The Arctic Circle: A Realm of Ice, Light, and Global Significance
Related Articles: The Arctic Circle: A Realm of Ice, Light, and Global Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Arctic Circle: A Realm of Ice, Light, and Global Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Arctic Circle: A Realm of Ice, Light, and Global Significance

The Arctic Circle, a geographically defined boundary, marks the southernmost latitude where the sun remains continuously above the horizon for at least 24 hours during the summer solstice and continuously below the horizon for at least 24 hours during the winter solstice. This unique phenomenon, known as the midnight sun and polar night, respectively, defines the Arctic as a region of extreme seasonal light variations.
A World of Ice and Permafrost:
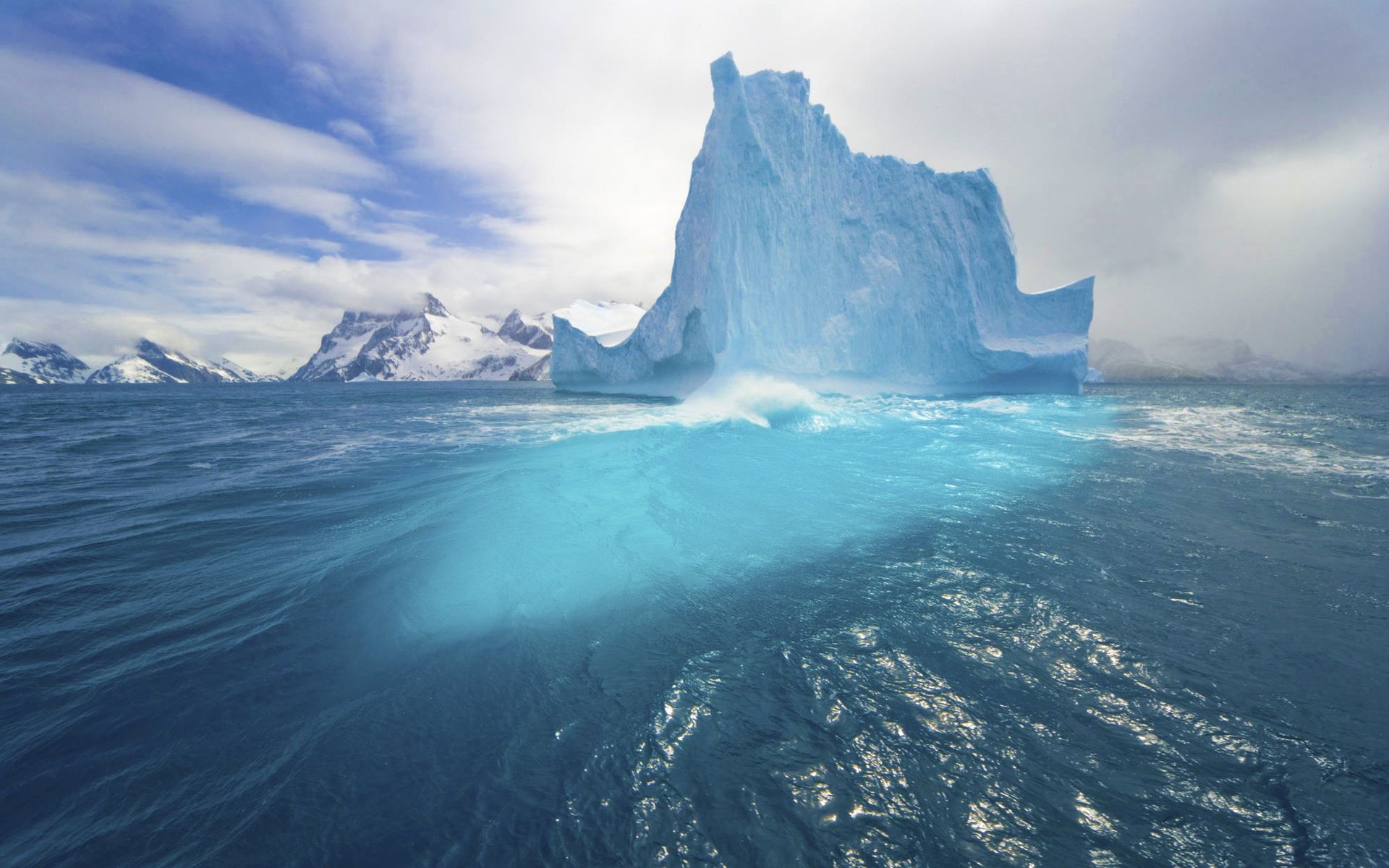
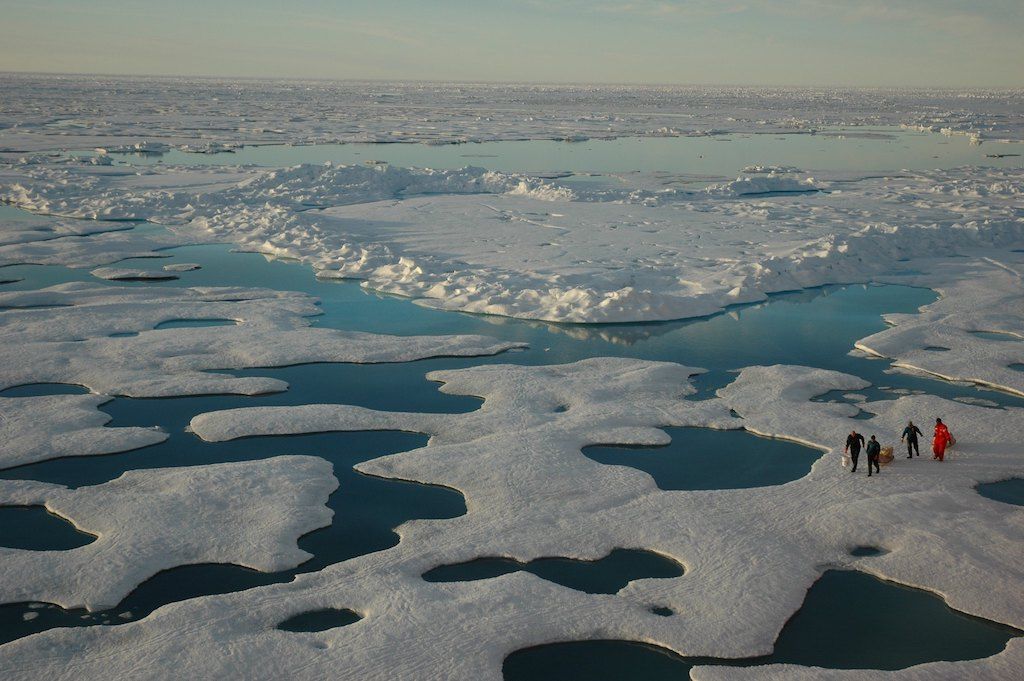
The Arctic Circle encompasses a vast expanse of land and sea, primarily covering the northernmost parts of eight countries: Canada, Russia, Greenland (Denmark), United States (Alaska), Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. This region is characterized by its frigid temperatures, frozen landscapes, and expansive ice sheets. The Arctic Ocean, a key component of the Arctic region, remains largely covered in sea ice throughout the year, with significant seasonal variations.
The underlying bedrock beneath the Arctic’s surface is permanently frozen, forming permafrost. This frozen ground, which can extend hundreds of meters deep, plays a crucial role in shaping the Arctic landscape and influencing the region’s ecosystem. The thawing of permafrost, a consequence of climate change, poses significant challenges to infrastructure, ecosystems, and human communities.
Arctic Biodiversity and Indigenous Peoples:
Despite the harsh conditions, the Arctic is home to a diverse array of flora and fauna. Polar bears, walruses, seals, and various species of whales are iconic inhabitants of the Arctic, thriving in the harsh environment. The region also supports a variety of land-based mammals like caribou and arctic foxes, as well as numerous bird species that migrate to the Arctic during the summer months.
The Arctic is also the ancestral homeland of indigenous peoples, including the Inuit, Sami, Nenets, and many others. These communities have lived in the Arctic for millennia, developing unique cultures and traditions adapted to the region’s extreme conditions. They rely on the Arctic’s resources for sustenance and have a deep understanding of the land and its interconnected ecosystems.
