The Atlantic Coastal Plain: A Tapestry of Land and Life
Related Articles: The Atlantic Coastal Plain: A Tapestry of Land and Life
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Atlantic Coastal Plain: A Tapestry of Land and Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Atlantic Coastal Plain: A Tapestry of Land and Life

The Atlantic Coastal Plain, a sprawling expanse of low-lying land stretching from Cape Cod in the north to the Florida Keys in the south, is a region of remarkable diversity and significance. This vast landscape, sculpted by ancient seas and shaped by the relentless forces of nature, harbors a rich tapestry of ecosystems, from sandy beaches and coastal marshes to vast forests and fertile farmlands. Understanding the Atlantic Coastal Plain’s geography, geology, and ecological features is crucial for appreciating its unique role in the North American landscape and its profound impact on human history, culture, and economy.
A Land Shaped by the Sea:
The Atlantic Coastal Plain’s defining characteristic is its low elevation, rarely exceeding 200 feet above sea level. This gentle topography is a direct consequence of its geological history. Millions of years ago, the region was submerged beneath a shallow sea, accumulating layers of sediment, primarily sand, silt, and clay. As sea levels fluctuated, these deposits were exposed and subjected to weathering and erosion, ultimately forming the flat, undulating landscape we see today.
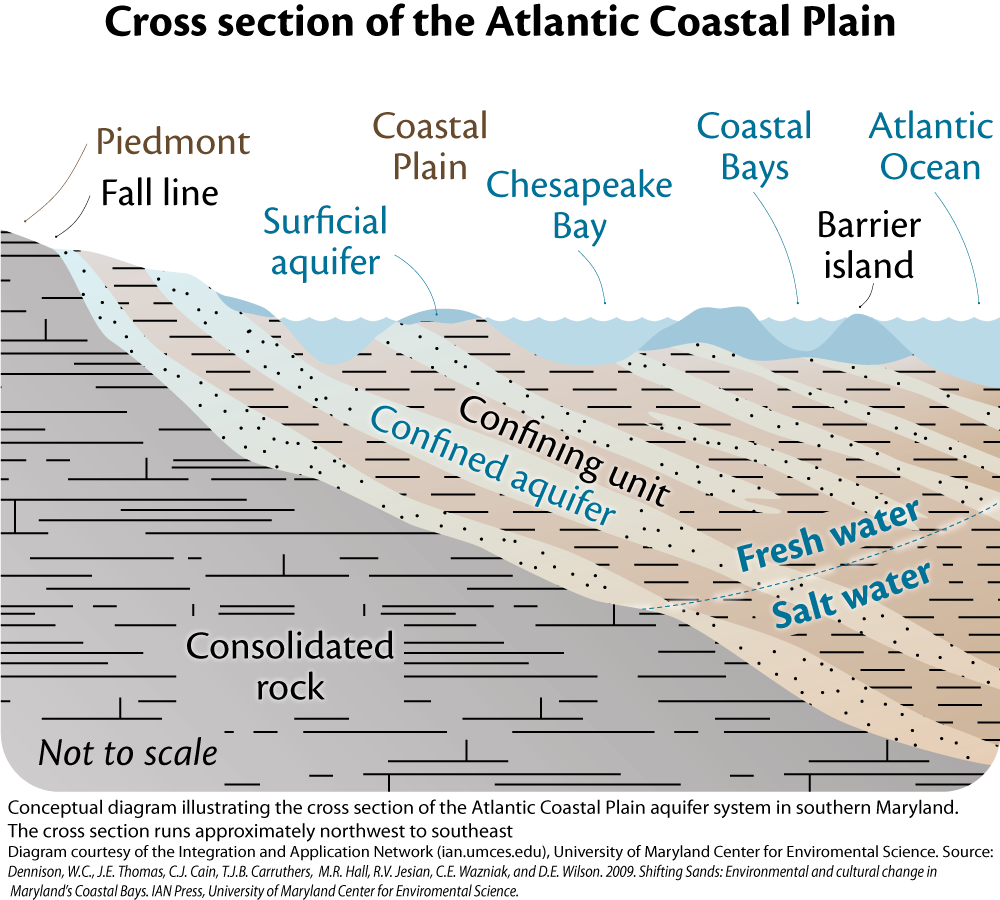
The presence of ancient marine deposits is evident in the region’s rich fossil record. Fossils of marine creatures, including sharks, whales, and prehistoric sea turtles, are frequently unearthed, offering glimpses into the region’s past. Furthermore, the Coastal Plain’s underlying geology plays a significant role in its water resources. The porous nature of the sediments allows for the formation of vast underground aquifers, providing a vital source of freshwater for the region’s population.
