Delving into the Depths: Understanding Ocean Trench Maps
Related Articles: Delving into the Depths: Understanding Ocean Trench Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Depths: Understanding Ocean Trench Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Depths: Understanding Ocean Trench Maps
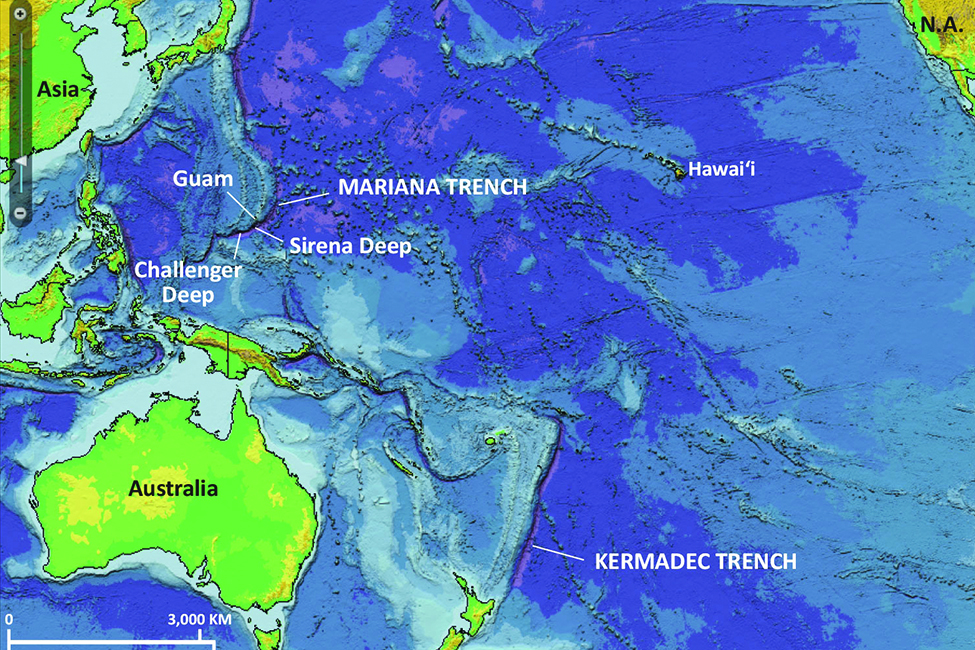
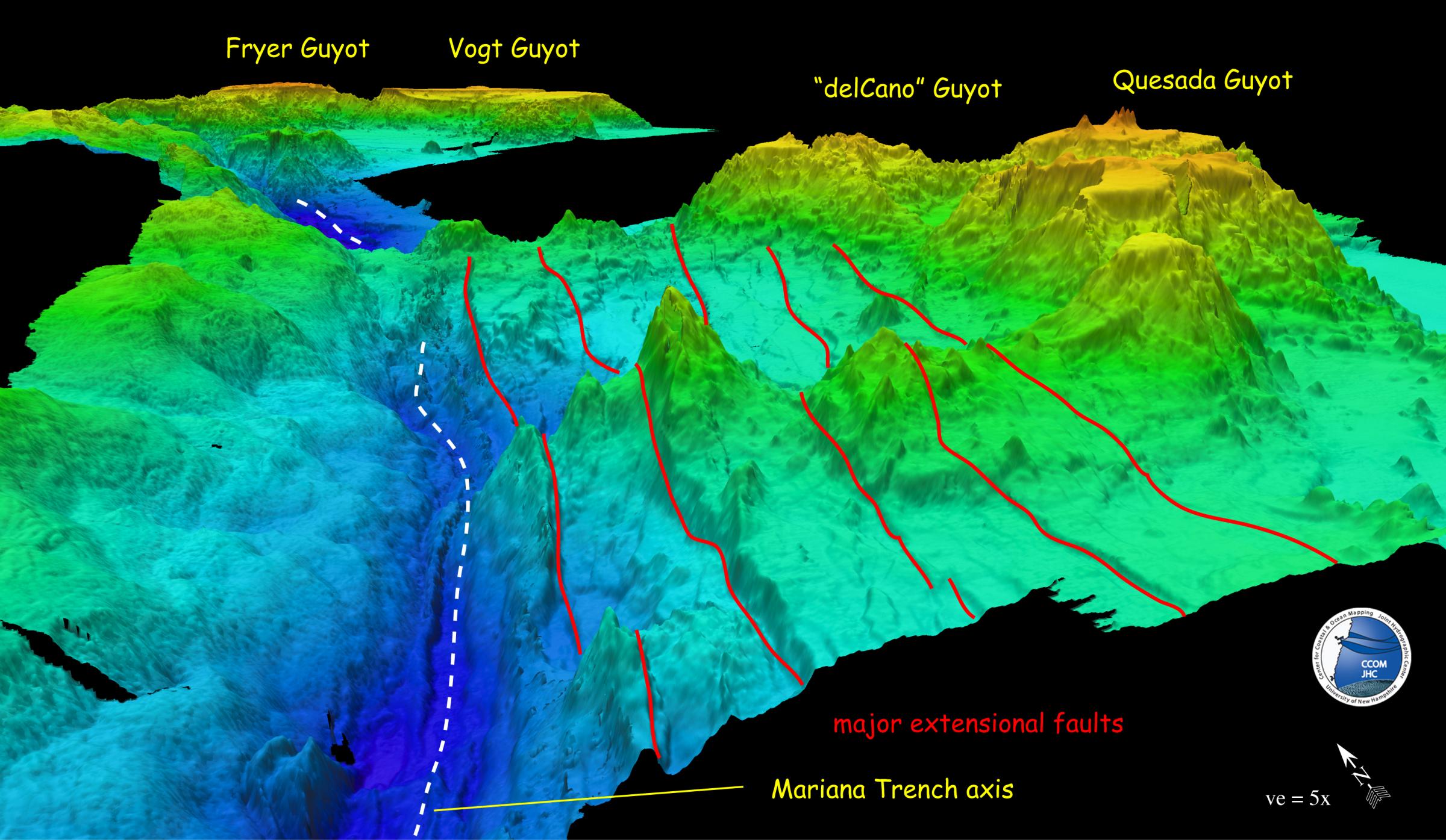
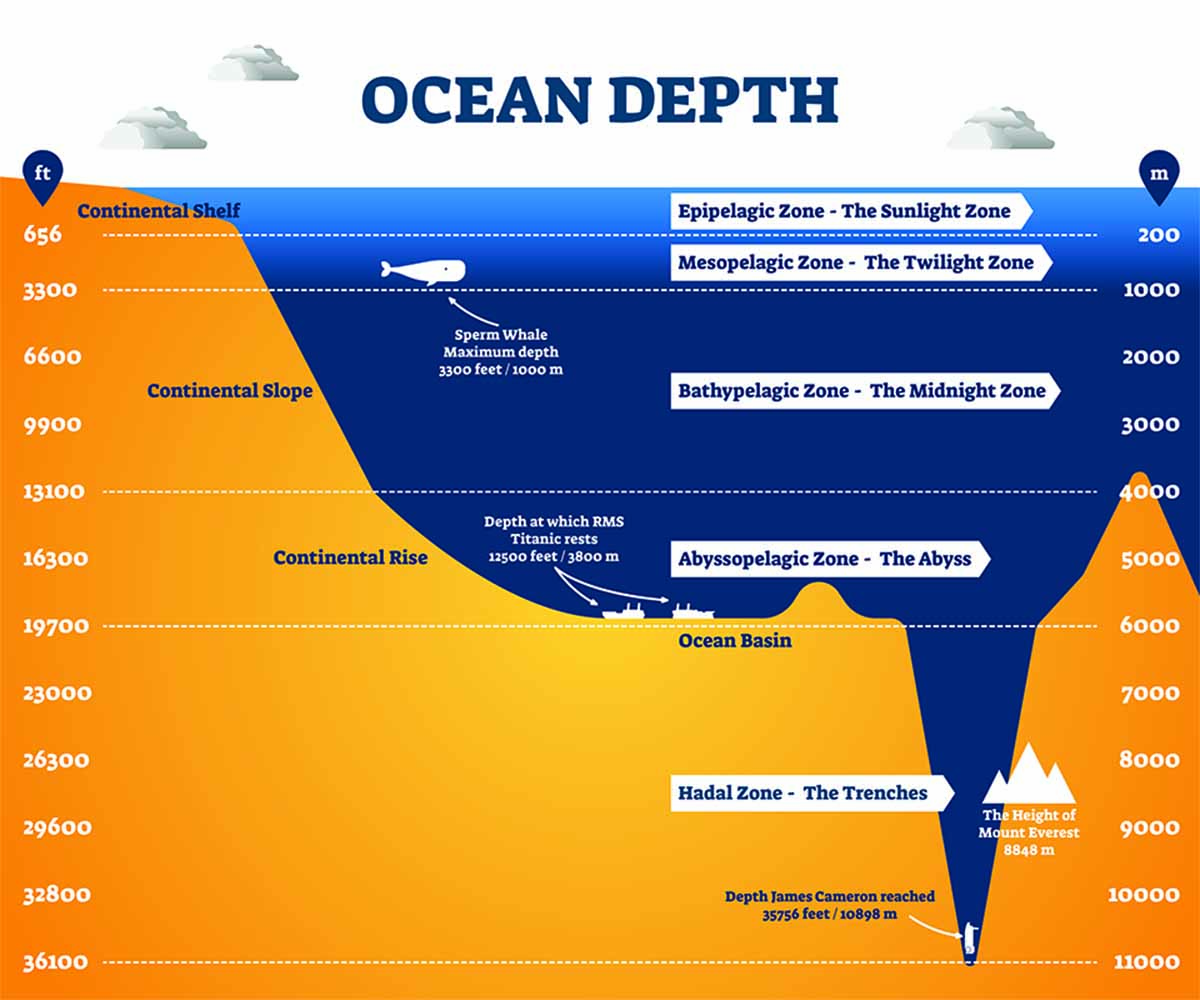
The Earth’s surface is not a smooth, uniform expanse. Beneath the vast, blue expanse of the oceans lie immense, enigmatic valleys known as ocean trenches. These deep, narrow depressions in the seafloor are among the most fascinating and least explored regions of our planet. Ocean trench maps, meticulously crafted representations of these subterranean canyons, serve as crucial tools for understanding the Earth’s dynamic geological processes, revealing hidden secrets of our planet’s history and offering insights into the biodiversity that thrives in these extreme environments.