The Arctic’s Role in Global Climate:
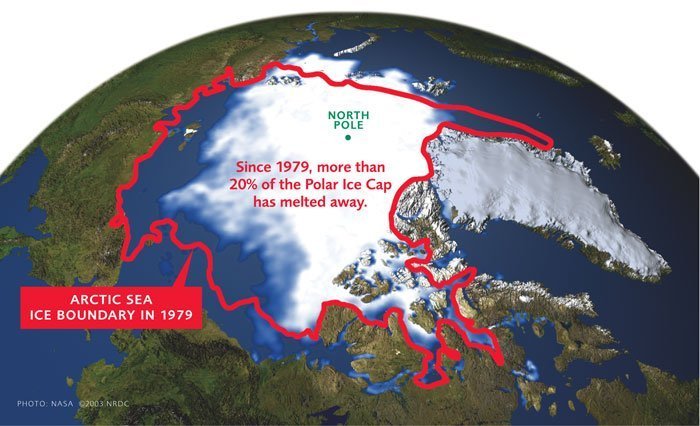
The Arctic plays a crucial role in regulating global climate. The vast expanse of sea ice reflects solar radiation back into space, helping to cool the planet. However, the melting of sea ice due to climate change is reducing this reflective capacity, leading to further warming and exacerbating the effects of climate change.
The Arctic is also a significant carbon sink, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. However, thawing permafrost releases stored carbon dioxide and methane, further contributing to global warming. This feedback loop highlights the interconnectedness of the Arctic’s climate system with the global climate.
The Arctic’s Economic and Strategic Significance:
The Arctic holds significant economic potential. The region is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, minerals, and fisheries. As ice melts, new shipping routes are opening up, potentially offering shorter and faster transportation routes between Asia and Europe.
The Arctic’s strategic importance is also growing. The region is home to major military installations and is increasingly becoming a focus of geopolitical competition. The melting of sea ice is opening up new opportunities for military access and control, leading to increased military activity and potential conflicts.
Navigating the Challenges of a Changing Arctic:
The Arctic is facing significant challenges due to climate change. Rising temperatures are leading to the melting of sea ice, permafrost thawing, and changes in weather patterns. These changes are having profound impacts on the Arctic environment, ecosystems, and human communities.
Addressing these challenges requires international cooperation and collaboration. Countries bordering the Arctic are working together through the Arctic Council, a forum for addressing Arctic issues, to develop sustainable management plans and address the impacts of climate change.
FAQs about the Arctic Circle:
Q: What is the exact location of the Arctic Circle?
A: The Arctic Circle is located at 66°33′44.3″ N latitude. This latitude marks the southernmost point where the sun remains continuously above the horizon for at least 24 hours during the summer solstice and continuously below the horizon for at least 24 hours during the winter solstice.
Q: Why is the Arctic Circle important?
A: The Arctic Circle is important for its unique geographical features, its role in global climate regulation, its rich biodiversity, and its significant economic and strategic potential.
Q: What are the main challenges facing the Arctic?
A: The main challenges facing the Arctic include climate change, its impacts on ecosystems and human communities, and the increasing geopolitical competition for resources and influence.
Q: How is climate change affecting the Arctic?
A: Climate change is causing significant changes in the Arctic, including rising temperatures, melting sea ice, permafrost thawing, and changes in weather patterns. These changes are impacting the Arctic environment, ecosystems, and human communities.
Q: What are some of the potential benefits of the Arctic’s melting sea ice?
A: The melting of sea ice opens up new shipping routes, potentially offering shorter and faster transportation routes between Asia and Europe. It also opens up new opportunities for resource extraction, including oil, gas, and minerals.
Q: What are some of the risks associated with the Arctic’s melting sea ice?
A: The melting of sea ice contributes to rising sea levels, which threatens coastal communities worldwide. It also disrupts the Arctic ecosystem and threatens the livelihoods of indigenous communities.
Tips for Understanding the Arctic Circle:
- Explore maps and resources: Use online maps and resources to visualize the Arctic Circle and its surrounding regions.
- Learn about indigenous cultures: Research the history, culture, and traditions of the indigenous peoples who have lived in the Arctic for millennia.
- Follow the latest research: Stay informed about the latest scientific research on climate change and its impacts on the Arctic.
- Engage in conversations: Discuss the importance of the Arctic and the challenges it faces with family, friends, and colleagues.
- Support conservation efforts: Contribute to organizations working to protect the Arctic environment and its ecosystems.
Conclusion:
The Arctic Circle is a region of unparalleled beauty, harsh conditions, and immense global significance. Its unique geographical features, rich biodiversity, and role in regulating global climate make it a critical region for understanding the Earth’s interconnected systems. The challenges facing the Arctic, primarily driven by climate change, necessitate international cooperation and sustainable management strategies. By fostering a deeper understanding of the Arctic and its complexities, we can work towards preserving this vital region for future generations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Arctic Circle: A Realm of Ice, Light, and Global Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!