The Indian Railway Network: A Vital Lifeline Across the Subcontinent
Related Articles: The Indian Railway Network: A Vital Lifeline Across the Subcontinent
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Indian Railway Network: A Vital Lifeline Across the Subcontinent. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Indian Railway Network: A Vital Lifeline Across the Subcontinent
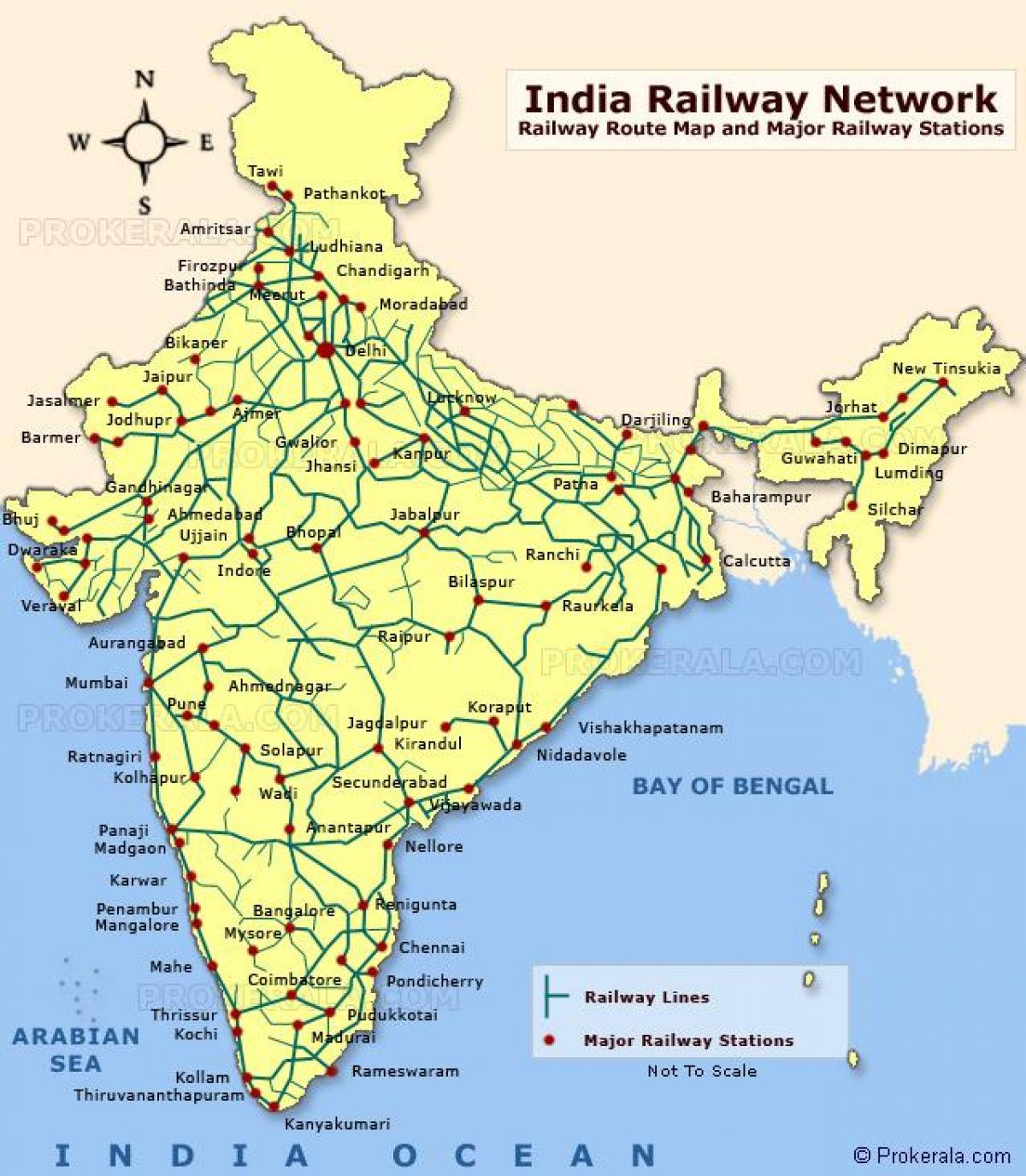
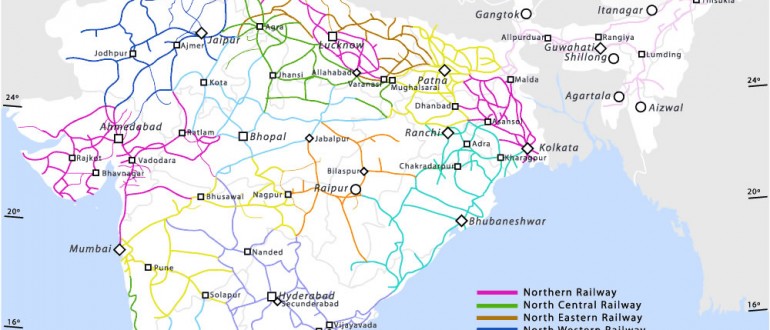
The Indian Railway network, a sprawling web of tracks traversing the length and breadth of the nation, is more than just a transportation system. It is a vital lifeline, connecting diverse communities, facilitating economic growth, and playing a crucial role in the everyday lives of millions. Understanding the intricacies of this vast network, as depicted on the Indian Railway Map, unveils the intricate tapestry of India’s development and the profound impact it has on the lives of its people.
A Glimpse into the Map:
The Indian Railway Map reveals a complex and interconnected network, with major trunk lines radiating outwards from key cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata, and Chennai. These lines form the backbone of the system, connecting major urban centers and facilitating long-distance travel. Branching off from these main arteries are numerous smaller lines, penetrating into rural areas, linking distant villages and towns to the national network. This intricate web, spanning over 67,000 kilometers, represents the largest railway network in Asia and the second largest in the world.
Beyond the Lines: A Network of Connectivity and Development:
The Indian Railway Map is more than just a visual representation of tracks and stations. It is a powerful tool for understanding the socio-economic landscape of India. The network’s reach into remote areas fosters connectivity, bridging geographical divides and bringing communities together. By facilitating the movement of people and goods, the railways play a pivotal role in promoting economic growth, supporting industries, and creating employment opportunities.
