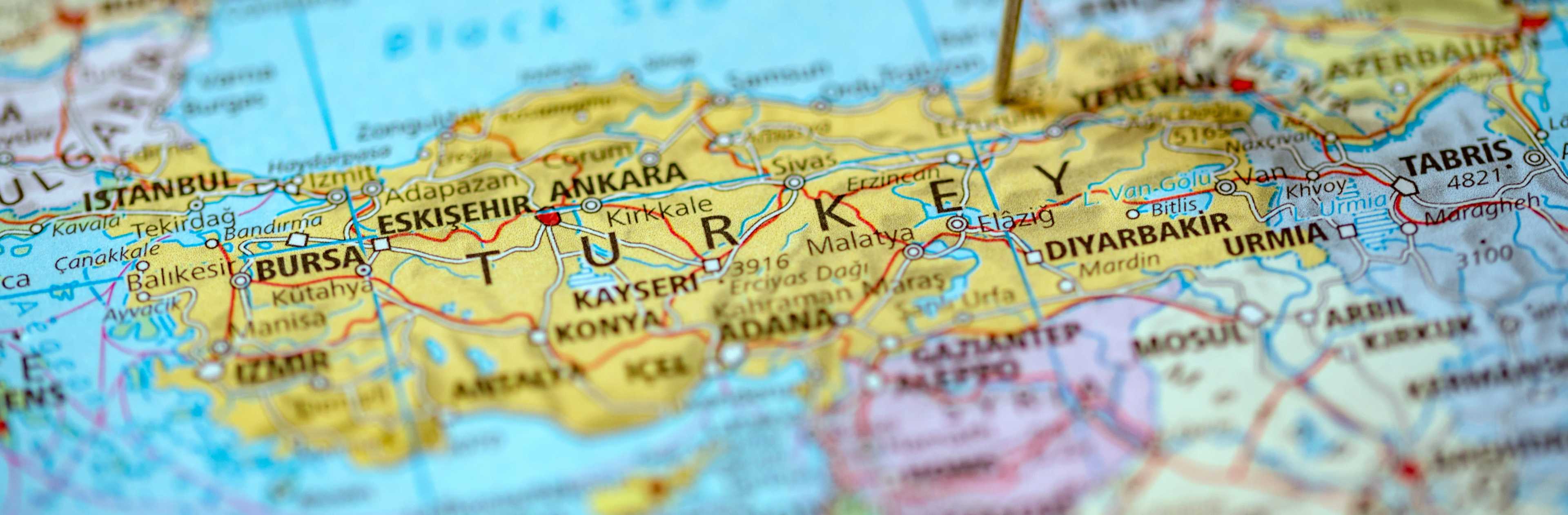
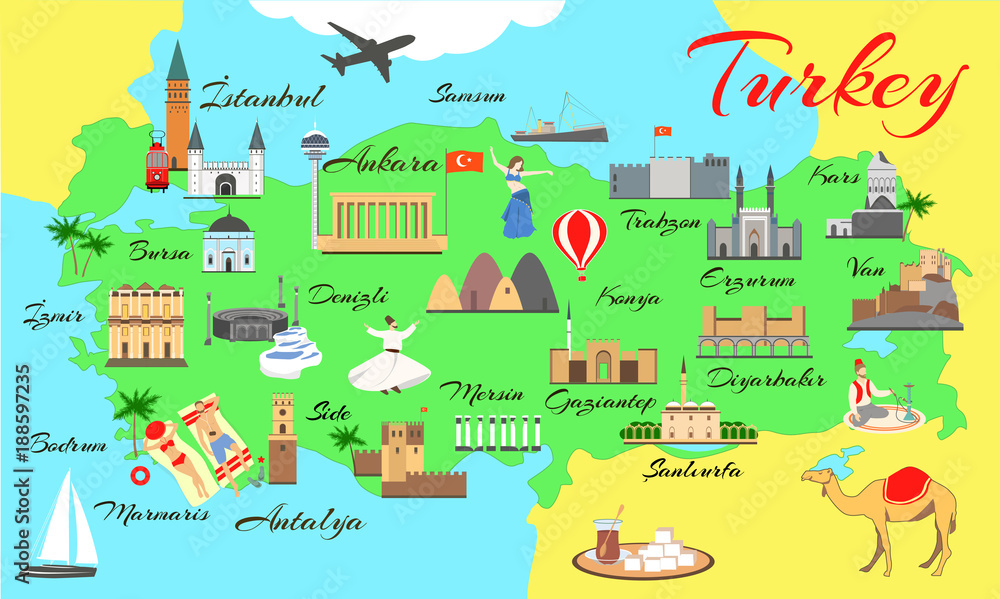
This comprehensive guide will explore the various aspects of the map of Turkey, including its regions, major cities, geographical features, and political boundaries. Whether you’re a student, a traveler, or simply curious about this fascinating country, this article will provide you with a detailed overview.
