Mapping the Legacy: An Exploration of Mexico’s Indigenous Peoples
Related Articles: Mapping the Legacy: An Exploration of Mexico’s Indigenous Peoples
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Legacy: An Exploration of Mexico’s Indigenous Peoples. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Legacy: An Exploration of Mexico’s Indigenous Peoples
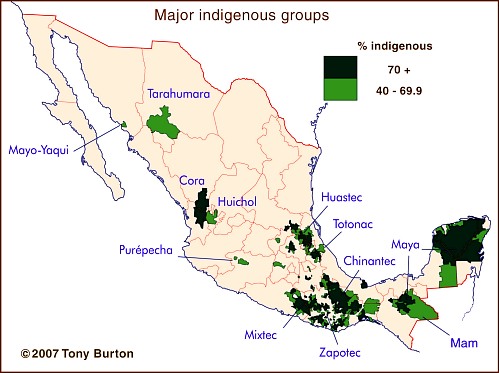
Mexico’s rich cultural tapestry is woven with the threads of its indigenous heritage. For centuries, diverse indigenous groups have inhabited the land, each with its own unique language, traditions, and cultural practices. Understanding the geographical distribution of these groups is crucial to appreciating the depth and complexity of Mexico’s history and present-day cultural landscape. A map depicting the locations of Mexican indigenous tribes serves as a visual guide, illuminating the legacy of these communities and their enduring presence in the country’s social fabric.
Historical Significance:
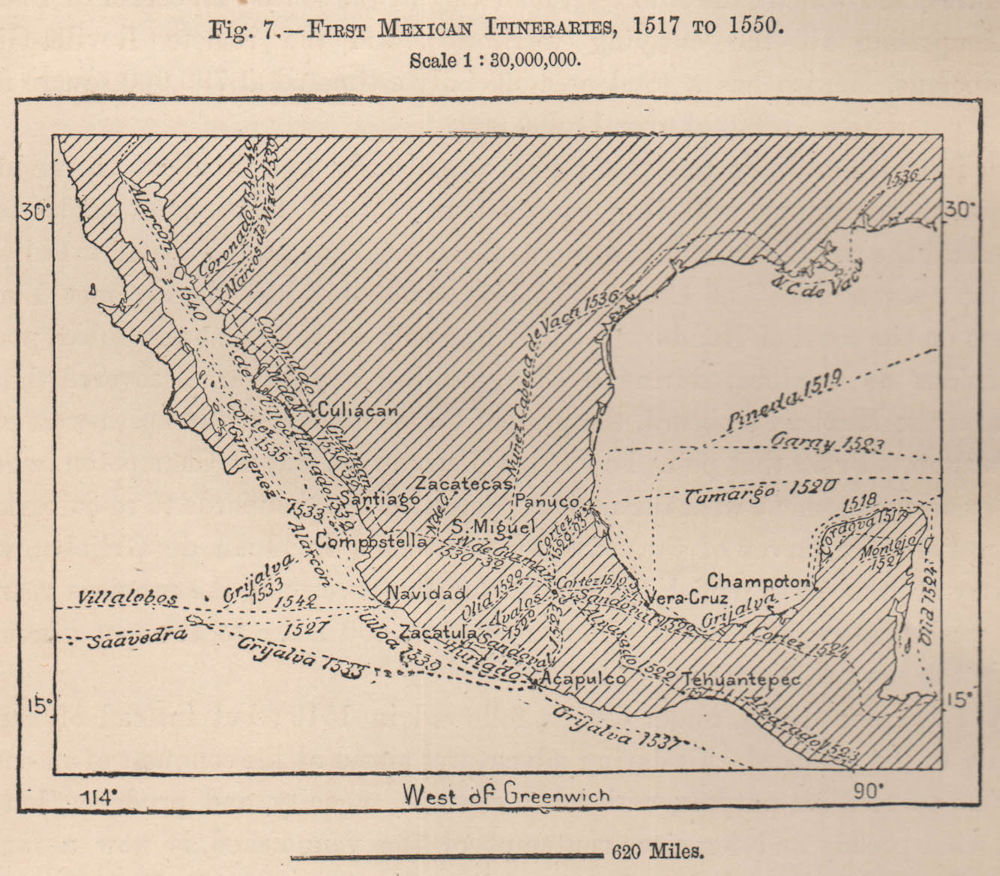
The map provides a tangible representation of the pre-Columbian era, showcasing the territorial divisions and cultural boundaries that existed before European colonization. It highlights the diverse linguistic families and cultural groups that flourished across the vast expanse of what is now Mexico. For instance, the map reveals the presence of the Aztec Empire in central Mexico, the Maya civilization in the Yucatan Peninsula, and the Zapotec and Mixtec cultures in Oaxaca. These distinct groups, with their unique languages, art forms, and social structures, contributed to the rich tapestry of Mexican indigenous history.