The Lifeline of Commerce:
The Indian Railway network is a crucial artery for the transportation of goods, playing a vital role in the country’s economy. From agricultural produce to industrial raw materials, the railways move vast quantities of goods across the nation, ensuring the efficient flow of trade and commerce. This efficient transportation system helps maintain stable prices, reduces transportation costs, and contributes to the overall economic well-being of the nation.
A Catalyst for Social Development:
The railway network is a powerful tool for social development, connecting communities and fostering social inclusion. By providing affordable and accessible transportation, the railways enable access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities, particularly in rural areas. This connectivity breaks down barriers, fosters cultural exchange, and contributes to the overall social progress of the nation.
Navigating the Network: Understanding Key Features:
The Indian Railway Map is replete with information, offering insights into the network’s key features:
- Gauge: The map depicts the different gauges of the network, including broad gauge (1.676 mm), meter gauge (1.000 mm), and narrow gauge (762 mm).
- Zones: The Indian Railways is divided into 18 zones, each with its own administrative structure and operational responsibilities. The map clearly delineates these zones, providing a geographical context for understanding the network’s organization.
- Stations: The map identifies major railway stations, highlighting their significance in the network. These stations serve as hubs for passengers and freight, facilitating connections across different routes.
- Major Lines: The map emphasizes key trunk lines, highlighting the major arteries that connect important cities and regions. These lines form the backbone of the network, carrying the majority of passenger and freight traffic.
- Electrification: The map indicates electrified lines, signifying areas where trains are powered by electricity. This feature highlights the network’s modernization efforts and the shift towards sustainable transportation.
