Navigating the North American Landscape: A Guide to Longitude and Latitude
Related Articles: Navigating the North American Landscape: A Guide to Longitude and Latitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the North American Landscape: A Guide to Longitude and Latitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the North American Landscape: A Guide to Longitude and Latitude

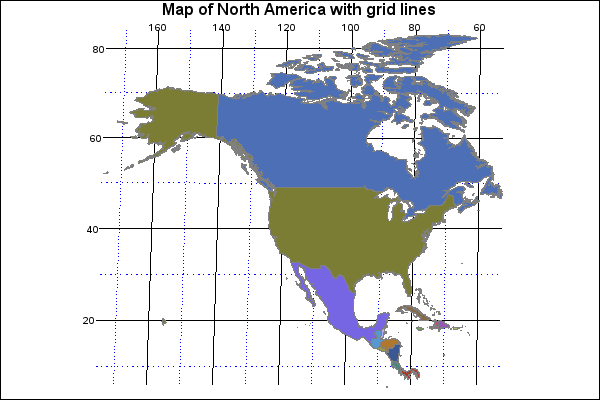
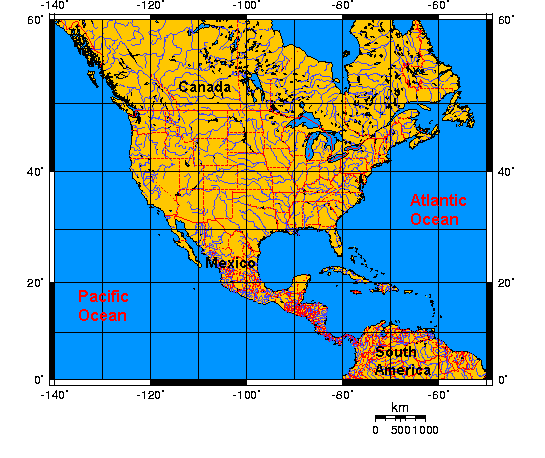
The North American continent, a vast and diverse landmass, is intricately woven together by a system of invisible lines known as longitude and latitude. These lines, forming a grid across the globe, provide a precise and standardized method for locating any point on Earth, including every corner of North America. Understanding this grid system is crucial for navigation, mapping, and comprehending the continent’s geography.
Longitude: Measuring East to West
Longitude lines, also known as meridians, run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, like slices of an orange. Each meridian represents a specific distance east or west of the prime meridian, an imaginary line that passes through Greenwich, England. The prime meridian is designated as 0 degrees longitude, with values increasing to 180 degrees east and west.
In North America, the westernmost point falls on the 168th meridian west, while the easternmost point reaches the 55th meridian west. This vast span encompasses a diverse range of landscapes, from the icy peaks of the Rocky Mountains to the lush forests of the Appalachian Mountains, and from the arid deserts of the Southwest to the fertile plains of the Midwest.
Latitude: Measuring North to South
Latitude lines, also known as parallels, run horizontally around the globe, parallel to the equator. The equator, the imaginary line circling the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, divides the globe into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Latitude values increase from 0 degrees at the equator to 90 degrees at the North and South Poles.
North America extends from approximately 10 degrees north latitude, encompassing parts of Central America, to 83 degrees north latitude, encompassing the Arctic islands. This range encompasses a wide variety of climates, from the tropical rainforests of Central America to the frigid tundra of the Arctic.
The Power of the Grid: Applications of Longitude and Latitude
The intersection of longitude and latitude lines creates a unique coordinate for every point on Earth, allowing for precise location identification. This system has numerous applications across various fields:
- Navigation: Navigational systems, such as GPS, rely heavily on longitude and latitude coordinates to pinpoint locations and guide users.
- Mapping: Cartographers use longitude and latitude to create accurate maps, providing a standardized framework for representing the Earth’s surface.
- Geography: Understanding longitude and latitude is essential for studying geographical features, such as mountains, rivers, and oceans, and for analyzing their spatial relationships.
- Climate Studies: Climate scientists use latitude to understand global climate patterns and the impact of varying solar radiation across the globe.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use latitude to determine the position of stars and celestial objects in the sky.
- Resource Management: Understanding the distribution of natural resources, such as forests, minerals, and water, relies heavily on the precise location information provided by longitude and latitude.
Navigating the Grid: Understanding North American Geography
The longitude and latitude grid system unveils the intricate geographical tapestry of North America, revealing the continent’s diverse landscapes, climates, and cultural regions:
- The West Coast: This region, characterized by its mountainous terrain and Pacific coastline, spans from approximately 120 degrees west longitude to the Pacific Ocean.
- The Rocky Mountains: This majestic mountain range, stretching from Canada to Mexico, forms a natural barrier between the eastern and western parts of the continent.
- The Great Plains: This vast expanse of flat land, extending from the Rocky Mountains to the Mississippi River, is a major agricultural region.
- The Mississippi River: This vital waterway, flowing from north to south through the heart of the continent, plays a crucial role in transportation and commerce.
- The Great Lakes: These five freshwater lakes, located in the northern part of the continent, form a major transportation route and a source of freshwater.
- The Appalachian Mountains: This mountain range, located in the eastern part of the continent, is known for its scenic beauty and rich history.
- The Eastern Seaboard: This coastal region, stretching from Maine to Florida, is home to major cities and harbors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How are longitude and latitude used in everyday life?
A: Longitude and latitude are embedded in many aspects of our daily lives, often without us consciously noticing. GPS systems in our cars, smartphones, and other devices utilize these coordinates for navigation. Online maps rely on them to display locations accurately. Even weather forecasts often use latitude to indicate the location of weather systems and predict local conditions.
Q: What are the benefits of understanding longitude and latitude?
A: Understanding longitude and latitude empowers individuals to navigate the world more effectively, comprehend geographical concepts more readily, and appreciate the interconnectedness of different regions. It also fosters a deeper understanding of the Earth’s diverse landscapes, climates, and cultures.
Q: How can I learn more about longitude and latitude?
A: There are numerous resources available for learning more about longitude and latitude, including online articles, educational videos, and interactive maps. Consulting textbooks and atlases can also provide detailed information.
Tips for Using Longitude and Latitude
- Use online tools: Interactive maps and online resources provide a visual representation of longitude and latitude lines, making it easier to understand their application.
- Practice with examples: Look at maps and identify the longitude and latitude coordinates of specific locations to solidify your understanding.
- Connect to real-world applications: Think about how longitude and latitude are used in everyday life, such as in navigation, weather forecasting, and resource management.
Conclusion
The longitude and latitude grid system is a fundamental tool for understanding and navigating the Earth. It provides a standardized framework for locating any point on the globe, revealing the intricate geography of North America and its diverse landscapes, climates, and cultural regions. By comprehending this system, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of the world and navigate the North American continent with greater ease and accuracy.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the North American Landscape: A Guide to Longitude and Latitude. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
