The Middle Passage: Mapping the Horror of the Transatlantic Slave Trade
Related Articles: The Middle Passage: Mapping the Horror of the Transatlantic Slave Trade
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Middle Passage: Mapping the Horror of the Transatlantic Slave Trade. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Middle Passage: Mapping the Horror of the Transatlantic Slave Trade
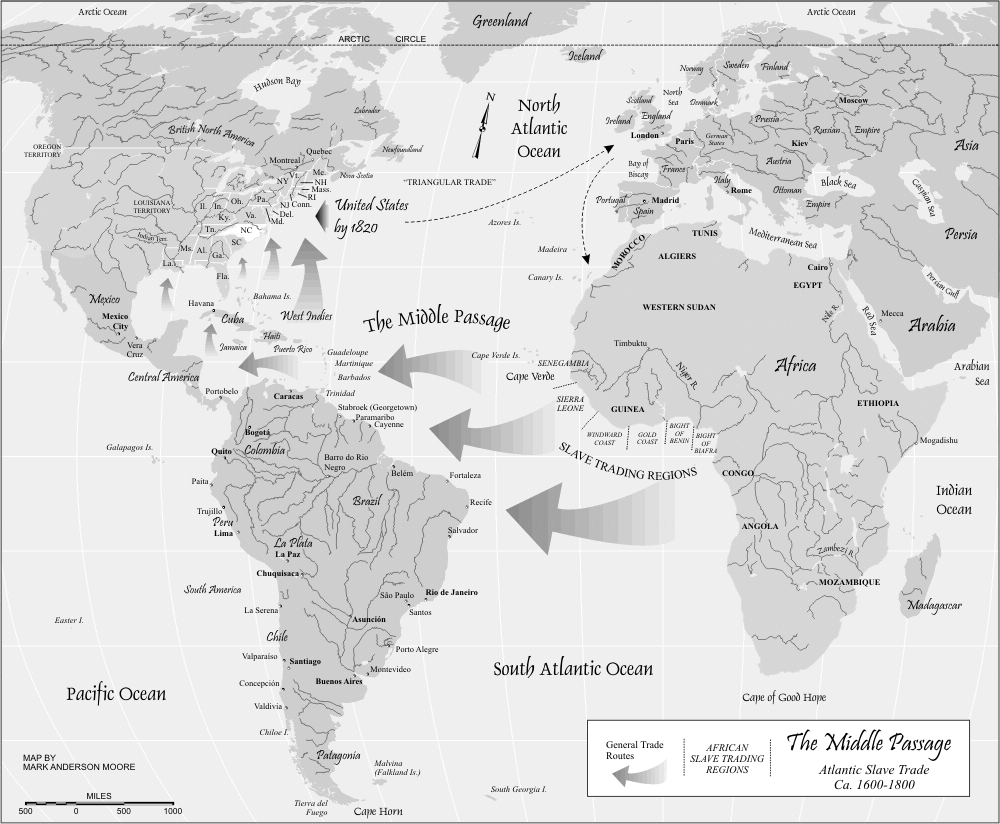
The Middle Passage, a term that evokes images of unimaginable suffering and brutality, stands as a stark reminder of the horrors of the transatlantic slave trade. This infamous journey, spanning the vast expanse of the Atlantic Ocean, transported millions of Africans from their homelands to the Americas, forever altering the course of history. While the physical route of the Middle Passage is a well-documented geographical path, its true significance lies in the human stories it encapsulates, stories of resilience, resistance, and unspeakable tragedy.
