Japan: A Nation at the Crossroads of East Asia
Related Articles: Japan: A Nation at the Crossroads of East Asia
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Japan: A Nation at the Crossroads of East Asia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Japan: A Nation at the Crossroads of East Asia

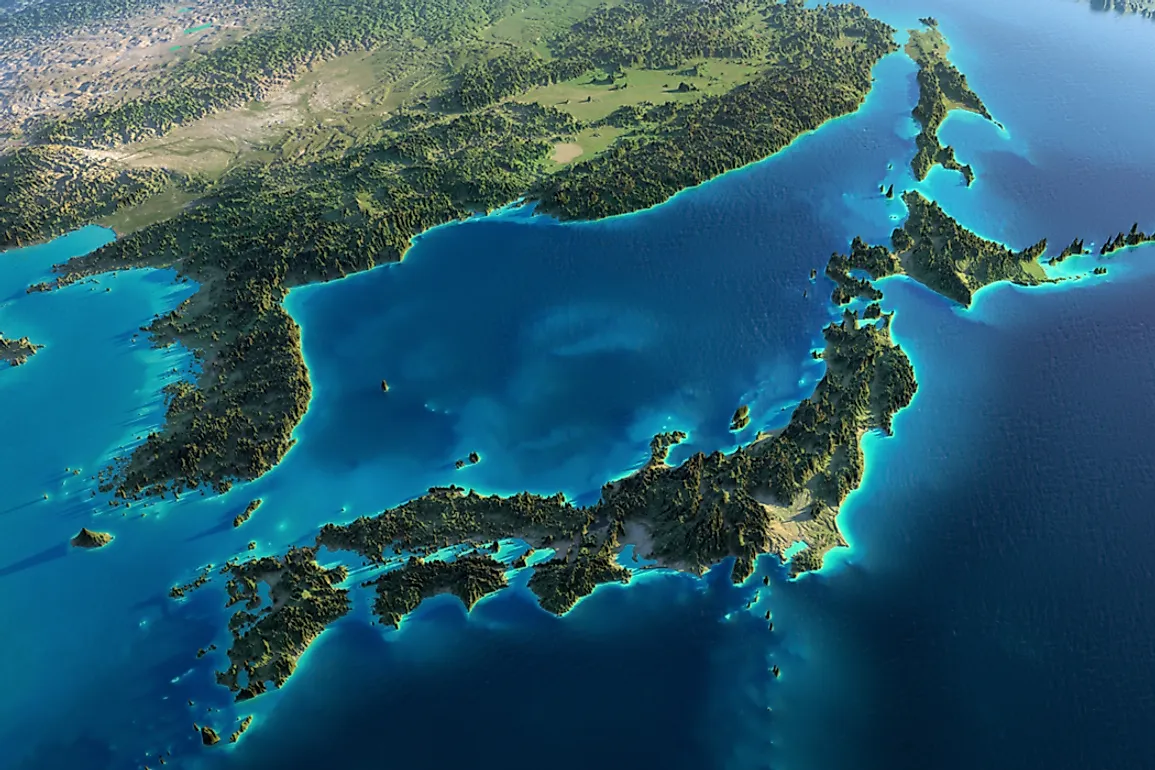
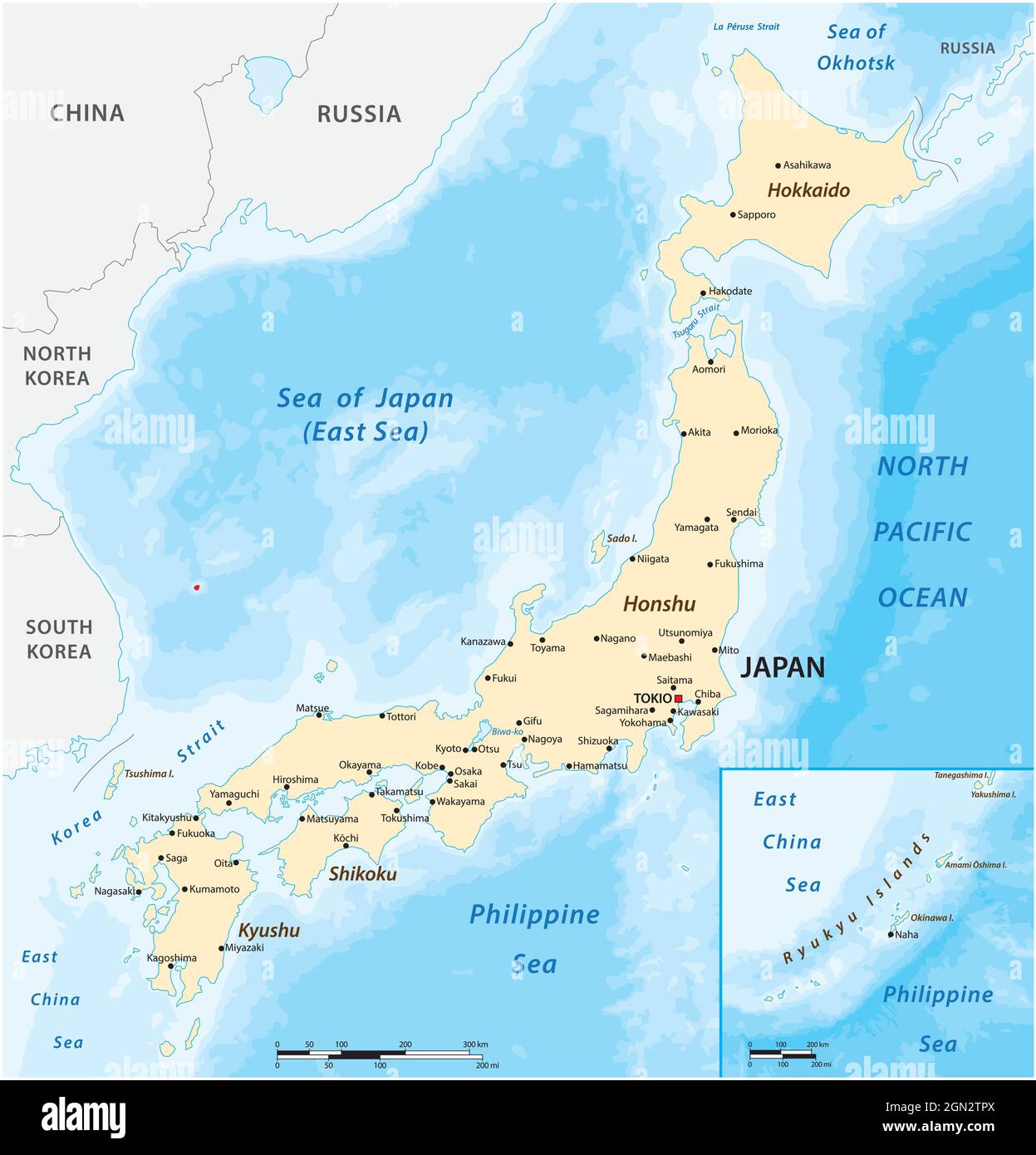
Japan, an archipelago nation located in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, holds a unique position on the Asian map. Composed of four main islands – Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu – and thousands of smaller islands, Japan’s geographical location has profoundly shaped its history, culture, and contemporary significance.
