The Arctic Circle: A Realm of Ice, Light, and Global Significance
Related Articles: The Arctic Circle: A Realm of Ice, Light, and Global Significance
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Arctic Circle: A Realm of Ice, Light, and Global Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Arctic Circle: A Realm of Ice, Light, and Global Significance

The Arctic Circle, an imaginary line encircling the Earth at approximately 66.5° north latitude, marks a significant boundary in our planet’s geography and climate. It defines the northernmost region where the sun remains continuously above the horizon for at least 24 hours during the summer solstice and below the horizon for at least 24 hours during the winter solstice. This unique phenomenon, known as the midnight sun and polar night, respectively, shapes the Arctic’s environment and the lives of its inhabitants.
A Frozen Frontier:
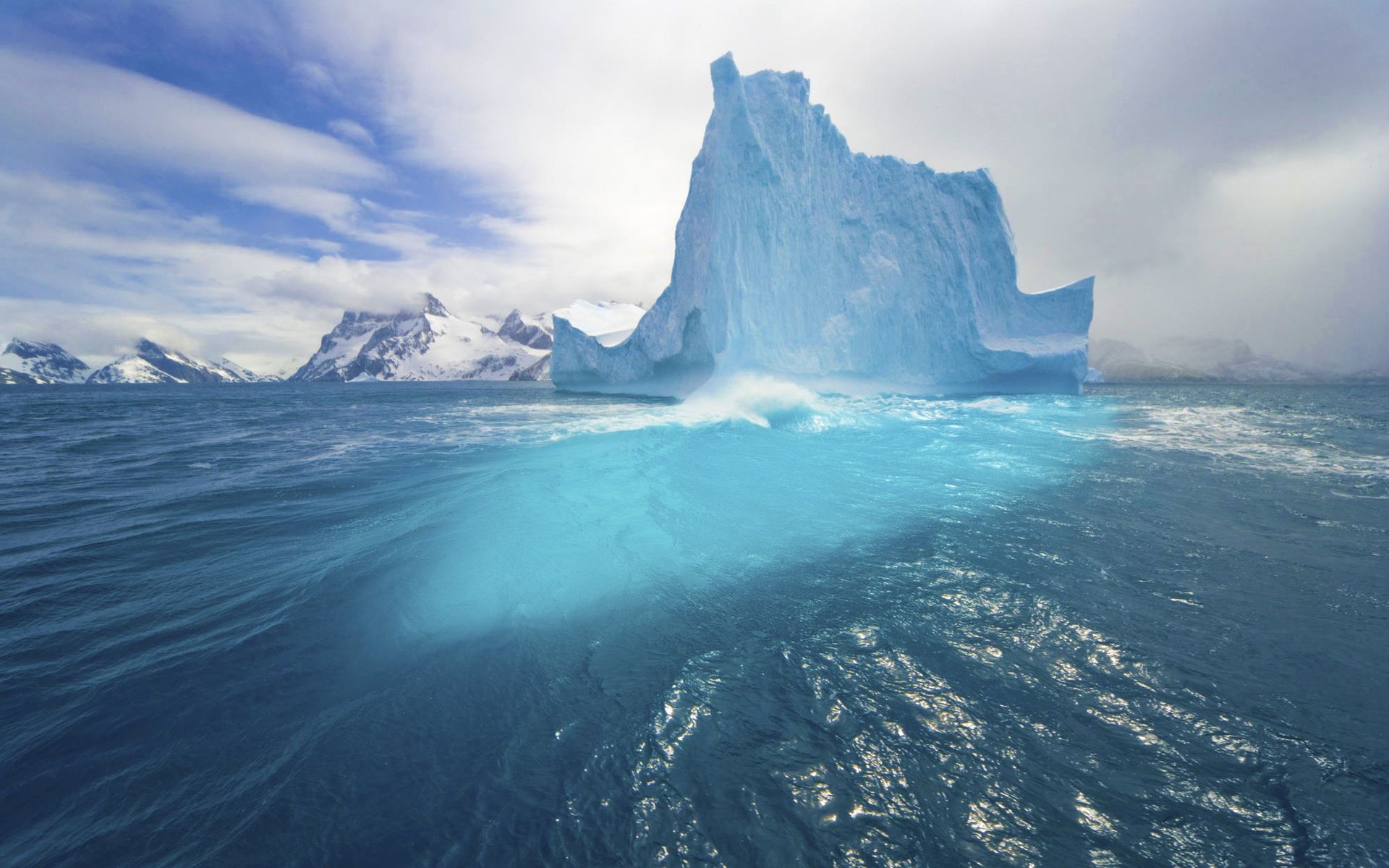
The Arctic Circle encompasses a vast and diverse region, including parts of eight countries: Canada, Russia, Greenland (Denmark), Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and the United States (Alaska). This region is characterized by its predominantly frozen landscape, encompassing vast expanses of sea ice, glaciers, permafrost, and tundra. The Arctic’s icy environment is not only a defining feature but also a key factor in global climate regulation.