Mapping the Middle Passage: A Geographical Overview
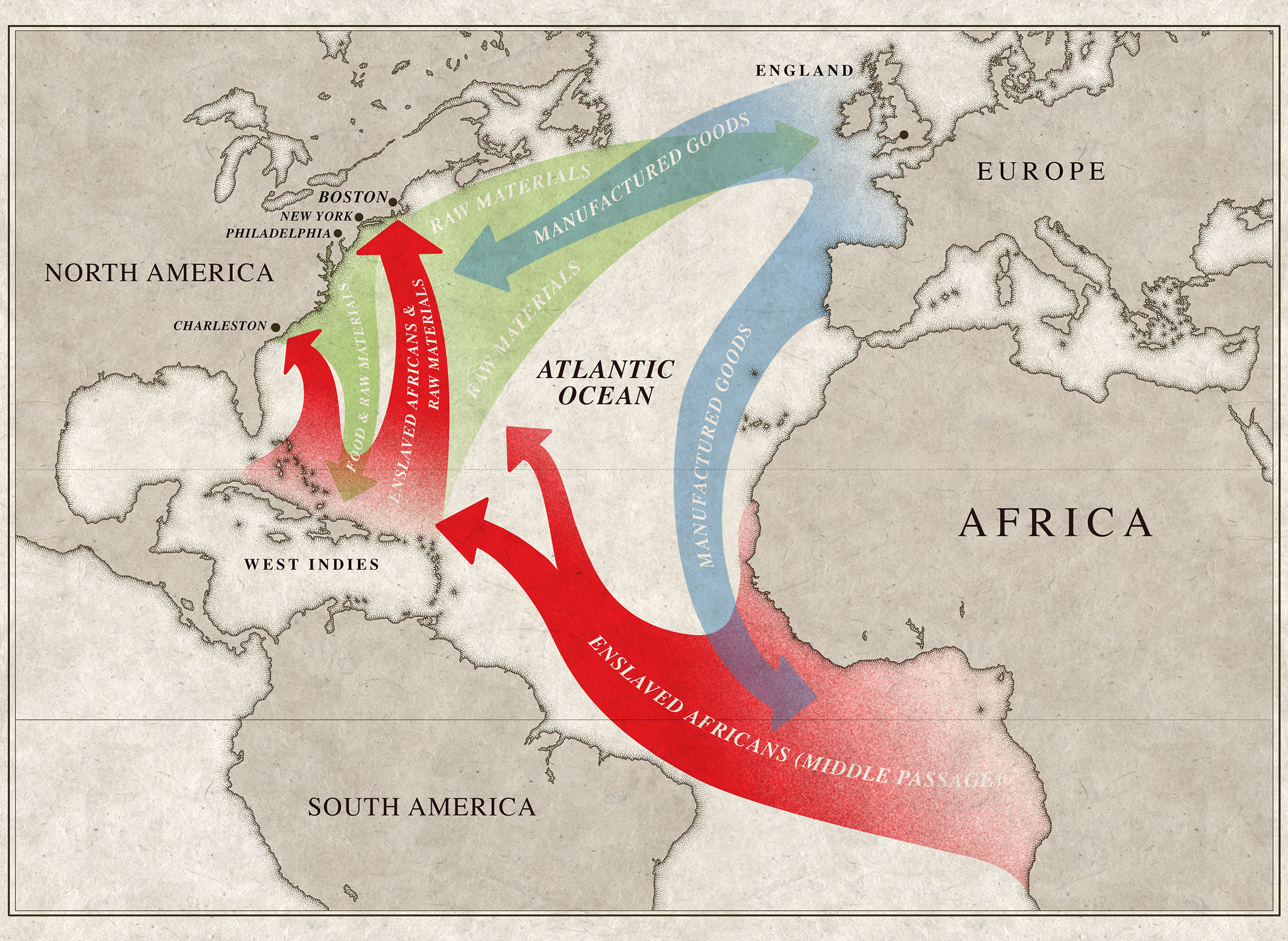
The Middle Passage, a term coined in the 18th century, refers to the forced voyage of enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean. It was a critical component of the triangular trade system, a complex network that involved the exchange of goods between Europe, Africa, and the Americas. The journey began on the coast of West Africa, where captives were forcibly taken from their homes and loaded onto ships. These vessels, often referred to as "slave ships," were designed to maximize profits by cramming as many enslaved people as possible into their cramped and unsanitary holds.