Beyond the Map: A Dynamic Network in Constant Evolution:
The Indian Railway network is a dynamic entity, constantly evolving to meet the growing demands of the nation. The map serves as a snapshot of the network at a particular point in time, but the reality is a system in continuous flux. Ongoing infrastructure projects, modernization initiatives, and technological advancements are constantly shaping the network, making the Indian Railway Map a living document that reflects the country’s progress.
FAQs about the Indian Railway Network:
1. What are the different types of trains operating on the Indian Railway network?
The Indian Railway network operates a diverse range of trains, catering to different needs and travel preferences. These include:
- Mail/Express Trains: These trains provide fast and efficient long-distance travel, connecting major cities and towns.
- Passenger Trains: These trains offer affordable and convenient travel for short and medium distances, serving as a vital mode of transportation for commuters and local residents.
- Shatabdi Express: These trains offer high-speed travel between major cities, prioritizing comfort and convenience.
- Rajdhani Express: These trains provide premium travel services, connecting the capital city Delhi with other major cities.
- Duronto Express: These trains operate non-stop, offering faster travel times and a more streamlined experience.
- Freight Trains: These trains are dedicated to transporting goods, playing a crucial role in the country’s economy.
2. What are the benefits of traveling by train in India?
Traveling by train in India offers numerous advantages:
- Affordability: Train travel is generally more affordable than air travel, making it accessible to a wider range of people.
- Accessibility: The vast network of trains reaches even remote areas, providing connectivity to communities that may lack access to other modes of transportation.
- Comfort: Modern trains offer comfortable seating, air conditioning, and other amenities, making long journeys more pleasant.
- Scenic Views: Train travel provides an opportunity to experience the diverse landscapes of India, offering breathtaking views of mountains, plains, and rivers.
- Cultural Immersion: Train journeys offer a unique opportunity to interact with people from different backgrounds, fostering cultural understanding and enriching the travel experience.
3. What are some of the challenges faced by the Indian Railways?
Despite its vast network and significant role in the nation’s development, the Indian Railways faces several challenges:
- Overcrowding: The network experiences high passenger volumes, leading to overcrowding and long waiting times.
- Aging Infrastructure: Many sections of the network require modernization and upgrades to improve safety and efficiency.
