The Art of Mind Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Unlocking Your Thoughts
Related Articles: The Art of Mind Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Unlocking Your Thoughts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Art of Mind Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Unlocking Your Thoughts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Art of Mind Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Unlocking Your Thoughts
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Art of Mind Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Unlocking Your Thoughts
- 3.1 The Fundamentals of Mind Mapping
- 3.2 The Benefits of Mind Mapping
- 3.3 Practical Steps to Create a Mind Map
- 3.4 Tools and Resources for Mind Mapping
- 3.5 FAQs on Mind Mapping
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Mind Mapping
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Art of Mind Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Unlocking Your Thoughts
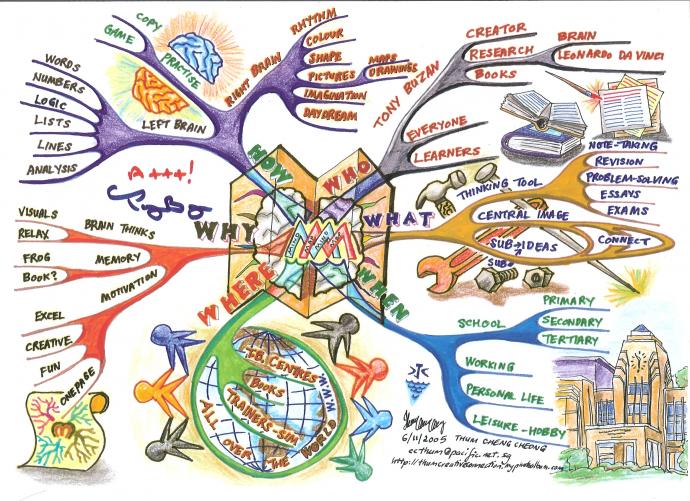
Mind mapping is a visual thinking tool that allows individuals to structure and organize information in a hierarchical and radial manner. This method, often described as a "brain dump" on paper, is a powerful technique for brainstorming, note-taking, problem-solving, and idea generation. By visually connecting concepts and ideas, mind mapping helps to stimulate creativity, enhance memory retention, and facilitate a deeper understanding of complex information.
The Fundamentals of Mind Mapping
At its core, a mind map consists of a central topic or theme, represented by a central image or word. Branching out from this core are main ideas, which are further subdivided into sub-ideas and supporting details. This branching structure, resembling a tree with its roots and branches, allows for the organic growth of information, reflecting the natural way the human brain processes thoughts.
Key Elements of a Mind Map:
- Central Topic: The core idea or concept around which the entire map is built.
- Branches: Main ideas or categories that stem from the central topic.
- Sub-branches: Supporting details or sub-categories that further elaborate on the main ideas.
- Keywords: Concise and evocative words that represent the essence of each branch or sub-branch.
- Images and Symbols: Visual cues that enhance comprehension and recall, adding a layer of visual appeal and mnemonic value.
- Colors and Fonts: Color coding and varied font sizes can be used to emphasize key points and visually differentiate branches.
