Power Line Maps: Illuminating the Electrical Grid
Related Articles: Power Line Maps: Illuminating the Electrical Grid
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Power Line Maps: Illuminating the Electrical Grid. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Power Line Maps: Illuminating the Electrical Grid
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Power Line Maps: Illuminating the Electrical Grid
- 3.1 Decoding the Grid: A Visual Representation of Power
- 3.2 Navigating the Complexity: Types and Features of Power Line Maps
- 3.3 Navigating the Grid: Importance and Benefits of Power Line Maps
- 3.4 Unlocking the Potential: FAQs about Power Line Maps
- 3.5 Illuminating the Path: Tips for Effective Power Line Map Utilization
- 3.6 Conclusion: Power Line Maps – A Vital Tool for a Modern World
- 4 Closure
Power Line Maps: Illuminating the Electrical Grid

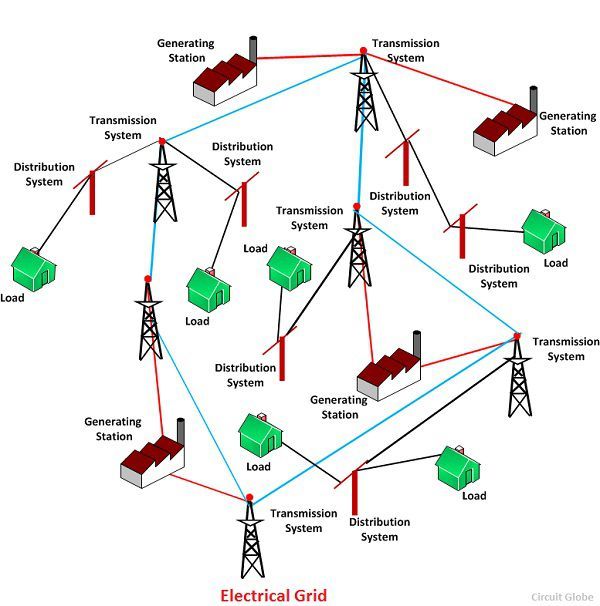
Power lines, the unsung heroes of modern life, form a vast, intricate network that delivers electricity to our homes, businesses, and industries. Understanding this network is crucial for ensuring reliable power supply, planning infrastructure development, and mitigating potential hazards. This is where power line maps come into play, offering a comprehensive visual representation of the electrical grid, revealing its complexities and facilitating informed decision-making.
Decoding the Grid: A Visual Representation of Power
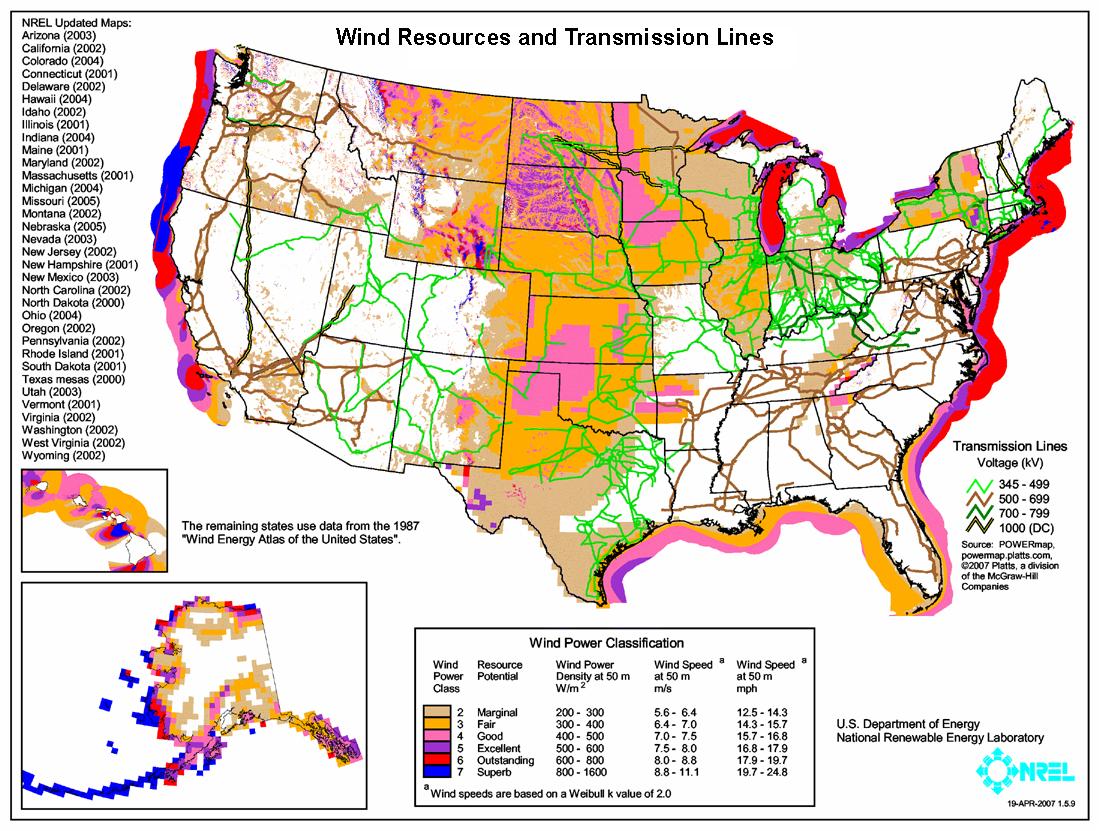
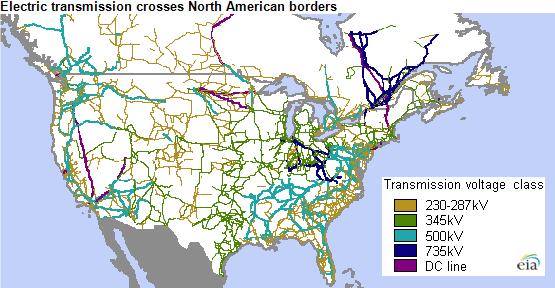
Power line maps, also known as transmission line maps, are specialized geographical maps that depict the high-voltage transmission lines and substations that constitute the electrical grid. They provide a visual representation of the interconnected network of towers, cables, and transformers that transport electricity from power generation plants to consumers.
These maps are not merely static diagrams; they are dynamic representations that incorporate real-time data, enabling users to track electricity flow, monitor system performance, and identify potential vulnerabilities. This data-driven approach enhances the map’s utility, making it an indispensable tool for various stakeholders, including:
1. Utility Companies: Power line maps empower utility companies to:
- Optimize grid operations: By visualizing the flow of electricity across the network, companies can identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, enabling them to optimize power distribution and reduce losses.
- Plan maintenance and upgrades: The maps highlight critical infrastructure components, enabling companies to prioritize maintenance schedules and plan strategic upgrades to enhance grid reliability and resilience.
- Respond to outages: In the event of power outages, power line maps help companies quickly pinpoint the affected areas and dispatch crews to restore power efficiently.
2. Government Agencies: Power line maps play a crucial role in government agencies’ efforts to:
- Plan urban development: Understanding the existing power infrastructure enables agencies to make informed decisions regarding new developments and ensure sufficient power capacity for future growth.
- Manage environmental impact: Power line maps can be used to assess the potential environmental impact of new transmission lines, helping agencies to minimize ecological disturbances and optimize project planning.
- Respond to emergencies: In natural disasters or emergencies, power line maps provide critical information about the location of critical infrastructure, enabling agencies to coordinate relief efforts effectively.
3. Researchers and Engineers: Power line maps are invaluable for researchers and engineers working on:
- Grid modeling and simulation: By providing a detailed representation of the network, maps facilitate the development of advanced models and simulations, helping researchers to analyze grid behavior and predict future trends.
- Developing new technologies: Understanding the existing power infrastructure is essential for developing and integrating new technologies, such as renewable energy sources and smart grids, into the existing network.
- Optimizing power system design: Power line maps provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the existing system, enabling engineers to design new power infrastructure that is efficient, resilient, and cost-effective.