A Mosaic of Ecosystems:
The Atlantic Coastal Plain is a haven for a diverse array of ecosystems, each with its own unique characteristics and ecological significance. The coastline itself is a dynamic environment, shaped by the relentless forces of waves and tides. Sandy beaches, characterized by their shifting sands and sparse vegetation, provide nesting grounds for sea turtles and migratory shorebirds. Further inland, coastal marshes, often referred to as "nurseries of the sea," are dominated by salt-tolerant grasses and provide essential habitat for a wide range of fish, shellfish, and migratory birds.
The Coastal Plain’s interior is marked by a transition from the salt-tolerant ecosystems of the coast to the freshwater habitats of the inland forests and swamps. The vast pine forests, with their towering trees and acidic soils, are home to a diverse array of reptiles, amphibians, and birds, including the endangered red-cockaded woodpecker. The region’s numerous rivers and streams support a rich diversity of freshwater fish, while the wetlands, with their abundance of water and vegetation, provide vital habitat for a wide range of amphibians, reptiles, and birds.
Human Impact and Conservation:
The Atlantic Coastal Plain has long been a focal point for human settlement, attracting people drawn to its fertile soils, abundant resources, and access to waterways. The region’s agricultural heritage is deeply intertwined with its history, with vast tracts of land devoted to the cultivation of crops like cotton, tobacco, and soybeans. The Coastal Plain also holds significant deposits of fossil fuels, including oil and natural gas, which have played a vital role in the region’s economic development.
However, human activities have also had a profound impact on the region’s natural resources. Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural practices have led to habitat loss, soil erosion, and water pollution. Furthermore, the Coastal Plain’s low elevation makes it particularly vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including sea-level rise, increased storm intensity, and saltwater intrusion.
Recognizing the importance of protecting the Atlantic Coastal Plain’s natural resources, conservation efforts are underway to address these challenges. Protected areas, such as national parks, wildlife refuges, and state forests, provide refuge for endangered species and safeguard critical ecosystems. Efforts to restore degraded habitats, promote sustainable land management practices, and mitigate the impacts of climate change are essential for ensuring the long-term health and resilience of this vital region.
FAQs about the Atlantic Coastal Plain:
1. What are the major geological features of the Atlantic Coastal Plain?
The Atlantic Coastal Plain is characterized by its low elevation, flat topography, and underlying sedimentary rocks. These deposits, primarily sand, silt, and clay, were formed over millions of years by the accumulation of sediment in a shallow sea.
2. What are the major ecosystems found in the Atlantic Coastal Plain?
The Atlantic Coastal Plain supports a diverse array of ecosystems, including sandy beaches, coastal marshes, pine forests, swamps, and rivers. These ecosystems are home to a wide range of plant and animal species, including endangered and threatened species.
3. How has human activity impacted the Atlantic Coastal Plain?
Human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, and agriculture, have led to habitat loss, soil erosion, and water pollution in the Atlantic Coastal Plain. The region is also vulnerable to the impacts of climate change, including sea-level rise and increased storm intensity.
4. What are some of the conservation efforts underway to protect the Atlantic Coastal Plain?
Conservation efforts include the establishment of protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife refuges, habitat restoration projects, and the promotion of sustainable land management practices.
5. What is the importance of the Atlantic Coastal Plain?
The Atlantic Coastal Plain is a vital region for its diverse ecosystems, natural resources, and cultural heritage. It provides essential habitat for a wide range of plant and animal species, supports a significant human population, and plays a crucial role in the regional economy.
Tips for Understanding the Atlantic Coastal Plain:
- Explore the region’s diverse ecosystems: Visit national parks, wildlife refuges, and state forests to experience firsthand the beauty and diversity of the Atlantic Coastal Plain’s ecosystems.
- Learn about the region’s history and culture: Visit museums, historical sites, and local communities to gain a deeper understanding of the region’s rich history and cultural heritage.
- Support conservation efforts: Become involved in conservation efforts by volunteering, donating, or advocating for policies that protect the region’s natural resources.
- Be mindful of your impact: Practice sustainable land management practices, reduce your carbon footprint, and support businesses that prioritize environmental sustainability.
Conclusion:
The Atlantic Coastal Plain is a remarkable region, a testament to the power of nature and the ingenuity of human civilization. From its ancient geological origins to its diverse ecosystems and rich cultural heritage, the Coastal Plain offers a unique perspective on the interconnectedness of the natural world and the human experience. By understanding the region’s unique characteristics and challenges, we can better appreciate its importance and work to ensure its continued health and vitality for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Atlantic Coastal Plain: A Tapestry of Land and Life. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!