Unveiling the Depths: A Visual Journey into the Abyss
Ocean trench maps are not merely static depictions of the ocean floor. They are dynamic representations, showcasing the intricate topography of these underwater canyons. These maps utilize various data sources, including sonar readings, satellite imagery, and submersible explorations, to create detailed representations of the trenches’ shape, depth, and geological features.
The Importance of Ocean Trench Maps
Understanding ocean trenches is critical for several reasons:
-
Geological Insights: Ocean trenches are the result of plate tectonics, the slow but powerful movement of the Earth’s lithospheric plates. The formation of trenches occurs at convergent plate boundaries, where one plate slides beneath another in a process called subduction. Ocean trench maps provide crucial data for understanding the dynamics of these processes, helping scientists unravel the complex interplay of forces that shape our planet.
-
Exploring the Unknown: Ocean trenches are home to a unique and diverse ecosystem, hosting a wide range of organisms adapted to survive in extreme conditions of pressure, darkness, and cold. Ocean trench maps guide exploration efforts, enabling scientists to locate and study these fascinating creatures, shedding light on the evolution of life in extreme environments.
-
Understanding Climate Change: Ocean trenches play a vital role in global carbon cycling. They act as significant carbon sinks, absorbing large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Ocean trench maps help scientists understand the role of these trenches in regulating climate change and the potential impact of rising temperatures on these delicate ecosystems.
-
Resource Exploration: Ocean trenches may hold untapped mineral resources. Ocean trench maps help identify potential sites for resource exploration, providing valuable information for sustainable resource management and economic development.
-
Natural Hazard Assessment: Subduction zones, where ocean trenches form, are often associated with earthquakes and tsunamis. Ocean trench maps provide essential data for understanding the risk of these natural hazards, enabling the development of early warning systems and disaster preparedness strategies.
A Glimpse into the Abyss: Notable Ocean Trenches
Ocean trench maps reveal a world of immense depths and remarkable diversity. Some of the most notable trenches include:
-
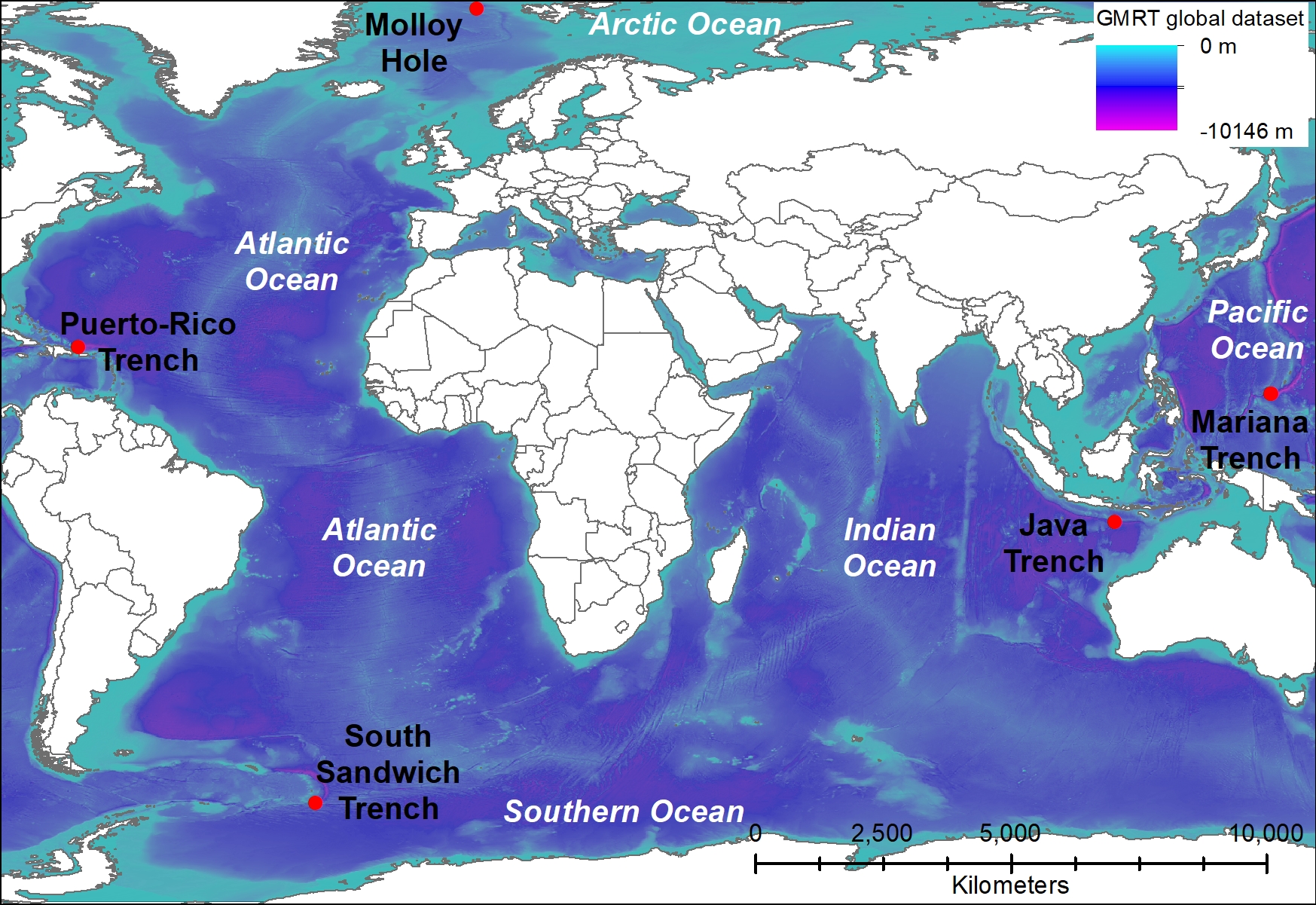
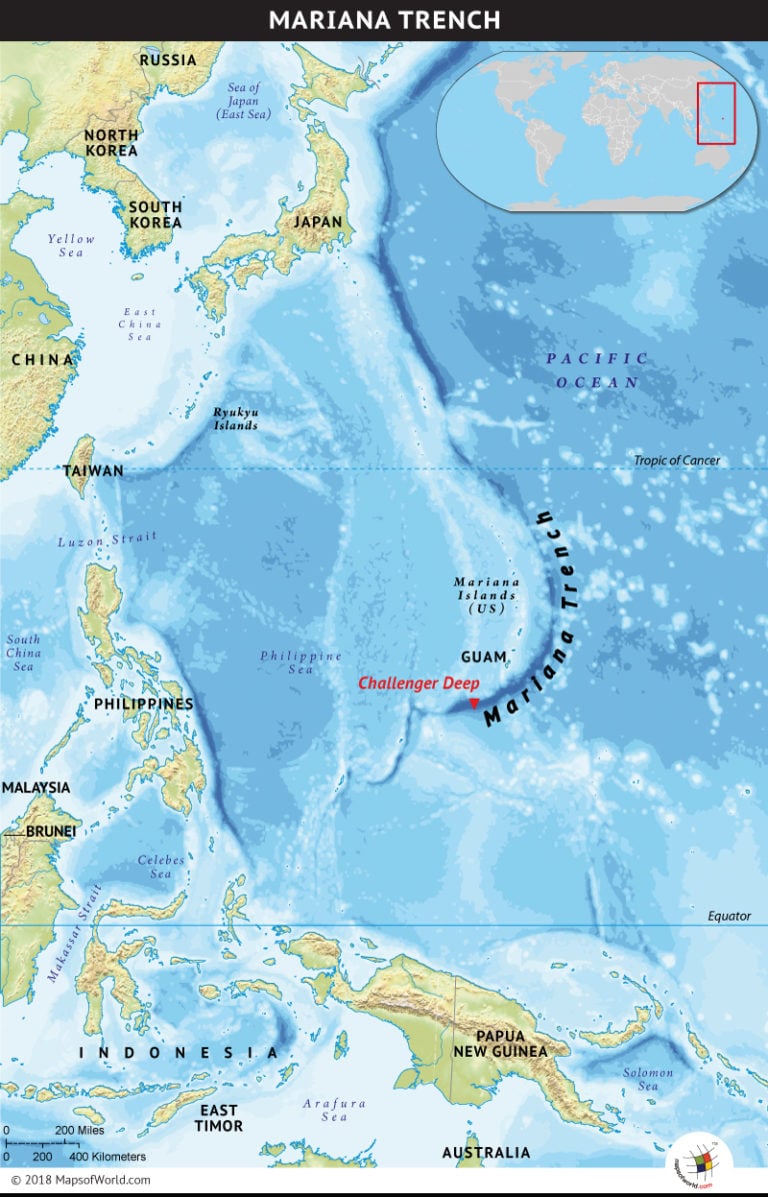
The Mariana Trench: The deepest known point on Earth, reaching a depth of over 10,900 meters (35,760 feet), the Mariana Trench is a testament to the immense forces at play within our planet.
