Nigeria: A Giant on the African Continent
Related Articles: Nigeria: A Giant on the African Continent
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Nigeria: A Giant on the African Continent. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Nigeria: A Giant on the African Continent

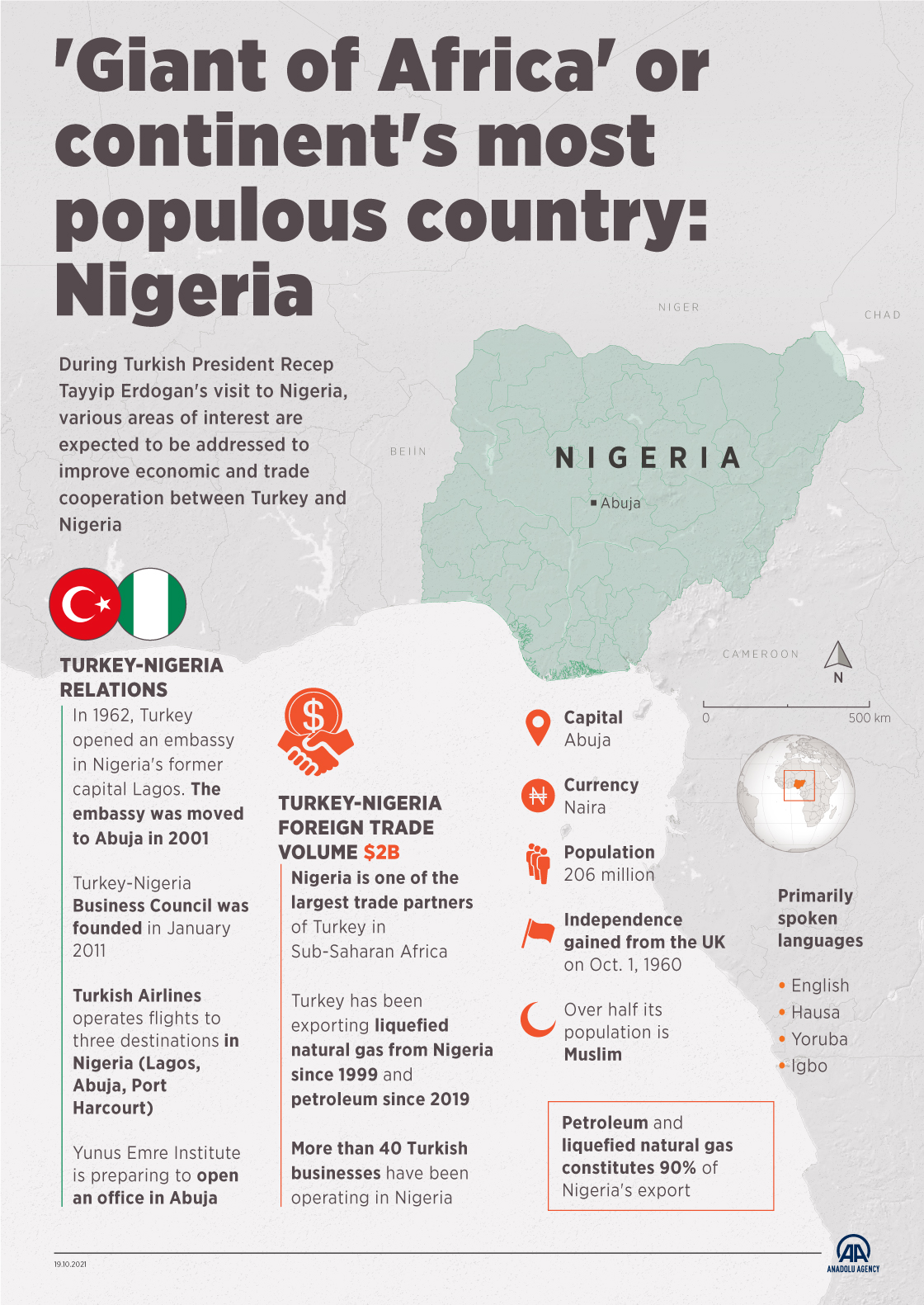
Nigeria, the most populous country in Africa, occupies a strategically important position on the continent’s western coast. It is situated in West Africa, bordering the Gulf of Guinea, and shares borders with Benin, Niger, Chad, and Cameroon. Understanding Nigeria’s location on the map reveals its significance in the regional and global context.
