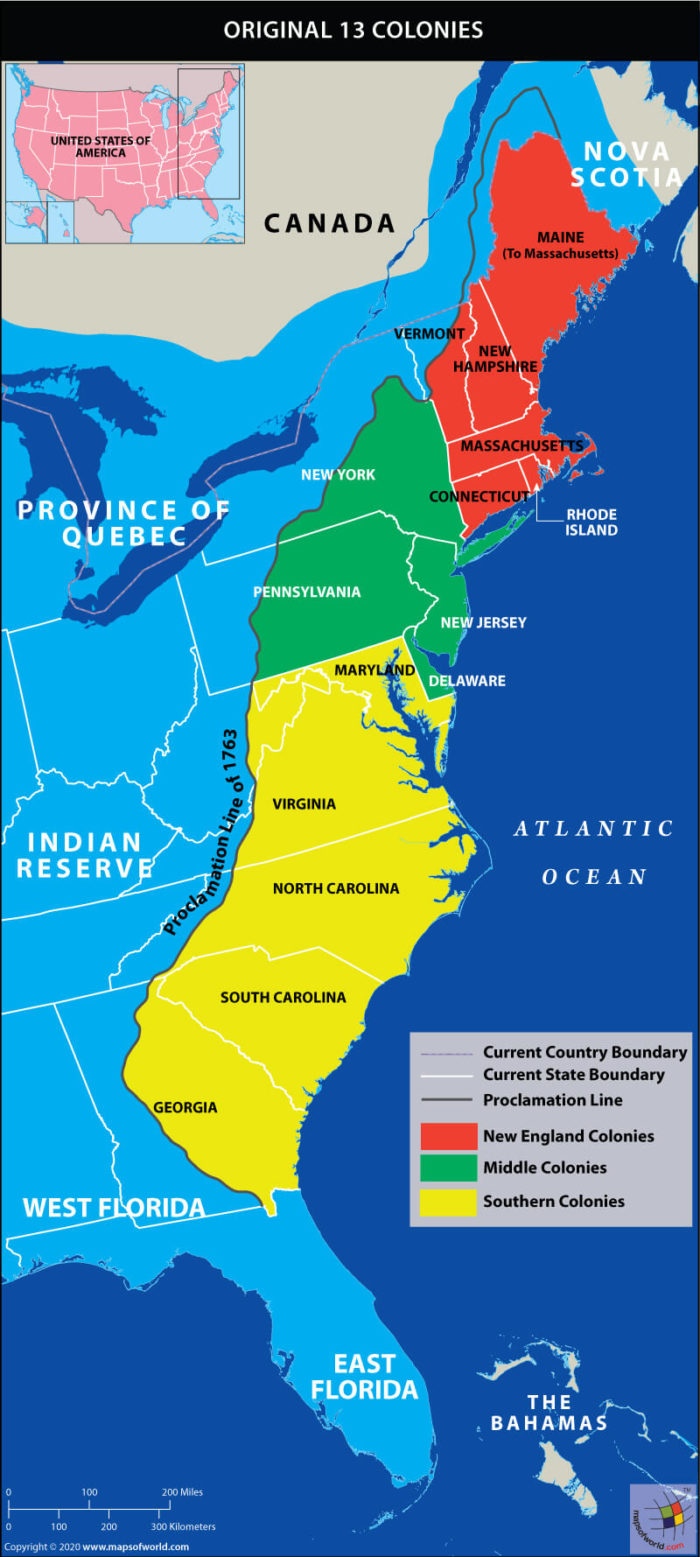
The thirteen colonies, stretching along the Atlantic coast from Maine to Georgia, were a diverse collection of settlements, each with its own distinct character.
- New England: The northernmost colonies – Maine, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut – were known for their rugged terrain, cold winters, and strong Puritan influence. These colonies focused on shipbuilding, fishing, and trade.
- The Middle Colonies: New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware possessed a more moderate climate and fertile soil, attracting a mix of settlers, including Dutch, German, and Swedish. These colonies developed a strong agricultural economy, growing grains and livestock.
- The Southern Colonies: Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia, characterized by warm climates and vast expanses of land, were primarily focused on plantation agriculture, particularly the cultivation of tobacco, rice, and indigo.
The Seeds of Independence:
The thirteen colonies, while united under British rule, experienced growing dissatisfaction with the policies of the British government. The imposition of taxes without representation, restrictions on trade, and the tightening of colonial control fueled a sense of resentment and a desire for self-governance.
A Map of Revolution:
The thirteen colonies were not just geographical entities but also the battlegrounds for the American Revolution. The map of the colonies became a canvas of significant events:
- The Boston Tea Party (1773): This act of defiance, where colonists disguised as Native Americans dumped tea into Boston Harbor, marked a turning point in the struggle for independence.