- Maintenance Backlog: The extensive network requires significant resources for maintenance and repairs, which can pose a challenge to the railways’ financial sustainability.
- Safety Concerns: Accidents and derailments remain a concern, highlighting the need for continuous improvement in safety standards and infrastructure.
4. What are the future plans for the Indian Railways?
The Indian Railways has ambitious plans to modernize and expand its network, aiming to improve efficiency, safety, and connectivity:
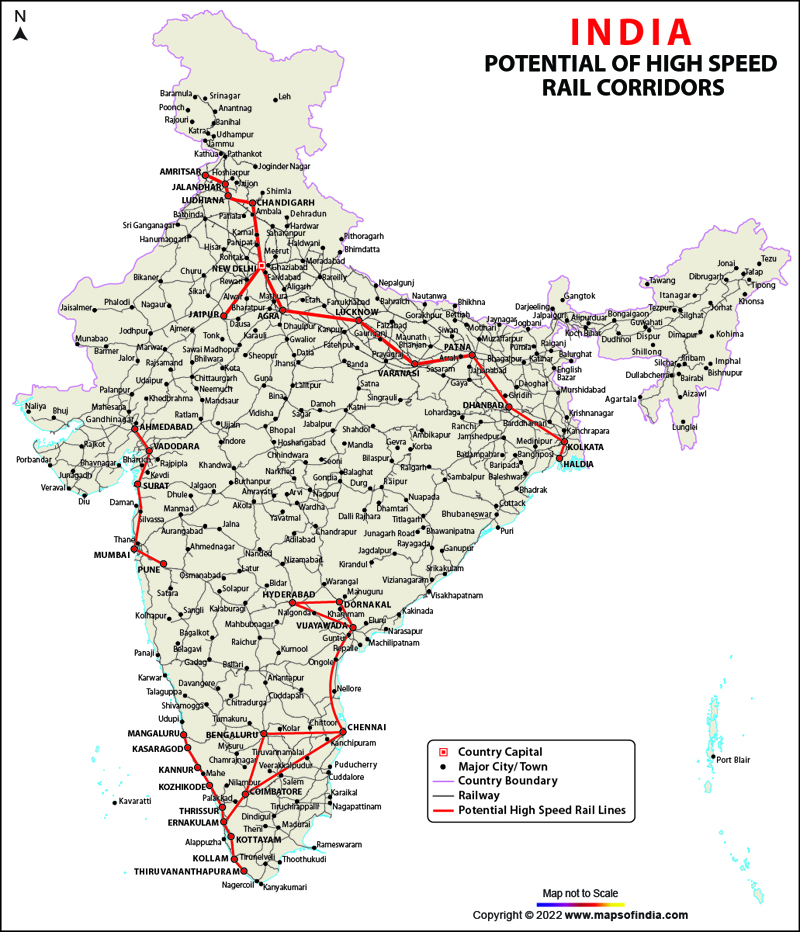
- High-Speed Rail: The development of high-speed rail lines is a key priority, aiming to reduce travel times and enhance connectivity between major cities.
- Freight Corridor Development: The development of dedicated freight corridors will improve the efficiency of goods transportation, supporting economic growth and industrial development.
- Electrification: The ongoing electrification of the network aims to reduce reliance on fossil fuels, promoting sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation.
- Digitalization: The adoption of digital technologies, including online ticketing, real-time tracking, and advanced communication systems, aims to enhance passenger convenience and operational efficiency.
Tips for Planning a Train Journey in India:
- Book in Advance: Due to high passenger volumes, it is highly recommended to book tickets in advance, especially for popular routes and during peak seasons.
- Choose the Right Class: The Indian Railways offers various classes of travel, ranging from basic unreserved seating to luxurious air-conditioned coaches. Choose the class that best suits your budget and comfort needs.
- Pack Light: Train journeys can involve long distances, so it is essential to pack light and avoid carrying unnecessary baggage.
- Stay Hydrated: It is important to stay hydrated during long train journeys, especially in hot climates. Carry a reusable water bottle and refill it at stations.
- Be Prepared for Delays: Train delays are common in India, so it is essential to be prepared and have backup plans in case of unexpected delays.
- Respect Other Passengers: Train travel is a shared experience, so it is important to be respectful of other passengers and maintain a courteous and considerate demeanor.
Conclusion:
The Indian Railway network is a testament to the country’s ambition and its commitment to connectivity and development. The intricate web of tracks, spanning the vast subcontinent, serves as a vital lifeline for millions of people, facilitating trade, commerce, and social progress. The railway map is a powerful tool for understanding the network’s significance and its profound impact on the lives of the Indian people. As the network continues to evolve and expand, its role in shaping India’s future will only grow, cementing its position as a symbol of national pride and a vital driver of progress.