-
The Peru-Chile Trench: Stretching over 5,900 kilometers (3,660 miles) along the western coast of South America, the Peru-Chile Trench is a prime example of a subduction zone, responsible for the formation of the Andes mountain range.
-
The Japan Trench: This trench, located off the coast of Japan, is a major source of seismic activity, responsible for devastating earthquakes and tsunamis.
-
The Tonga Trench: Known for its remarkable depth and diverse marine life, the Tonga Trench is one of the deepest trenches in the Pacific Ocean.
-
The Puerto Rico Trench: The deepest point in the Atlantic Ocean, the Puerto Rico Trench is a vital area for understanding the tectonic activity in the Caribbean region.
FAQs about Ocean Trench Maps
1. How are ocean trench maps created?
Ocean trench maps are created using a combination of data sources, including:
-
Sonar mapping: This technique utilizes sound waves to map the seafloor. Sound waves are emitted from a vessel and travel through the water, bouncing off the seafloor and returning to the vessel. The time it takes for the sound waves to return is used to calculate the depth of the seafloor.
-
Satellite altimetry: Satellites measure the height of the ocean surface, which can be used to infer the shape of the seafloor. Areas with deeper water exert a weaker gravitational pull on the ocean surface, causing it to be slightly lower.
-
Submersible exploration: Submersibles, manned or unmanned underwater vehicles, can directly explore the ocean floor, capturing images and collecting data about the geology and biology of trenches.
2. What are the benefits of using ocean trench maps?
Ocean trench maps offer numerous benefits, including:
-
Understanding geological processes: Maps provide valuable data for understanding plate tectonics, subduction zones, and the formation of trenches.
-
Exploring marine biodiversity: Maps guide research efforts to study the unique and diverse life forms found in these extreme environments.
-
Assessing natural hazards: Maps help identify areas prone to earthquakes, tsunamis, and other natural hazards, aiding in disaster preparedness.
-
Managing resources: Maps assist in identifying potential sites for mineral resource exploration and promoting sustainable resource management.
3. What are some of the challenges associated with mapping ocean trenches?
Mapping ocean trenches poses several challenges:
-
Vastness of the ocean: The ocean is incredibly vast and deep, making it challenging to map the entire seafloor.
-
Technological limitations: Current sonar technology has limitations in penetrating sediment layers and accurately mapping the seafloor in areas with complex topography.
-
Cost and time: Mapping ocean trenches is a time-consuming and expensive endeavor, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
Tips for Using Ocean Trench Maps
-
Consider the scale: Ocean trench maps are available at various scales. Choosing the appropriate scale for your needs is crucial for understanding the details of the map.
-
Analyze the data sources: Pay attention to the data sources used to create the map, as this can affect the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
-
Interpret the map context: Consider the geological and geographical context of the map to gain a deeper understanding of the features depicted.
-
Utilize additional resources: Combine ocean trench maps with other data sources, such as geological surveys, oceanographic studies, and biological data, to create a more comprehensive picture of the area.
Conclusion
Ocean trench maps are essential tools for exploring and understanding the Earth’s hidden depths. They provide valuable insights into the dynamic processes that shape our planet, reveal the diversity of life in extreme environments, and offer critical information for managing resources and mitigating natural hazards. As technology advances and exploration efforts continue, ocean trench maps will undoubtedly play an increasingly important role in unraveling the mysteries of our planet’s hidden depths.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Depths: Understanding Ocean Trench Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!