A Geographical Overview
Nigeria stretches across a vast expanse of land, encompassing a diverse range of landscapes. Its geography is characterized by:
- Coastal Plains: The southern region is dominated by coastal plains, where the Niger River Delta forms a crucial economic hub. This region boasts fertile land, ideal for agriculture and rich in natural resources like oil and gas.
- Plateau Region: Central Nigeria is marked by a plateau region, characterized by rolling hills and valleys. This area is home to various ethnic groups and boasts a diverse ecosystem, including forests, grasslands, and savannas.
- Northern Plains: The northern region is dominated by vast plains, transitioning into the Sahel region, known for its semi-arid climate and sparse vegetation. This region is primarily used for cattle ranching and agriculture.
Strategic Location and Regional Importance
Nigeria’s location on the Gulf of Guinea, a major shipping route, grants it access to global markets. It is also a key player in the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), a regional bloc promoting economic integration and cooperation.
- Economic Hub: Nigeria’s strategic location makes it a vital economic hub for West Africa. Its oil and gas reserves are crucial for the region’s energy needs, while its thriving agricultural sector provides food security for neighboring countries.
- Political Influence: As the most populous nation in West Africa, Nigeria holds significant political influence in the region. It plays a crucial role in maintaining peace and stability, contributing to regional security and development initiatives.
- Cultural Diversity: Nigeria’s location at the crossroads of various cultures and ethnicities makes it a melting pot of traditions and languages. Its diverse population contributes to a vibrant cultural landscape, attracting tourists and fostering intercultural exchange.
Navigating Nigeria’s Landscape
Understanding Nigeria’s geography is essential for navigating its diverse landscape. Here are some key points to consider:
- Transportation: Nigeria has a well-developed road network, connecting major cities and towns. However, travel can be challenging due to road conditions and traffic congestion. Air travel is also a viable option, with major airports in Lagos, Abuja, and Port Harcourt.
- Climate: Nigeria experiences a tropical climate with distinct wet and dry seasons. The southern region receives higher rainfall than the northern region, which experiences a more arid climate. Travelers should be aware of the rainy season and pack accordingly.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Nigeria is a culturally diverse country, with a wide array of customs and traditions. Respecting local customs and showing sensitivity to cultural differences is essential for a positive travel experience.
FAQs
Q: What is the capital of Nigeria?
A: The capital of Nigeria is Abuja, located in the central part of the country.
Q: What is the official language of Nigeria?
A: The official language of Nigeria is English, inherited from its colonial past. However, over 500 indigenous languages are spoken across the country.
Q: What are the major cities in Nigeria?
A: Some of the major cities in Nigeria include Lagos, Abuja, Kano, Ibadan, Port Harcourt, and Benin City.
Q: What are some of the major tourist attractions in Nigeria?
A: Nigeria offers a range of tourist attractions, including:
- National Parks: Nigeria has several national parks, including the Yankari National Park, known for its wildlife, and the Cross River National Park, home to diverse flora and fauna.
- Historical Sites: The country boasts historical sites like the ancient city of Kano, the Nok Culture sites, and the Osun-Osogbo Sacred Grove, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Cultural Experiences: Travelers can experience Nigeria’s rich culture by visiting traditional markets, attending cultural festivals, and exploring the country’s diverse art and music scene.
Tips for Traveling to Nigeria
- Obtain a Visa: Visitors require a visa to enter Nigeria, except for citizens of certain countries who may be eligible for visa-free entry.
- Currency Exchange: The official currency of Nigeria is the Naira. It is advisable to exchange currency at authorized exchange bureaus.
- Health Precautions: It is recommended to consult a healthcare professional regarding necessary vaccinations and health precautions before traveling to Nigeria.
- Safety and Security: Be aware of your surroundings and exercise caution in crowded areas. It is advisable to stay informed about security advisories issued by relevant authorities.
Conclusion
Nigeria’s location on the map, its strategic position in West Africa, and its rich cultural heritage make it a country of immense importance and potential. Its diverse landscape, vibrant culture, and burgeoning economy offer a unique and rewarding experience for travelers. Understanding Nigeria’s geographical context and cultural nuances is crucial for navigating its diverse landscape and appreciating its unique identity.




![#NIGERIA, GIANT OF AFRICA? [JULY 2020] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/EYLZcYTdYU8/maxresdefault.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Nigeria: A Giant on the African Continent. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!