Navigating the Night Sky: A Guide to Tonight’s Constellations
Related Articles: Navigating the Night Sky: A Guide to Tonight’s Constellations
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Night Sky: A Guide to Tonight’s Constellations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Night Sky: A Guide to Tonight’s Constellations
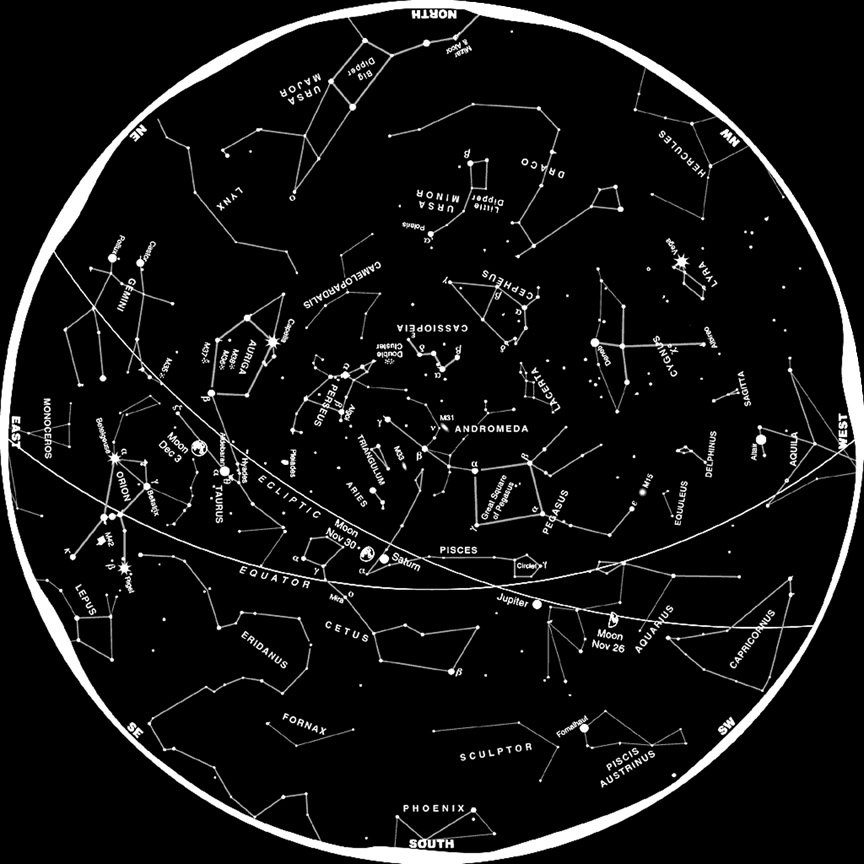
The night sky, a vast canvas of darkness punctuated by twinkling lights, has captivated humanity for millennia. From ancient civilizations to modern stargazers, the patterns formed by stars have inspired stories, guided navigation, and fueled scientific curiosity. This celestial tapestry, known as constellations, offers a window into the universe, revealing the vastness of space and the intricate dance of celestial bodies.
To understand tonight’s constellations, one must first grasp the fundamental concept of celestial coordinates. The celestial sphere, an imaginary sphere surrounding Earth, serves as a framework for mapping the sky. Like the terrestrial globe, the celestial sphere uses a system of coordinates, declination (latitude) and right ascension (longitude), to pinpoint the position of stars and other celestial objects.
Identifying Constellations:
Tonight’s constellations, like all celestial bodies, shift their positions across the sky due to Earth’s rotation and orbit around the Sun. To identify them, several resources can be employed:
-
Star Charts and Apps: Numerous star charts, both physical and digital, provide detailed maps of the night sky. These charts often include constellation outlines, names, and relevant information like magnitude (brightness) and distance. Mobile applications like Stellarium or SkySafari offer interactive sky maps, allowing users to input their location and time to view a customized depiction of the constellations visible from their vantage point.
-
Naked-Eye Observation: While star charts are invaluable, observing the night sky with the naked eye can be a rewarding experience. Recognizing familiar patterns, such as the Big Dipper or Orion, can serve as starting points for exploring the constellations.
-
Telescopes: For a more detailed view, telescopes magnify distant objects, revealing fainter stars and intricate celestial features. Telescopes often come with star charts or software specifically designed for astronomical observation.
Key Constellations:
-
Ursa Major (The Great Bear): This prominent constellation is easily recognizable by its seven brightest stars, forming the shape of a dipper. The two stars at the end of the dipper’s handle point towards Polaris, the North Star.
-
Ursa Minor (The Little Bear): Located near Ursa Major, this constellation contains Polaris, the North Star, which is crucial for navigation.
-
Orion (The Hunter): One of the most recognizable constellations, Orion is characterized by its three stars forming Orion’s belt and the prominent red star Betelgeuse.
-
Taurus (The Bull): This constellation features the bright star Aldebaran and the Pleiades star cluster, a group of young, hot stars visible to the naked eye.