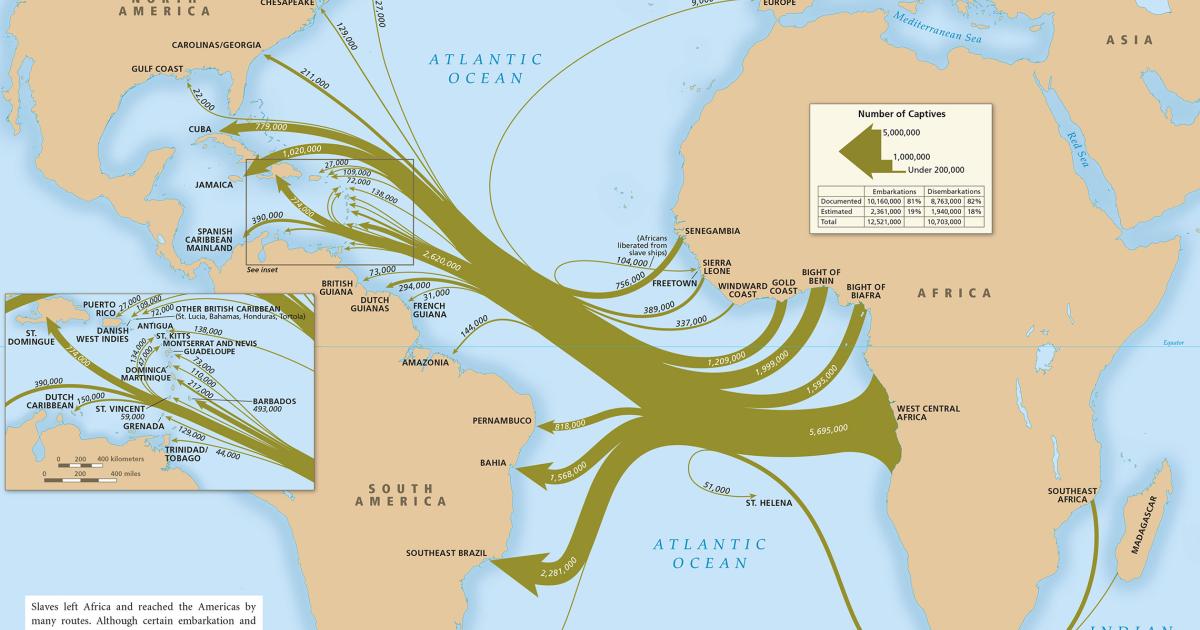
The route of the Middle Passage varied depending on the destination and the prevailing winds. However, the journey typically followed a westward trajectory from the coast of Africa to the Caribbean, South America, or North America. The voyage could last anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on the weather conditions and the distance traveled.
The Human Cost of the Middle Passage
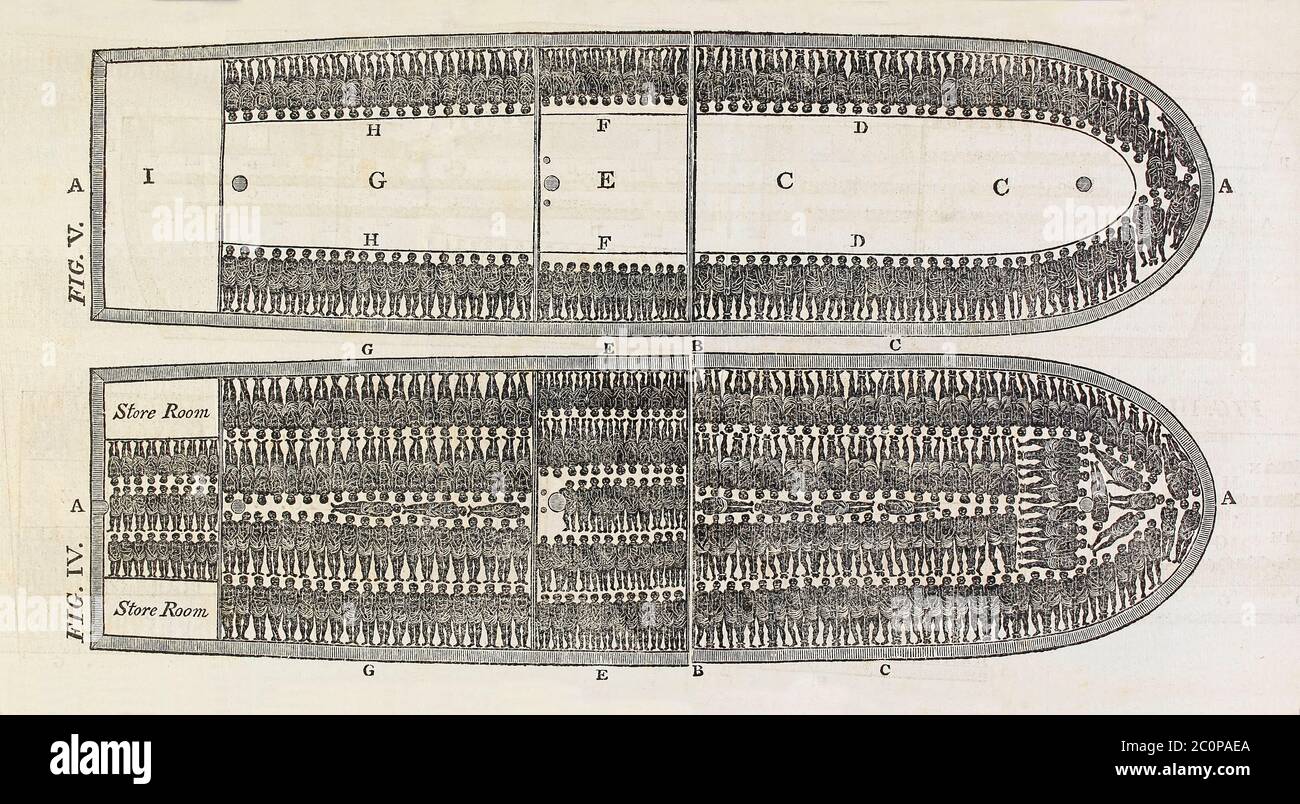
The Middle Passage was not merely a geographical route; it was a horrific journey that claimed the lives of millions of Africans. The conditions on board slave ships were appalling, characterized by overcrowding, disease, and brutality. Enslaved Africans were packed into cramped spaces, often chained together, with minimal access to food, water, or sanitation. The lack of hygiene and ventilation fostered the spread of diseases like smallpox, measles, and yellow fever, leading to widespread sickness and death.