Understanding Present-Day Diversity:
While the map reflects the historical distribution of indigenous groups, it also offers insights into the present-day distribution of indigenous populations. Though the colonial period and subsequent waves of migration have significantly impacted the demographics, indigenous communities continue to thrive in various regions of Mexico. The map reveals the concentration of indigenous populations in specific areas, such as the states of Oaxaca, Chiapas, and Veracruz, where indigenous languages and cultural practices remain strong.
Cultural Preservation and Recognition:
The map serves as a powerful tool for cultural preservation and recognition. By visually representing the geographical distribution of indigenous groups, it underscores the importance of their unique identities and contributions to Mexican culture. It emphasizes the need for continued efforts to protect indigenous languages, traditions, and knowledge systems, ensuring their survival and transmission to future generations.
Educational Value:
The map serves as a valuable educational resource, offering a visual representation of the diverse indigenous communities of Mexico. It can be used in classrooms and museums to engage students and visitors in learning about the history, culture, and contributions of these communities. It provides a framework for understanding the complexities of Mexican history and the enduring influence of indigenous cultures on the present-day nation.
Policy and Advocacy:
The map serves as a valuable tool for policy makers and advocates working to improve the lives of indigenous communities. By highlighting the geographical distribution of these groups, it provides a visual representation of their specific needs and challenges. This information can be used to develop targeted programs and policies aimed at addressing issues such as poverty, lack of access to education and healthcare, and land rights.
Tourism and Cultural Exchange:
The map can be used to promote responsible tourism and cultural exchange. By highlighting the locations of indigenous communities and cultural sites, it encourages travelers to engage with the diverse cultural heritage of Mexico. It promotes respect and understanding for indigenous cultures and encourages sustainable tourism practices that benefit local communities.
Navigating the Map:
A comprehensive Mexican indigenous tribes map should include the following elements:
- Geographical Boundaries: Clearly defined state boundaries and regional divisions within Mexico.
- Indigenous Groups: Representation of the major indigenous groups, with their respective names and territories.
- Linguistic Families: Indication of the different linguistic families present in Mexico, with examples of languages spoken by each group.
- Cultural Sites: Identification of significant archaeological sites, traditional villages, and cultural centers associated with indigenous communities.
- Key Resources: Information on resources available for further research and engagement, such as online databases, cultural organizations, and government agencies.
Benefits of Using a Mexican Indigenous Tribes Map:
- Enhanced Understanding: The map provides a visual representation of the diversity and geographical distribution of indigenous communities in Mexico, fostering a deeper understanding of their history and cultural significance.
- Cultural Awareness: The map raises awareness about the importance of cultural preservation and the need to recognize the contributions of indigenous groups to Mexican society.
- Policy and Advocacy: The map serves as a valuable tool for policy makers and advocates working to address the needs of indigenous communities.
- Educational Resource: The map can be used in classrooms and museums to educate students and visitors about the rich indigenous heritage of Mexico.
- Tourism and Cultural Exchange: The map promotes responsible tourism and cultural exchange, encouraging travelers to engage with indigenous communities and their cultural traditions.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How many indigenous groups are there in Mexico?
There are over 60 recognized indigenous groups in Mexico, each with its own unique language, traditions, and cultural practices.
2. What are the major indigenous languages spoken in Mexico?
The major indigenous languages spoken in Mexico include Nahuatl, Maya, Zapotec, Mixtec, Otomí, and Tzotzil.
3. Where can I find a map of Mexican indigenous tribes?
There are several online resources and publications that provide maps of Mexican indigenous tribes. The National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) and the National Commission for the Development of Indigenous Peoples (CDI) are valuable sources.
4. What are some of the challenges faced by indigenous communities in Mexico?
Indigenous communities in Mexico face numerous challenges, including poverty, lack of access to education and healthcare, land rights disputes, and discrimination.
5. How can I support indigenous communities in Mexico?
You can support indigenous communities in Mexico by learning about their cultures and traditions, engaging with indigenous-owned businesses, and advocating for policies that promote their well-being.
Tips for Using a Mexican Indigenous Tribes Map:
- Explore the map thoroughly: Pay attention to the geographical distribution of different groups, their linguistic families, and cultural sites.
- Research specific groups: Use the map as a starting point to delve deeper into the history, culture, and traditions of particular indigenous groups.
- Engage with indigenous communities: Seek out opportunities to connect with indigenous communities, learn from their experiences, and support their efforts to preserve their cultural heritage.
- Share your knowledge: Educate others about the importance of indigenous cultures and the need to support their rights and well-being.
Conclusion:
A map of Mexican indigenous tribes serves as a powerful tool for understanding the rich cultural tapestry of the nation. It provides a visual representation of the diverse indigenous communities that have inhabited the land for centuries, highlighting their historical significance, present-day presence, and the importance of cultural preservation. By engaging with this map and learning about the stories and experiences of these communities, we can foster a deeper appreciation for the enduring legacy of indigenous cultures in Mexico.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Legacy: An Exploration of Mexico’s Indigenous Peoples. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!