-
Gemini (The Twins): This constellation is marked by two bright stars, Castor and Pollux, representing the twins.
-
Leo (The Lion): This constellation is easily identified by its distinctive shape resembling a lion’s head and mane.
-
Virgo (The Virgin): This constellation is home to the bright star Spica, a blue giant star.
Understanding Constellations:
Constellations are not static, unchanging formations but rather groupings of stars that appear close together from Earth’s perspective. The stars in a constellation are often vastly distant from each other, separated by light-years.
The constellations we see tonight are influenced by Earth’s position in its orbit around the Sun. As Earth travels along its path, different constellations become visible in the night sky.
Benefits of Observing Constellations:
-
Appreciation of the Universe: Observing constellations fosters a deeper appreciation for the vastness and beauty of the universe.
-
Navigation: Constellations, particularly Polaris, have historically served as navigational aids, guiding sailors and travelers.
-
Cultural Understanding: Constellations are deeply rooted in human history and mythology, reflecting different cultures’ interpretations of the night sky.
-
Scientific Exploration: Studying constellations allows astronomers to understand the composition, evolution, and distribution of stars.
FAQs:
-
Q: What are constellations and how are they formed?
-
A: Constellations are patterns of stars that appear close together from Earth’s perspective. They are formed by the random distribution of stars in the vastness of space, with the illusion of patterns arising from our vantage point.
-
Q: Why do constellations change throughout the year?
-
A: Constellations change throughout the year due to Earth’s orbit around the Sun. As Earth moves along its orbit, the perspective from which we view the stars changes, revealing different constellations in the night sky.