The Arctic’s Vital Role in the Global Climate System:
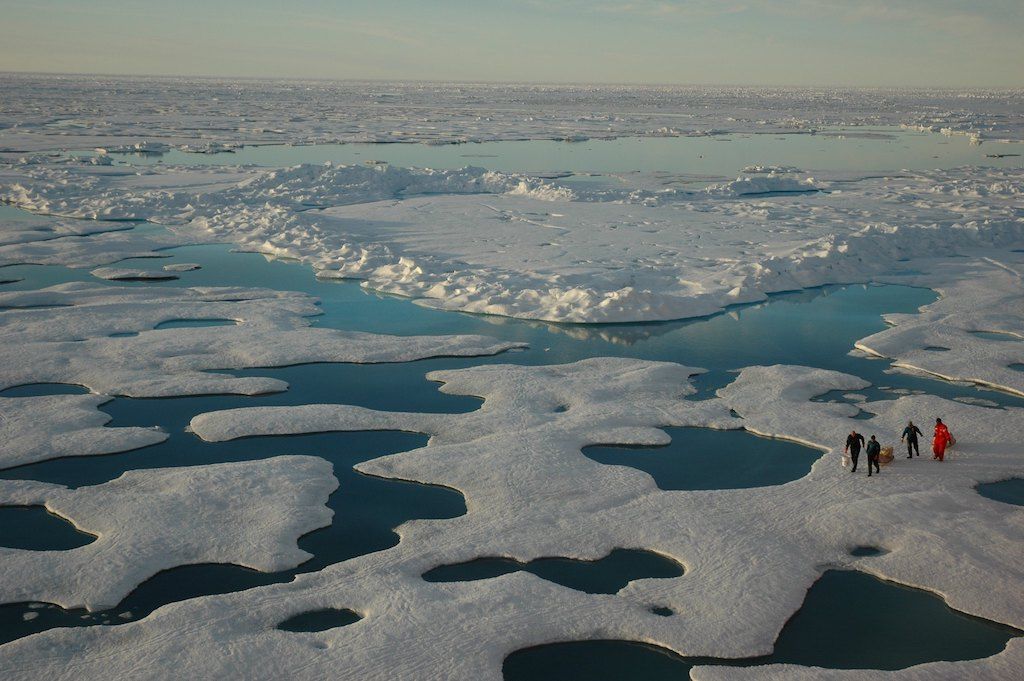
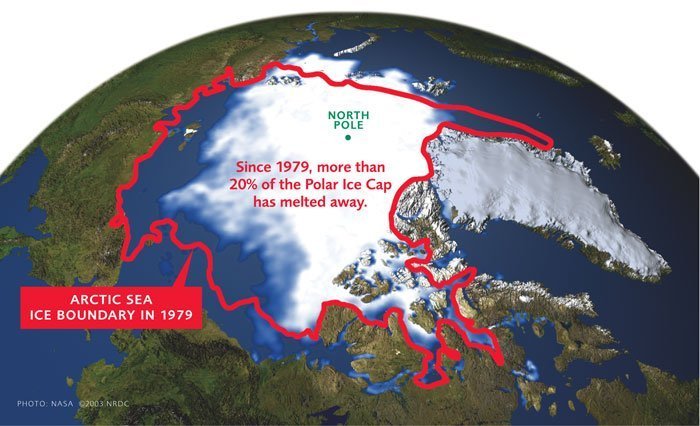
The Arctic plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate. Its vast ice cover reflects sunlight back into space, helping to cool the planet. As the Arctic ice melts due to rising global temperatures, it exposes darker ocean surfaces, which absorb more heat, further accelerating the warming process. This phenomenon, known as the Arctic amplification effect, has significant implications for global climate patterns and weather events.