4. Public and Consumers: Power line maps can also be beneficial for the general public and consumers by:
- Increasing awareness of the electrical grid: By providing a visual representation of the complex network that powers our lives, maps can foster public understanding and appreciation for the vital role of power infrastructure.
- Facilitating informed decision-making: Consumers can use power line maps to understand the potential impact of new power projects on their communities, enabling them to participate in public discussions and advocate for informed decisions.
- Promoting energy efficiency: Understanding the electricity flow and potential losses within the grid can encourage consumers to adopt energy-saving practices and contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
Navigating the Complexity: Types and Features of Power Line Maps
Power line maps are not a one-size-fits-all solution. They come in various forms, tailored to specific needs and applications. Here’s a breakdown of the common types:
1. Static Maps: These maps depict the power grid infrastructure at a fixed point in time. They typically show the location of transmission lines, substations, and other key components, but lack real-time data or dynamic information. Static maps are useful for planning purposes, understanding the overall network layout, and identifying potential areas for improvement.
2. Dynamic Maps: These maps incorporate real-time data, allowing users to visualize the flow of electricity, track system performance, and monitor potential issues. Dynamic maps are crucial for operational management, enabling utility companies to respond quickly to changing conditions and optimize grid performance.
3. Geographic Information System (GIS) Maps: These maps leverage GIS technology to integrate spatial data, such as elevation, land cover, and population density, with power line data. GIS maps provide a comprehensive understanding of the power grid within its geographical context, enabling informed decisions regarding environmental impact, land use planning, and emergency response.
4. 3D Maps: These maps provide a three-dimensional representation of the power grid, allowing users to visualize the physical layout of transmission lines, towers, and other infrastructure components. 3D maps are particularly useful for planning new power lines, assessing environmental impact, and visualizing potential hazards.
5. Interactive Maps: These maps allow users to interact with the data, zooming in on specific areas, filtering information, and accessing detailed data about individual components. Interactive maps are highly user-friendly, providing a customizable and intuitive experience for exploring the power grid.
Beyond their basic structure, power line maps can incorporate various features to enhance their functionality and provide valuable insights:
- Real-time data: This includes information about power flow, voltage levels, system load, and other critical parameters, enabling users to monitor grid performance and identify potential issues.
- Historical data: Access to historical data allows users to analyze trends, identify patterns, and make informed predictions about future grid behavior.
- Fault detection and analysis: Maps can incorporate algorithms that detect and analyze faults within the power grid, enabling companies to identify potential problems and take preventative measures.
- Environmental data: Integrating environmental data, such as weather patterns, vegetation, and soil conditions, allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the power grid’s impact on the environment.
- Integration with other systems: Power line maps can be integrated with other systems, such as SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, enabling users to access a wider range of data and gain a more holistic view of the grid.
Navigating the Grid: Importance and Benefits of Power Line Maps
Power line maps are not merely visual representations; they are powerful tools that provide critical insights into the electrical grid, enabling stakeholders to:
- Improve grid reliability: By understanding the network’s strengths and weaknesses, companies can identify potential vulnerabilities and take proactive steps to prevent outages and ensure uninterrupted power supply.
- Optimize grid performance: Real-time data and advanced analysis capabilities allow for efficient power distribution, minimizing losses and maximizing grid efficiency.
- Reduce operational costs: By identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies, companies can streamline operations, optimize maintenance schedules, and reduce overall costs associated with grid management.
- Plan future development: Power line maps provide valuable data for planning new power projects, ensuring that new infrastructure is integrated seamlessly with the existing network and meets future demand.
- Minimize environmental impact: By incorporating environmental data and assessing the potential impact of new projects, power line maps help companies make informed decisions that minimize ecological disturbances and promote sustainable development.
- Improve emergency response: In the event of natural disasters or emergencies, power line maps provide critical information about the location of critical infrastructure, enabling agencies to coordinate relief efforts effectively.
Unlocking the Potential: FAQs about Power Line Maps
1. What are the different types of data included in power line maps?
Power line maps can incorporate a wide range of data, including:
- Geographic data: Location of transmission lines, substations, towers, and other infrastructure components.