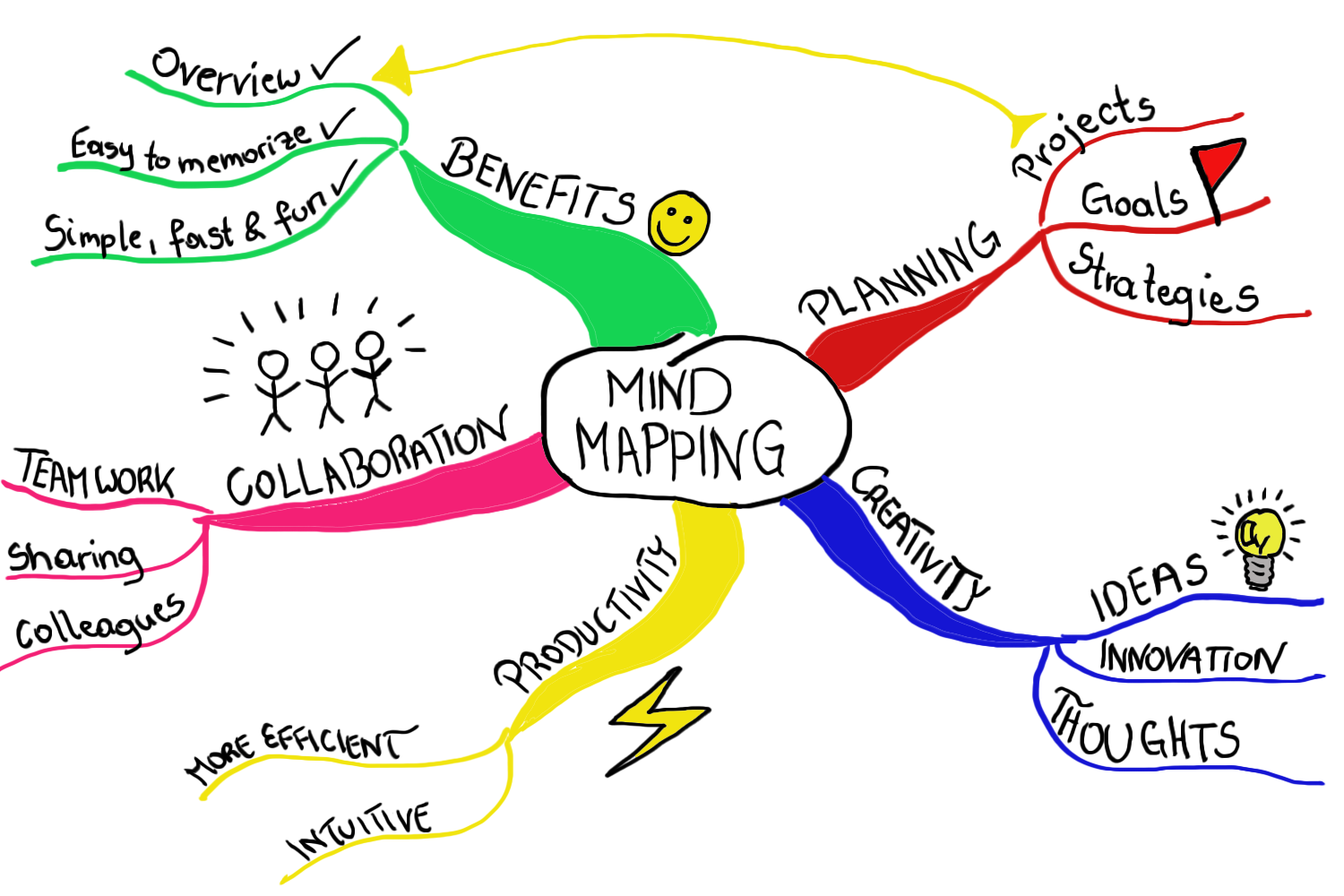
The Benefits of Mind Mapping
Mind mapping offers a plethora of benefits, making it a valuable tool for individuals across various disciplines and professions:
Enhanced Creativity: By visually connecting ideas and concepts, mind mapping encourages lateral thinking and the exploration of new connections, fostering a fertile ground for creative problem-solving and innovative thinking.
Improved Memory Retention: The visual nature of mind maps aids in memory recall, as the brain is better equipped to retain information presented in a visual and spatial format. The interconnectedness of ideas also helps to create a richer understanding and strengthens memory associations.
Effective Organization and Structure: Mind mapping provides a framework for organizing complex information, allowing individuals to break down large concepts into smaller, manageable units. This hierarchical structure facilitates a clear understanding of relationships and dependencies between different ideas.
Enhanced Focus and Concentration: The visual nature of mind mapping helps to maintain focus and concentration, as the act of creating the map itself requires active engagement with the information. The visual representation also provides a clear roadmap for navigating through the material, minimizing distractions and enhancing focus.
Improved Communication and Collaboration: Mind maps provide a visual language that can be easily understood and shared, facilitating effective communication and collaboration. They offer a common ground for discussion and brainstorming, allowing individuals to share their ideas and perspectives in a clear and concise manner.