A Rich Ecosystem and Diverse Inhabitants:
Despite its harsh conditions, the Arctic is teeming with life. Polar bears, walruses, seals, and various species of whales thrive in the icy waters and surrounding land. The region also supports a diverse array of birdlife, including migratory species that rely on the Arctic’s rich ecosystems for breeding and feeding grounds. The indigenous peoples of the Arctic, such as the Inuit, Sámi, and Nenets, have adapted to the unique challenges of this environment for centuries, developing intricate cultures and traditions deeply intertwined with the land and its resources.
The Arctic’s Resources and Economic Potential:
The Arctic holds significant economic potential, particularly in terms of natural resources. Vast reserves of oil, gas, and minerals lie beneath the Arctic seabed, attracting interest from various countries and corporations. Additionally, the region’s unique environment offers potential for tourism, fishing, and shipping, particularly as sea ice melts and opens new routes. However, these economic opportunities are often accompanied by environmental risks and ethical concerns, leading to debates about sustainable development and resource management.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The Arctic faces numerous challenges, primarily driven by climate change. Melting sea ice, permafrost thaw, and rising sea levels threaten the region’s ecosystems, infrastructure, and the livelihoods of its inhabitants. These changes also pose significant risks to global climate stability and necessitate international cooperation to address the interconnected challenges of the Arctic.
Despite the challenges, the Arctic also presents numerous opportunities for scientific research, conservation, and sustainable development. Understanding the region’s complex ecosystems, monitoring climate change impacts, and promoting sustainable resource management are essential for safeguarding the Arctic’s future.
FAQs about the Arctic Circle:
1. What is the Arctic Circle?
The Arctic Circle is an imaginary line of latitude encircling the Earth at approximately 66.5° north. It marks the southernmost point where the sun remains continuously above the horizon for at least 24 hours during the summer solstice and below the horizon for at least 24 hours during the winter solstice.
2. What countries are located within the Arctic Circle?
Eight countries share territory within the Arctic Circle: Canada, Russia, Greenland (Denmark), Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and the United States (Alaska).
3. What is the climate like in the Arctic?
The Arctic experiences extremely cold temperatures, with average winter temperatures well below freezing. The region is characterized by long periods of darkness during winter and long periods of daylight during summer.
4. What are the main environmental challenges facing the Arctic?
Climate change is the most significant challenge facing the Arctic. Melting sea ice, permafrost thaw, and rising sea levels threaten the region’s ecosystems, infrastructure, and the livelihoods of its inhabitants.
5. What is the importance of the Arctic Circle?
The Arctic Circle is important for several reasons. It plays a crucial role in regulating global climate, is home to diverse ecosystems and indigenous communities, and holds significant economic potential.
Tips for Understanding the Arctic Circle:
- Explore online resources: Numerous websites and organizations offer information about the Arctic, including its geography, climate, ecosystems, and inhabitants.
- Engage with research: Scientific publications and reports provide valuable insights into the Arctic’s changing environment and the challenges it faces.
- Support organizations working in the Arctic: Organizations dedicated to Arctic research, conservation, and sustainable development can benefit from your support.
- Stay informed about Arctic issues: News articles, documentaries, and public discussions can help you stay abreast of current events and developments related to the Arctic.
Conclusion:
The Arctic Circle is a fascinating and complex region, shaped by its unique geography, climate, and inhabitants. Its importance extends beyond its geographical boundaries, impacting global climate patterns, resource availability, and the lives of people worldwide. Understanding the Arctic’s challenges and opportunities is crucial for ensuring a sustainable future for this vital region.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Arctic Circle: A Realm of Ice, Light, and Global Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!