- The Battles of Lexington and Concord (1775): These skirmishes, considered the opening shots of the American Revolution, ignited the flames of rebellion.
- The Siege of Yorktown (1781): This decisive victory for the Continental Army, with the assistance of the French, forced the British to surrender and effectively ended the Revolutionary War.
The Birth of a Nation:
The thirteen colonies, united in their fight for freedom, eventually declared their independence from Great Britain in 1776. The Declaration of Independence, a powerful document outlining the principles of liberty, equality, and self-government, enshrined the colonies’ commitment to a new nation.
A Legacy of Growth and Transformation:
The thirteen colonies, once disparate settlements, forged a new identity as a nation. The Constitution, adopted in 1787, established a framework for a strong and unified government, balancing individual rights with the need for a cohesive nation.
The map of the thirteen colonies, beyond its geographical significance, stands as a testament to the enduring power of ideas, the resilience of the human spirit, and the transformative force of revolution. It is a reminder of the origins of a nation built on principles of liberty, equality, and the pursuit of a more perfect union.
FAQs about the Thirteen Colonies
1. What were the main reasons for the thirteen colonies’ desire for independence from Great Britain?
The thirteen colonies sought independence due to a combination of factors, including:
- Taxation without Representation: The British government imposed taxes on the colonies without granting them representation in Parliament, which was seen as a violation of their rights.
- Restrictions on Trade: The British government implemented policies that restricted colonial trade, limiting economic opportunities and creating resentment.
- Growing Sense of Self-Governance: As the colonies matured, they developed a strong sense of self-governance and autonomy, making them increasingly resistant to British control.
2. What were some of the key differences between the three regions of the thirteen colonies (New England, Middle Colonies, and Southern Colonies)?
The three regions of the thirteen colonies differed in terms of their:
- Geography and Climate: New England had a rugged terrain and cold winters, the Middle Colonies had a more moderate climate and fertile soil, and the Southern Colonies possessed a warm climate and vast expanses of land.
- Economy: New England focused on shipbuilding, fishing, and trade, the Middle Colonies developed a strong agricultural economy, and the Southern Colonies relied heavily on plantation agriculture.
- Population and Culture: New England was predominantly populated by Puritan settlers, the Middle Colonies attracted a diverse mix of immigrants, and the Southern Colonies were characterized by a large slave population.
3. How did the American Revolution impact the thirteen colonies?
The American Revolution transformed the thirteen colonies in several ways:
- Political Independence: The revolution resulted in the colonies gaining independence from Great Britain and establishing a new nation.
- Formation of a New Government: The revolution led to the creation of a new federal government based on the principles of democracy and republicanism.
- Shifting Power Dynamics: The revolution shifted power away from the British monarchy and toward the colonies, creating a new political landscape.
4. What is the lasting legacy of the thirteen colonies?
The thirteen colonies left a lasting legacy on the United States, including:
- Foundation of the Nation: The thirteen colonies were the foundation of the United States, laying the groundwork for its political, social, and economic development.
- Principles of Liberty and Self-Governance: The colonies’ struggle for independence enshrined principles of liberty, equality, and self-governance, which became cornerstones of American democracy.
- Diverse Cultural Heritage: The thirteen colonies’ diverse populations contributed to the rich cultural tapestry of the United States, shaping its traditions, language, and values.
Tips for Understanding the Thirteen Colonies
- Use a Map: A map of the thirteen colonies is essential for understanding their geographical distribution and relationships.
- Explore Primary Sources: Reading primary sources, such as letters, diaries, and historical documents, can provide valuable insights into the lives and experiences of people who lived in the thirteen colonies.
- Focus on Key Events: Understanding key events, such as the Boston Tea Party, the Battles of Lexington and Concord, and the Siege of Yorktown, can help you grasp the context of the American Revolution.
- Consider Different Perspectives: Explore the perspectives of various groups, including colonists, British officials, and enslaved people, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the period.
- Connect to Contemporary Issues: Reflect on how the issues faced by the thirteen colonies, such as taxation without representation, economic inequality, and the struggle for freedom, resonate with contemporary challenges.
Conclusion
The thirteen colonies, a collection of settlements on the eastern coast of North America, played a pivotal role in shaping the United States of America. Their struggle for independence, their diverse populations, and their unique experiences contributed to the creation of a nation built on the principles of liberty, equality, and self-governance. The map of the thirteen colonies serves as a constant reminder of the origins of a nation that has grown and evolved, yet continues to be shaped by the ideals and aspirations of its founding fathers. Understanding the history of the thirteen colonies is essential for appreciating the complexities of American history and its lasting impact on the world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Thirteen Colonies: A Foundation for a Nation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!