-
Q: How can I find my current location on a star chart?
-
A: Most star charts include a grid system based on latitude and longitude. By inputting your location’s coordinates, you can pinpoint your position on the chart.
-
Q: What is the significance of the North Star?
-
A: The North Star, Polaris, is located near the celestial north pole. It appears stationary in the sky, serving as a reliable reference point for navigation.
-
Q: How can I learn more about constellations?
-
A: Numerous resources, including books, websites, planetariums, and astronomy clubs, provide detailed information about constellations.
Tips for Observing Constellations:
-
Find a dark location: Light pollution from cities can obscure fainter stars, making constellation observation challenging.
-
Use a star chart or app: These resources can help you identify constellations and plan your observations.
-
Be patient: It takes time to familiarize yourself with the night sky and recognize constellations.
-
Join an astronomy club: Astronomy clubs offer opportunities for shared observations, learning, and stargazing events.
Conclusion:
Observing constellations is a captivating and rewarding experience that connects us to the vastness of the universe and the rich history of human exploration. By understanding the principles of celestial coordinates, identifying key constellations, and employing available resources, we can embark on a journey through the night sky, unraveling the mysteries and beauty of the cosmos.
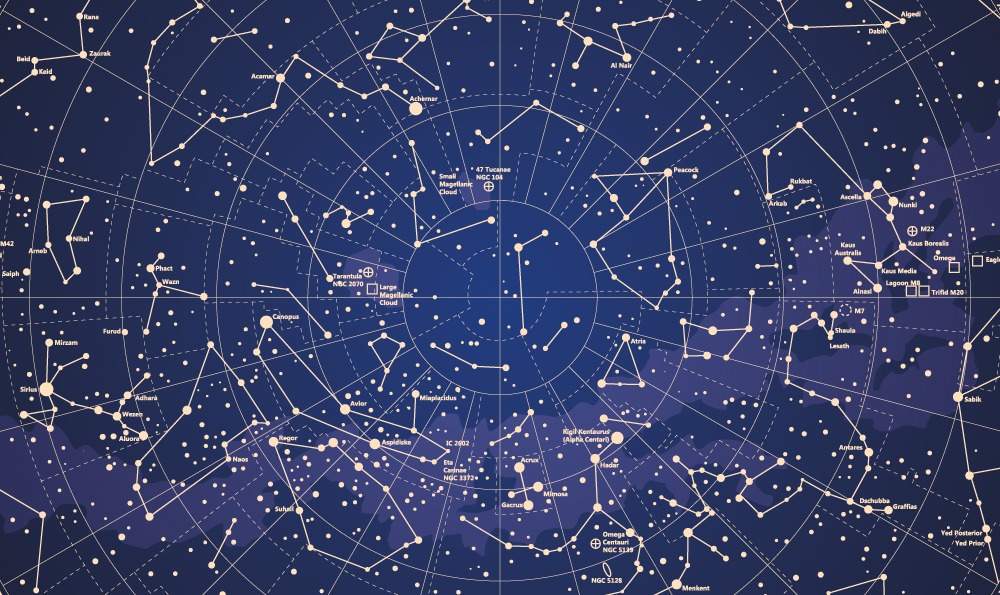
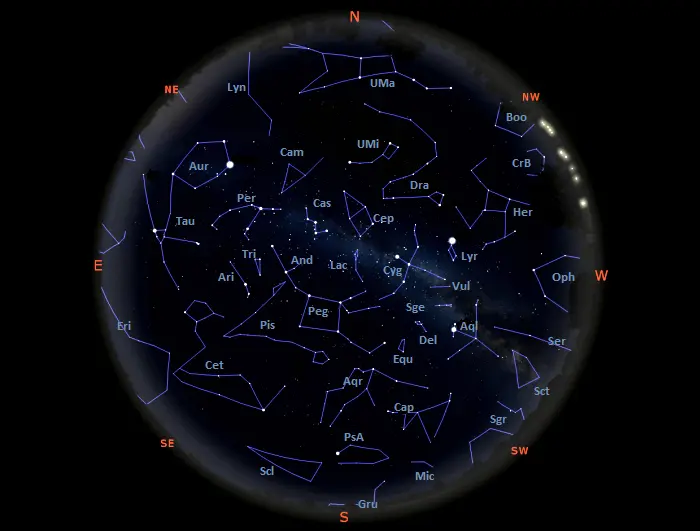



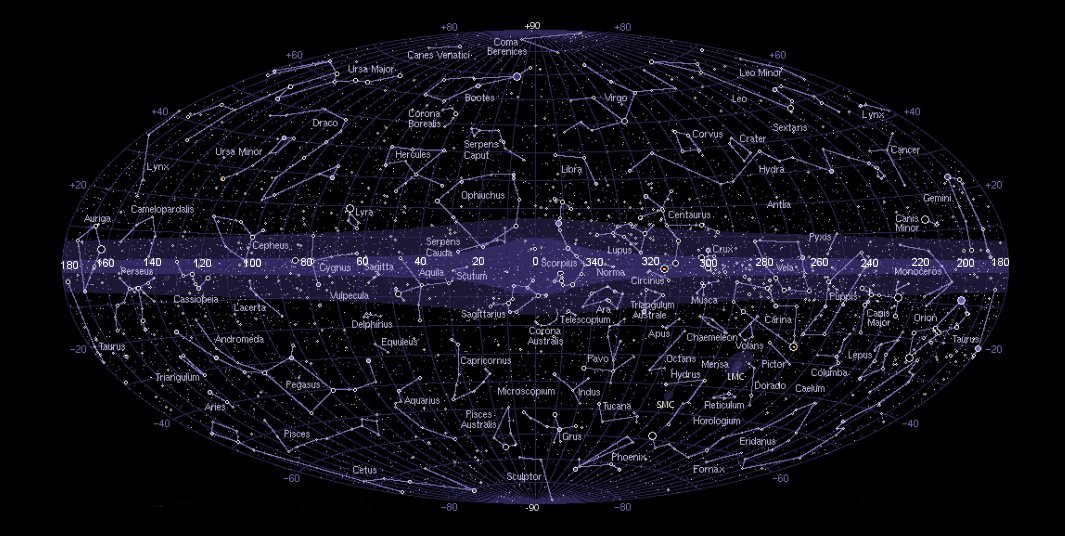


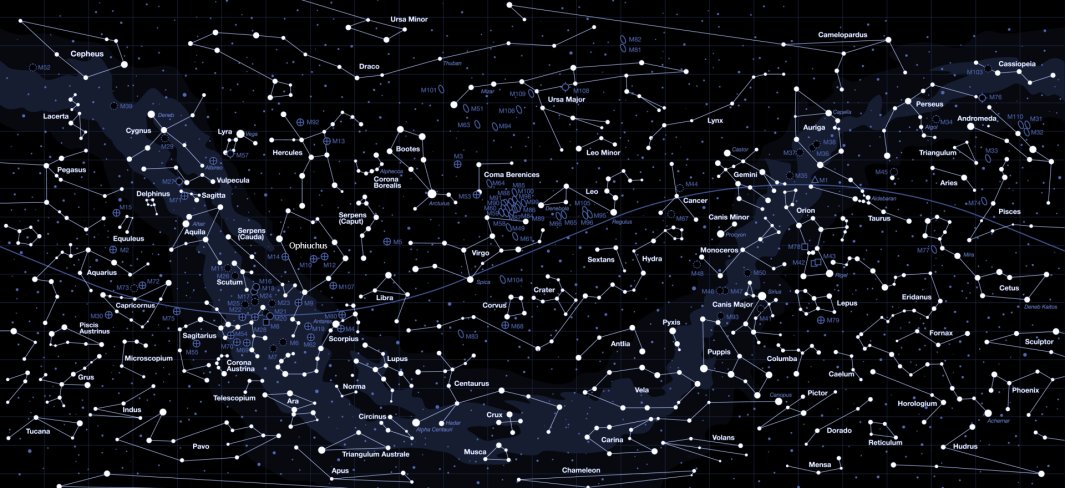
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Night Sky: A Guide to Tonight’s Constellations. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!