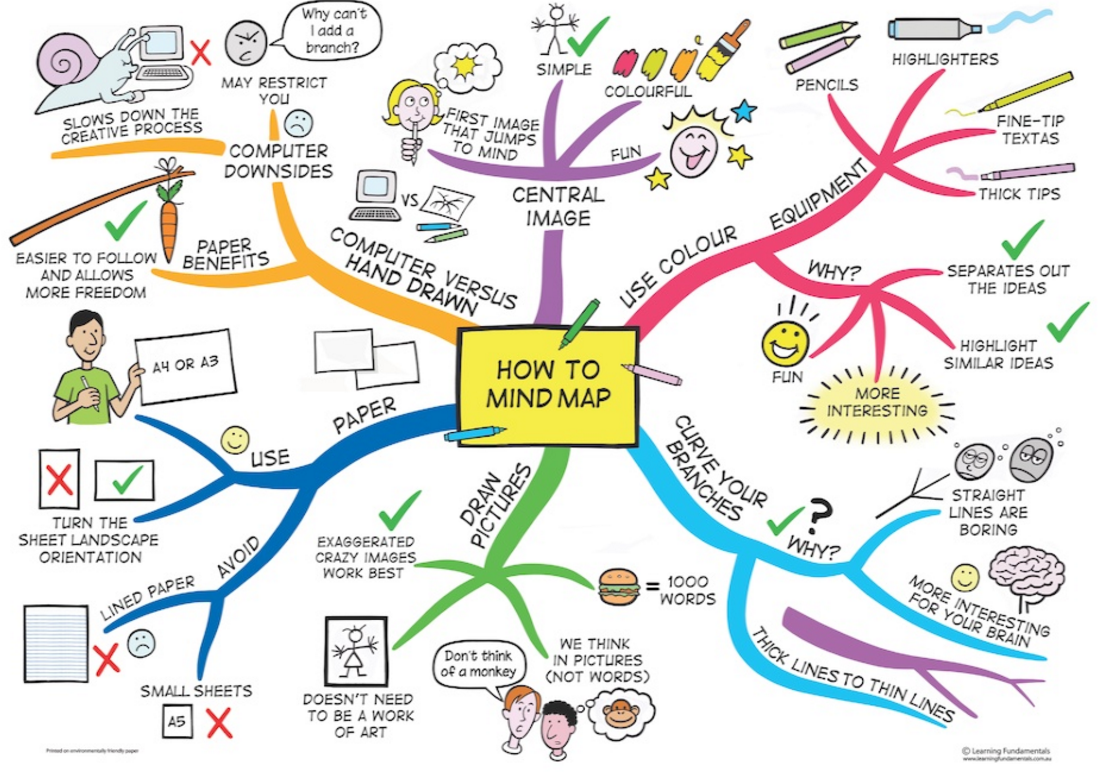
Practical Steps to Create a Mind Map
Creating a mind map is a relatively straightforward process that can be adapted to suit individual preferences and needs. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
-
Define the Central Topic: Begin by clearly identifying the core idea or concept that will be the focus of the mind map. This could be a specific topic, a problem to be solved, or a project to be planned.
-
Establish the Main Ideas: Brainstorm and identify the main ideas or categories that relate to the central topic. These should be the major branches stemming from the core.
-
Develop Sub-branches: For each main idea, identify supporting details, sub-categories, or examples that further elaborate on the concept. These will form the sub-branches of the main ideas.
-
Use Keywords and Phrases: Summarize each branch and sub-branch using concise and evocative keywords or short phrases. These should be clear and easily understood, representing the essence of each idea.
-
Incorporate Images and Symbols: Enhance the visual appeal and mnemonic value of the mind map by incorporating relevant images, icons, or symbols. These can be hand-drawn or sourced from online resources.
-
Employ Color and Font Variation: Use different colors to distinguish between main ideas and sub-branches. Varying font sizes can also be used to emphasize key points and create visual hierarchy.
-
Maintain a Clear Layout: Ensure that the mind map is visually organized and easy to follow. The branches should flow naturally from the central topic, and the overall layout should be balanced and aesthetically pleasing.
