The Essential Guide to Map Credit: Understanding and Attributing Sources
Related Articles: The Essential Guide to Map Credit: Understanding and Attributing Sources
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Essential Guide to Map Credit: Understanding and Attributing Sources. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Essential Guide to Map Credit: Understanding and Attributing Sources

Maps are powerful tools, offering visual representations of the world and guiding us through complex landscapes. Behind every map, however, lies a wealth of information, painstakingly gathered and meticulously compiled. Recognizing and acknowledging this effort through proper map credit is not merely a courtesy but a crucial element of ethical cartography and academic integrity.
What is Map Credit?
Map credit refers to the attribution of authorship, source material, and data used in creating a map. It functions as a clear and concise acknowledgment of the individuals, organizations, and resources that contributed to the map’s creation. Proper map credit is essential for several reasons:
- Ethical Considerations: Failing to credit sources is akin to plagiarism, undermining the credibility of the map and the cartographer.
- Transparency and Accuracy: Map credit provides users with a clear understanding of the map’s origins and potential limitations, fostering trust and enabling informed interpretation.
- Legal Compliance: In many cases, copyright laws require specific attribution for copyrighted data, ensuring fair use and avoiding legal repercussions.
- Building Reputation: By giving proper credit, cartographers demonstrate respect for their colleagues and collaborators, fostering a collaborative environment within the cartographic community.
Components of Effective Map Credit:
Effective map credit encompasses several key elements:
- Source Data: This includes the name of the organization or individual who collected the data used in the map, along with the specific dataset or source.
- Copyright Information: If the data is copyrighted, include the copyright holder’s name and the year of copyright.
- Map Projection: Clearly state the map projection used, as this influences the map’s accuracy and interpretation.
- Date of Creation: Indicate the date the map was created or last updated to reflect the currency of the information.
- Contact Information: Provide a contact address or website for the cartographer or organization responsible for the map.
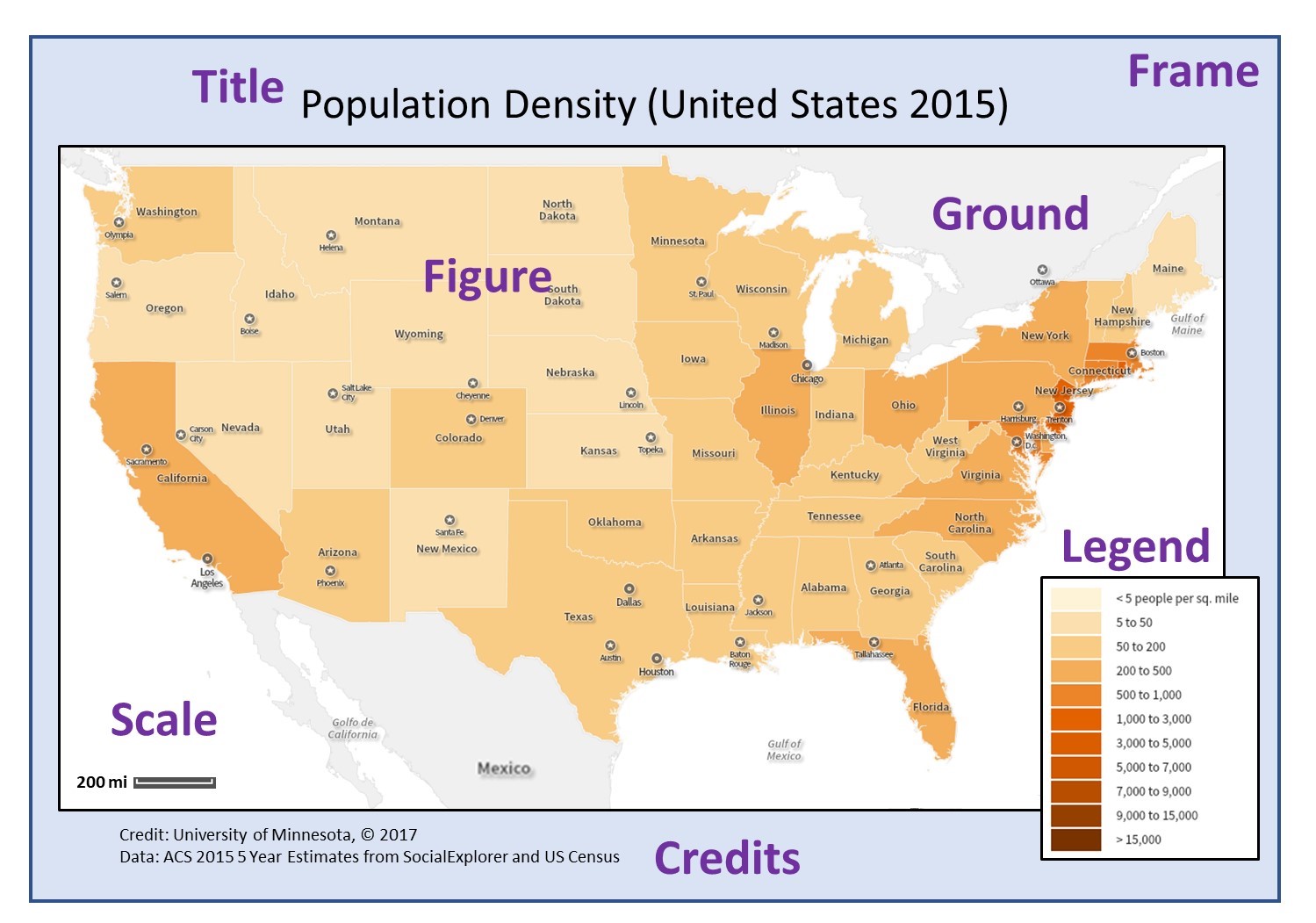
Where to Place Map Credit:
Map credit should be prominently displayed in a way that is easily accessible to the user. Common locations for map credit include:
- Map Legend: This is a standard location for map credit, providing a clear and concise summary of the map’s key information.
- **Map

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Essential Guide to Map Credit: Understanding and Attributing Sources. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!