- Electrical data: Power flow, voltage levels, system load, and other critical parameters.
- Operational data: Maintenance schedules, equipment specifications, and other relevant information.
- Environmental data: Elevation, land cover, vegetation, weather patterns, and other relevant information.
- Historical data: Past performance data, outage records, and other historical information.
2. How are power line maps used in grid planning and development?
Power line maps are essential for planning new transmission lines, expanding existing infrastructure, and integrating renewable energy sources into the grid. They provide valuable insights into:
- Identifying optimal routes for new transmission lines: Considering factors such as land use, environmental impact, and proximity to existing infrastructure.
- Assessing the capacity of existing infrastructure: Determining whether the grid can accommodate new loads and ensure reliable power supply.
- Planning for future demand: Predicting future energy needs and ensuring that the grid is adequately equipped to meet those demands.
3. How do power line maps contribute to grid security and resilience?
Power line maps play a crucial role in enhancing grid security and resilience by:
- Identifying potential vulnerabilities: Analyzing the network’s layout and identifying areas susceptible to outages or disruptions.
- Developing mitigation strategies: Implementing measures to strengthen the grid’s resilience against natural disasters, cyberattacks, and other threats.
- Monitoring grid performance in real-time: Enabling companies to identify and address potential issues before they escalate into major outages.
4. How are power line maps used in emergency response and disaster management?
Power line maps provide vital information during emergencies and disasters by:
- Locating critical infrastructure: Identifying the location of power plants, substations, and transmission lines, enabling responders to assess damage and prioritize repair efforts.
- Coordinating relief efforts: Providing information about power outages, enabling agencies to allocate resources efficiently and ensure that essential services remain operational.
- Facilitating communication: Providing a clear understanding of the grid’s status, enabling effective communication between emergency responders and affected communities.
5. What are the future trends in power line mapping?
Power line mapping is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in technology and the growing demand for a more reliable, resilient, and sustainable power grid. Future trends include:
- Integration with artificial intelligence (AI): AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict grid behavior, enabling more proactive grid management.
- Enhanced visualization capabilities: Advanced visualization techniques, such as 3D models and virtual reality (VR), will provide more immersive and intuitive experiences for users.
- Real-time data integration: The increasing availability of real-time data will enable more dynamic and responsive power line maps, providing critical insights into grid performance.
- Increased focus on sustainability: Power line maps will play a crucial role in integrating renewable energy sources into the grid, promoting energy efficiency, and minimizing environmental impact.
Illuminating the Path: Tips for Effective Power Line Map Utilization
- Define specific goals and objectives: Clearly identify the purpose of using the map, whether it’s for planning, operational management, or emergency response.
- Choose the appropriate map type: Select a map that aligns with the specific needs and objectives of the project or application.
- Ensure data accuracy and completeness: Verify the accuracy and completeness of the data used to create the map, as inaccurate information can lead to flawed decision-making.
- Develop user-friendly interfaces: Create maps that are easy to navigate, interpret, and interact with, ensuring that all users can understand and utilize the information effectively.
- Integrate with other systems: Connect power line maps with other systems, such as SCADA systems and GIS platforms, to access a wider range of data and gain a more comprehensive understanding of the grid.
- Continuously update and improve: Regularly update the map with new data, incorporate feedback from users, and explore new technologies to enhance its functionality and value.
Conclusion: Power Line Maps – A Vital Tool for a Modern World
Power line maps are not merely static diagrams; they are dynamic representations of the electrical grid, providing critical insights that enable stakeholders to optimize grid performance, ensure reliable power supply, and plan for the future. From utility companies to government agencies, researchers, engineers, and the public, power line maps empower informed decision-making, promoting a more efficient, resilient, and sustainable energy future. As technology continues to advance, power line maps will evolve, incorporating new features and capabilities, further enhancing their value and solidifying their role as a vital tool for navigating the complexities of the modern electrical grid.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Power Line Maps: Illuminating the Electrical Grid. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