A Land of Contrast: Geography and Climate
Japan’s geography is characterized by striking contrasts. Mountain ranges, volcanic peaks, and fertile plains create a diverse landscape. Mount Fuji, a dormant volcano and Japan’s highest peak, is a symbol of the nation’s natural beauty and a testament to its geological dynamism. The country is also known for its abundant forests, which cover nearly 70% of its landmass.
Climate, too, exhibits diversity. The northern island of Hokkaido experiences cold winters and cool summers, while the southern islands enjoy subtropical climates with warm winters and hot, humid summers. This variation in climate contributes to the richness of Japan’s flora and fauna, encompassing a wide range of ecosystems from alpine meadows to lush rainforests.
A Crossroads of Cultures: Historical Significance
Japan’s geographical location has placed it at a crossroads of cultural influences. Throughout history, the nation has been a bridge between East Asia and the rest of the world. The Japanese archipelago’s proximity to the Korean Peninsula and the Chinese mainland facilitated cultural exchanges, resulting in the adoption of Confucianism, Buddhism, and other cultural practices.
Japan’s isolationist policies during the Edo period (1603-1868) allowed for the development of a unique and distinct culture. However, with the opening of the country to the West in the mid-19th century, Japan underwent a period of rapid modernization and industrialization. This transformation led to a blend of traditional and modern elements, solidifying Japan’s position as a cultural powerhouse.
A Global Powerhouse: Economic and Political Influence
Today, Japan stands as a major economic and political force in the Asia-Pacific region and the world. Its technological prowess, particularly in electronics and automobiles, has made it a global leader in manufacturing and innovation. Japan’s economic influence extends far beyond its borders, with strong trade relationships across the globe.
Politically, Japan plays a crucial role in regional security and diplomacy. As a member of the G7, the United Nations Security Council, and other international organizations, Japan actively participates in global affairs and advocates for peace and stability.
Japan’s Importance on the Asian Map: A Multifaceted Perspective
Japan’s significance on the Asian map is multifaceted. It is a cultural hub, a technological innovator, an economic powerhouse, and a crucial player in regional and global affairs. The country’s unique history, geography, and culture have shaped its role as a bridge between East Asia and the rest of the world.
FAQs: Understanding Japan’s Position
Q1: What are the major geographical features of Japan?
A: Japan is an archipelago nation with four main islands: Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu. The country is known for its mountainous terrain, volcanic peaks, fertile plains, and abundant forests.
Q2: What are the major cultural influences on Japan?
A: Japan has been influenced by cultures from China, Korea, and the West. Confucianism, Buddhism, and Shintoism are major religious influences. The country also boasts a rich artistic tradition, encompassing calligraphy, painting, ceramics, and theater.
Q3: What is Japan’s role in the global economy?
A: Japan is a major economic power, known for its technological prowess, particularly in electronics, automobiles, and robotics. It has strong trade relationships with countries across the globe.
Q4: How does Japan contribute to regional and global security?
A: Japan is a key player in regional and global security. It is a member of the G7 and the United Nations Security Council, and it actively participates in international efforts to promote peace and stability.
Tips for Understanding Japan’s Role on the Asian Map
- Explore Japan’s history: Understanding the nation’s historical development, from ancient times to the present, is crucial to grasping its contemporary significance.
- Engage with Japanese culture: Immerse yourself in Japan’s diverse cultural expressions, from traditional art forms to modern pop culture.
- Follow Japan’s economic and political developments: Stay informed about the country’s economic performance and its role in international affairs.
- Travel to Japan: Experiencing Japan firsthand offers valuable insights into its unique culture, geography, and people.
Conclusion: A Nation of Resilience and Innovation
Japan’s position on the Asian map is a testament to its resilience, adaptability, and innovation. The nation has overcome numerous challenges throughout its history, emerging as a global leader in technology, culture, and diplomacy. Its unique blend of tradition and modernity continues to shape its role in the world, making it a vital player in the Asia-Pacific region and beyond.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Japan: A Nation at the Crossroads of East Asia. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!