Tools and Resources for Mind Mapping
While mind maps can be created using pen and paper, there are numerous digital tools available that offer enhanced functionality and flexibility:
Free Online Tools:
- MindMup: A free online mind mapping tool that allows for collaboration and export in various formats.
- Coggle: A simple and intuitive online tool with a clean interface and real-time collaboration features.
- XMind: A versatile mind mapping software with a free version that offers basic functionality.
Paid Software:
- MindManager: A powerful and comprehensive mind mapping software with advanced features and customization options.
- FreeMind: An open-source mind mapping tool with a wide range of features and a user-friendly interface.
- Scapple: A unique mind mapping tool that encourages free-flowing thought and non-linear brainstorming.
FAQs on Mind Mapping
1. What is the best way to choose a central topic for my mind map?
The best way to choose a central topic is to consider the purpose of the mind map. It could be a specific project, a complex problem, a concept you’re trying to understand, or a topic you’re researching. The central topic should be clear, concise, and relevant to your goals.
2. How many branches should I have in my mind map?
The number of branches is not fixed and depends on the complexity of the topic. Aim for a reasonable number of main ideas that capture the key aspects of the central topic. Avoid overwhelming the map with too many branches, but ensure that all essential concepts are represented.
3. What are some tips for using images and symbols effectively in mind mapping?
Use images and symbols that are relevant to the topic and easily recognizable. They should enhance comprehension and memory recall, not distract from the core ideas. Consider using a consistent style for images and symbols throughout the map to maintain visual coherence.
4. How can I use mind mapping for problem-solving?
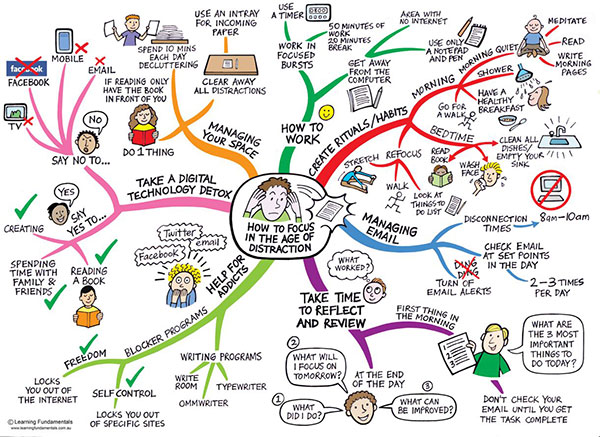
Mind mapping can be used to break down a problem into its constituent parts, identify potential solutions, and analyze the pros and cons of each option. The visual representation allows for a clear understanding of the problem and its potential solutions, facilitating a more structured and effective approach to problem-solving.
5. Can mind mapping be used for collaborative brainstorming?
Yes, mind mapping is an excellent tool for collaborative brainstorming. Digital mind mapping tools often include real-time collaboration features, allowing multiple individuals to contribute to the map simultaneously. This facilitates a shared understanding of the topic and encourages a more inclusive and dynamic brainstorming session.
Tips for Effective Mind Mapping
- Start with a blank page: Avoid pre-made templates or structures, as they can limit creativity and stifle the natural flow of ideas.
- Use a consistent style: Maintain a consistent style for branches, keywords, images, and colors throughout the map. This enhances readability and visual coherence.
- Keep it concise: Use short, evocative keywords and phrases to represent each branch and sub-branch. Avoid lengthy descriptions or complex sentences.
- Review and refine: After creating the initial mind map, take time to review and refine it. Eliminate unnecessary branches, adjust keywords, and ensure that the map is clear and easy to understand.
- Experiment with different formats: Explore different mind mapping formats and styles to find what works best for you. Some individuals prefer radial maps, while others prefer linear or hierarchical structures.
Conclusion
Mind mapping is a versatile and powerful tool that can unlock the potential of your thoughts and ideas. By harnessing the visual nature of mind maps, individuals can improve their creativity, memory, and organizational skills, leading to a more effective and efficient approach to learning, problem-solving, and idea generation. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply someone looking to enhance their cognitive abilities, embracing the art of mind mapping can significantly improve your ability to think, learn, and achieve your goals.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Art of Mind Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Unlocking Your Thoughts. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!