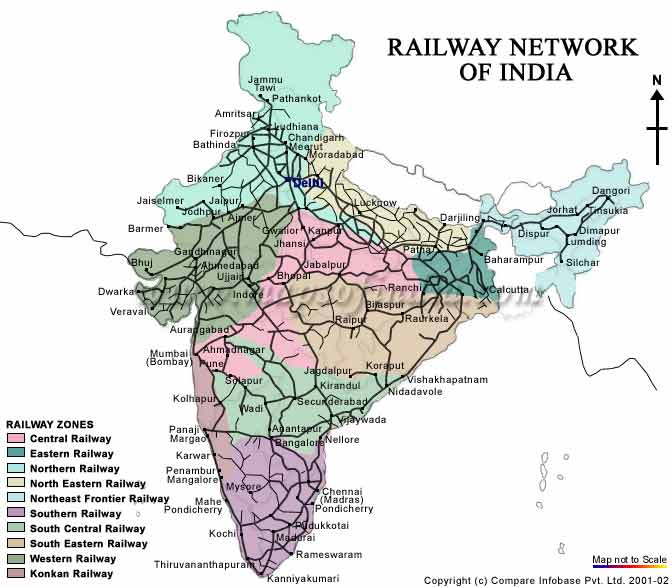


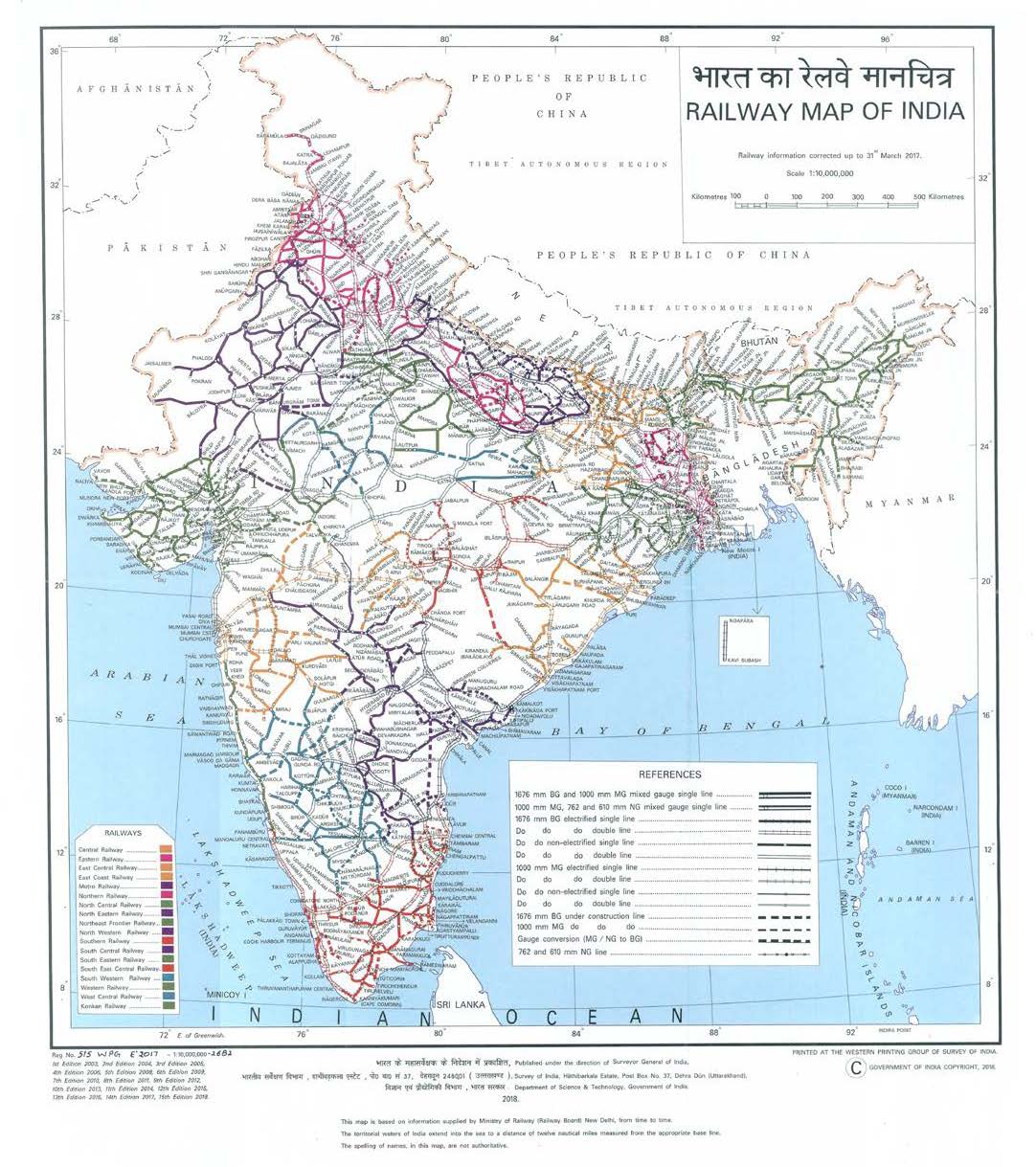
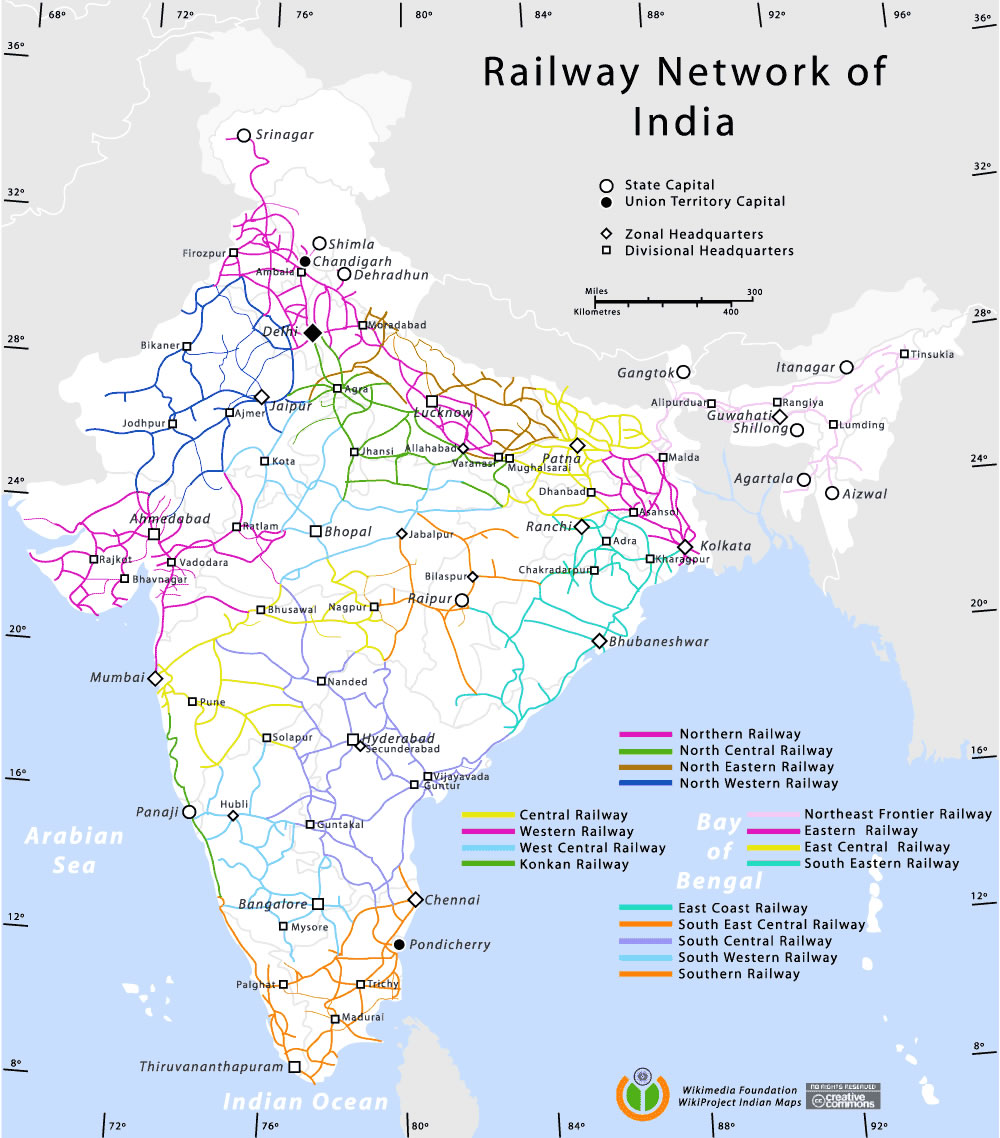

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Indian Railway Network: A Vital Lifeline Across the Subcontinent. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!