Geographical Overview of Turkey
Turkey boasts a diverse geography, ranging from coastal plains to rugged mountains, fertile valleys to semi-arid plateaus. Its location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia has shaped its climate, vegetation, and cultural landscape.
Key Geographical Features
-
Anatolian Peninsula: The major landmass of Turkey, also known as Asia Minor, is bordered by the Black Sea to the north, the Aegean Sea to the west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south.
-
Eastern Anatolia: Characterized by high mountains, plateaus, and river valleys. This region is home to Mount Ararat, the highest peak in Turkey.
-
Turkish Straits: The Bosphorus and Dardanelles straits connect the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara and the Aegean Sea, forming a crucial waterway for international trade.
-
Lakes and Rivers: Turkey has several significant lakes, including Lake Van, the largest lake in Turkey, and numerous rivers, such as the Tigris and Euphrates, which originate in the Eastern Anatolia region.
-
Coastal Regions: Turkey has a long coastline along the Black Sea, Aegean Sea, and Mediterranean Sea, featuring sandy beaches, rocky cliffs, and picturesque bays.
Regions of Turkey
-
Marmara Region: Located in the northwest, this region is home to Istanbul, Turkey’s largest city, and the Turkish Straits. It is a major industrial and commercial center.
-
Aegean Region: Situated along the Aegean coast, this region is known for its beautiful beaches, ancient ruins, and olive groves. Major cities include Izmir and Bodrum.
-
Mediterranean Region: Located along the Mediterranean coast, this region boasts a warm climate, sandy beaches, and historical sites. Antalya and Adana are prominent cities.
-
Black Sea Region: Situated along the Black Sea coast, this region is characterized by lush green mountains, tea plantations, and traditional villages. Trabzon and Rize are key cities.
-
Central Anatolia Region: Located in the heart of Turkey, this region features a semi-arid plateau, historical sites, and agricultural lands. Ankara, the capital city, is located here.
-
Eastern Anatolia Region: The largest and most mountainous region, known for its rugged landscapes, high peaks, and historical significance. Erzurum and Van are major cities.
-
Southeastern Anatolia Region: Located in the southeast, this region is characterized by its fertile plains, historical cities, and cultural diversity. Gaziantep and Şanlıurfa are important centers.
Major Cities on the Map of Turkey
-
Istanbul: A transcontinental city straddling Europe and Asia, Istanbul is a historical and cultural hub, known for its iconic landmarks such as the Hagia Sophia, Blue Mosque, and Grand Bazaar.
-
Ankara: The capital city of Turkey, Ankara is a modern metropolis with historical sites, museums, and government buildings.
-
Izmir: Located on the Aegean coast, Izmir is a bustling port city with a rich history, beautiful beaches, and a vibrant cultural scene.
-
Bursa: Situated near the Marmara Sea, Bursa is a historical city known for its Ottoman-era mosques, thermal baths, and ski resorts.
-
Adana: Located in the southern part of Turkey, Adana is a major agricultural and industrial center with a rich culinary heritage.
-
Gaziantep: Situated in the southeast, Gaziantep is famous for its delicious cuisine, historical sites, and industrial production.