Beyond the physical hardships, the psychological trauma of the Middle Passage was equally devastating. Africans were forcibly separated from their families and communities, subjected to unimaginable cruelty, and deprived of their basic human rights. The psychological scars of this journey were passed down through generations, impacting the lives of enslaved Africans and their descendants for centuries to come.
Mapping Resistance: The Fight for Freedom
Despite the overwhelming odds, enslaved Africans fought back against their captors. They staged rebellions, attempted escapes, and found ways to resist the system that sought to dehumanize them. While these acts of resistance were often met with brutal suppression, they served as powerful reminders of the indomitable spirit of the enslaved.
The Middle Passage: A Legacy of Pain and Resilience
The Middle Passage stands as a stark reminder of the horrors of the transatlantic slave trade and its devastating impact on the African continent and the Americas. It is a testament to the resilience of the enslaved, who endured unimaginable suffering and fought for their freedom. While the physical route of the Middle Passage has been mapped and documented, its true significance lies in the human stories it encapsulates, stories of loss, struggle, and the enduring spirit of hope.
FAQs about the Middle Passage
1. What were the conditions like on slave ships?
Conditions on slave ships were horrific. Enslaved Africans were crammed into cramped spaces, often chained together, with minimal access to food, water, or sanitation. The lack of hygiene and ventilation fostered the spread of diseases like smallpox, measles, and yellow fever, leading to widespread sickness and death.
2. How long did the Middle Passage typically last?
The duration of the Middle Passage varied depending on the weather conditions and the distance traveled, but it could last anywhere from a few weeks to several months.
3. How many Africans were transported during the Middle Passage?
Estimates vary, but historians believe that between 10 and 12 million Africans were forcibly transported across the Atlantic during the transatlantic slave trade.
4. Why was the Middle Passage considered a critical part of the triangular trade system?
The Middle Passage was crucial to the triangular trade system because it provided the labor force necessary to sustain the plantation economies of the Americas. The enslaved Africans were forced to work on plantations, producing crops like sugar, tobacco, and cotton that were then shipped back to Europe.
5. What were some of the ways enslaved Africans resisted the Middle Passage?
Enslaved Africans resisted the Middle Passage in various ways, including staging rebellions, attempting escapes, and finding ways to undermine the system that sought to dehumanize them. They also engaged in acts of sabotage and passive resistance.
Tips for Understanding the Middle Passage
1. Engage with Primary Sources: Explore firsthand accounts of the Middle Passage through journals, diaries, and letters written by enslaved Africans, ship captains, and other individuals involved in the trade. These sources provide valuable insights into the lived experiences of those affected by this horrific journey.
2. Explore Visual Representations: Examine artwork, maps, and photographs that depict the Middle Passage. These visual representations can offer a powerful and visceral understanding of the brutality and suffering endured by enslaved Africans.
3. Learn about the History of Resistance: Research the stories of enslaved Africans who fought back against their captors. Their acts of rebellion and resistance serve as powerful reminders of the human spirit’s ability to resist oppression.
4. Understand the Lasting Impact: Recognize the lasting impact of the Middle Passage on the African diaspora. The legacy of this journey continues to shape the lives of people of African descent today, impacting their culture, identity, and experiences.
Conclusion
The Middle Passage, a stark reminder of the horrors of the transatlantic slave trade, serves as a crucial chapter in the history of humanity. It is a testament to the resilience of the enslaved, who endured unimaginable suffering and fought for their freedom. By understanding the historical context of the Middle Passage, we can better comprehend the complex and enduring legacy of slavery and its impact on the world today.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Middle Passage: Mapping the Horror of the Transatlantic Slave Trade. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!