-
Konya: Located in Central Anatolia, Konya is known for its Seljuk-era architecture, Sufi traditions, and religious significance.
Political Map of Turkey
The political map of Turkey consists of 81 provinces (iller). Each province is administered by a governor appointed by the central government. Provinces are further divided into districts (ilçeler). Understanding this administrative division helps in navigating the country and understanding its governance.
Key Provinces and Their Capitals
-
Istanbul Province: Capital – Istanbul
-
Ankara Province: Capital – Ankara
-
Izmir Province: Capital – Izmir
-
Antalya Province: Capital – Antalya
-
Bursa Province: Capital – Bursa
Understanding Turkey’s Borders
-
Greece and Bulgaria: Located to the west, these European countries share land borders with Turkey in the Thracian region.
-
Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan (Nakhchivan exclave): Situated to the northeast, these countries share borders with Turkey in the Caucasus region.
-
Iran: Located to the east, Iran shares a long border with Turkey, influencing its cultural and historical landscape.
-
Iraq and Syria: Situated to the southeast, these countries share borders with Turkey in the Middle East, impacting its geopolitical dynamics.
Topography and Climate
Turkey’s diverse topography influences its climate. Coastal regions enjoy a Mediterranean climate with hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. The Black Sea region has a temperate climate with rainfall throughout the year. Central Anatolia experiences a continental climate with hot, dry summers and cold, snowy winters. Eastern Anatolia has a harsh continental climate with long, cold winters and short, cool summers.
Climate Zones
-
Mediterranean Climate: Hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters along the Aegean and Mediterranean coasts.
-
Temperate Oceanic Climate: Mild temperatures and rainfall throughout the year along the Black Sea coast.
-
Continental Climate: Hot, dry summers and cold, snowy winters in Central and Eastern Anatolia.
Natural Resources
-
Minerals: Chromium, iron ore, copper, bauxite, and coal.
-
Energy Resources: Natural gas, petroleum, and hydroelectric power.
-
Agricultural Resources: Fertile lands suitable for growing crops such as wheat, barley, cotton, and fruits.
Why Study the Map of Turkey?
-
Understanding Geography: It provides insights into the country’s diverse landscapes, regions, and geographical features.
-
Historical Context: It helps understand the historical significance of Turkey as a bridge between Europe and Asia.
-
Cultural Appreciation: It fosters an appreciation for the cultural diversity of Turkey, influenced by its geographical location and historical interactions.
-
Travel Planning: It assists in planning trips, exploring different regions, and discovering hidden gems.
-
Geopolitical Awareness: It enhances awareness of Turkey’s strategic importance in the region and its role in international relations.
People Also Ask (PAA) about the Map of Turkey
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in Turkey?
A: Turkey has several prominent mountain ranges, including the Taurus Mountains in the south, the Pontic Mountains along the Black Sea coast, and Mount Ararat in the east.
Q: What are the main rivers in Turkey?
A: The main rivers in Turkey include the Tigris, Euphrates, Kızılırmak (Red River), and Gediz River.
Q: How many regions are there in Turkey?
A: Turkey is divided into seven geographical regions: Marmara, Aegean, Mediterranean, Black Sea, Central Anatolia, Eastern Anatolia, and Southeastern Anatolia.
Q: What is the largest lake in Turkey?
A: The largest lake in Turkey is Lake Van, located in the Eastern Anatolia region.
Q: Which countries border Turkey?
A: Turkey shares borders with Greece, Bulgaria, Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan (Nakhchivan exclave), Iran, Iraq, and Syria.
Conclusion
The map of Turkey is a window into a country of incredible diversity and strategic importance. From its bustling cities to its rugged mountains, fertile plains to stunning coastlines, Turkey offers a wealth of geographical, historical, and cultural treasures. Understanding the map of Turkey is key to appreciating its unique position in the world and its rich tapestry of landscapes and cultures. Whether you’re planning a trip, studying its history, or simply curious about this transcontinental nation, the map of Turkey is an invaluable tool for exploration and discovery.