Decoding the Landscape: Understanding Plant Hardiness Zones
Related Articles: Decoding the Landscape: Understanding Plant Hardiness Zones
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Decoding the Landscape: Understanding Plant Hardiness Zones. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Decoding the Landscape: Understanding Plant Hardiness Zones
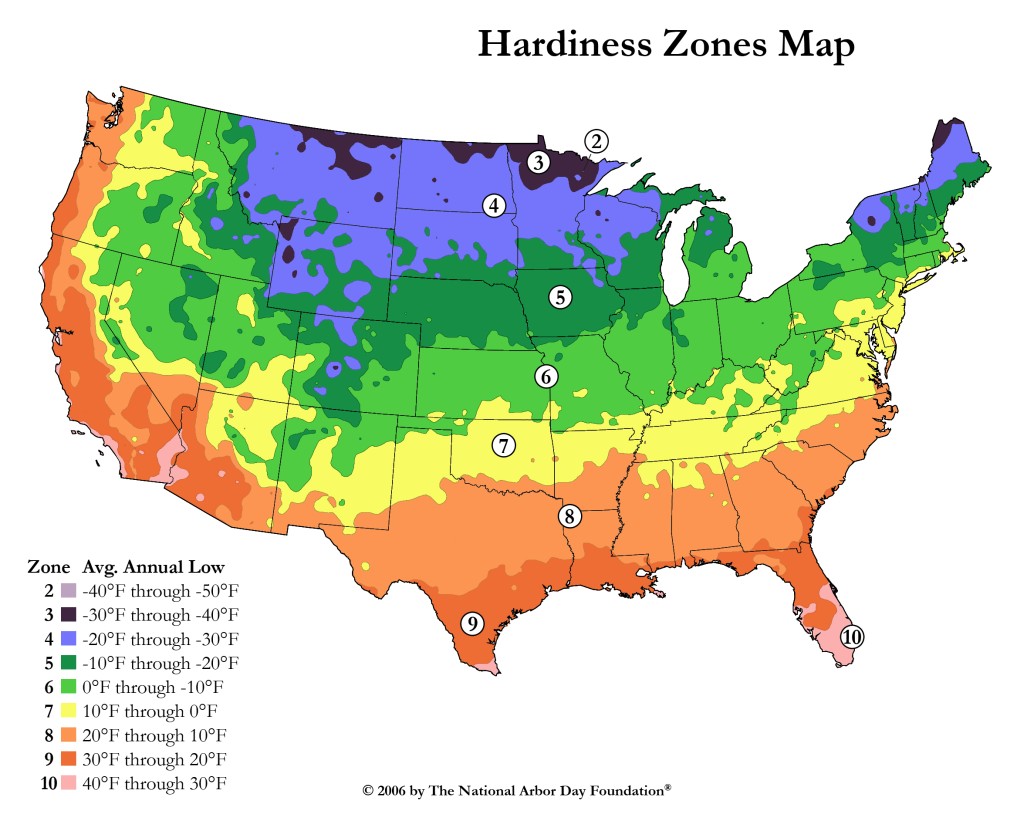
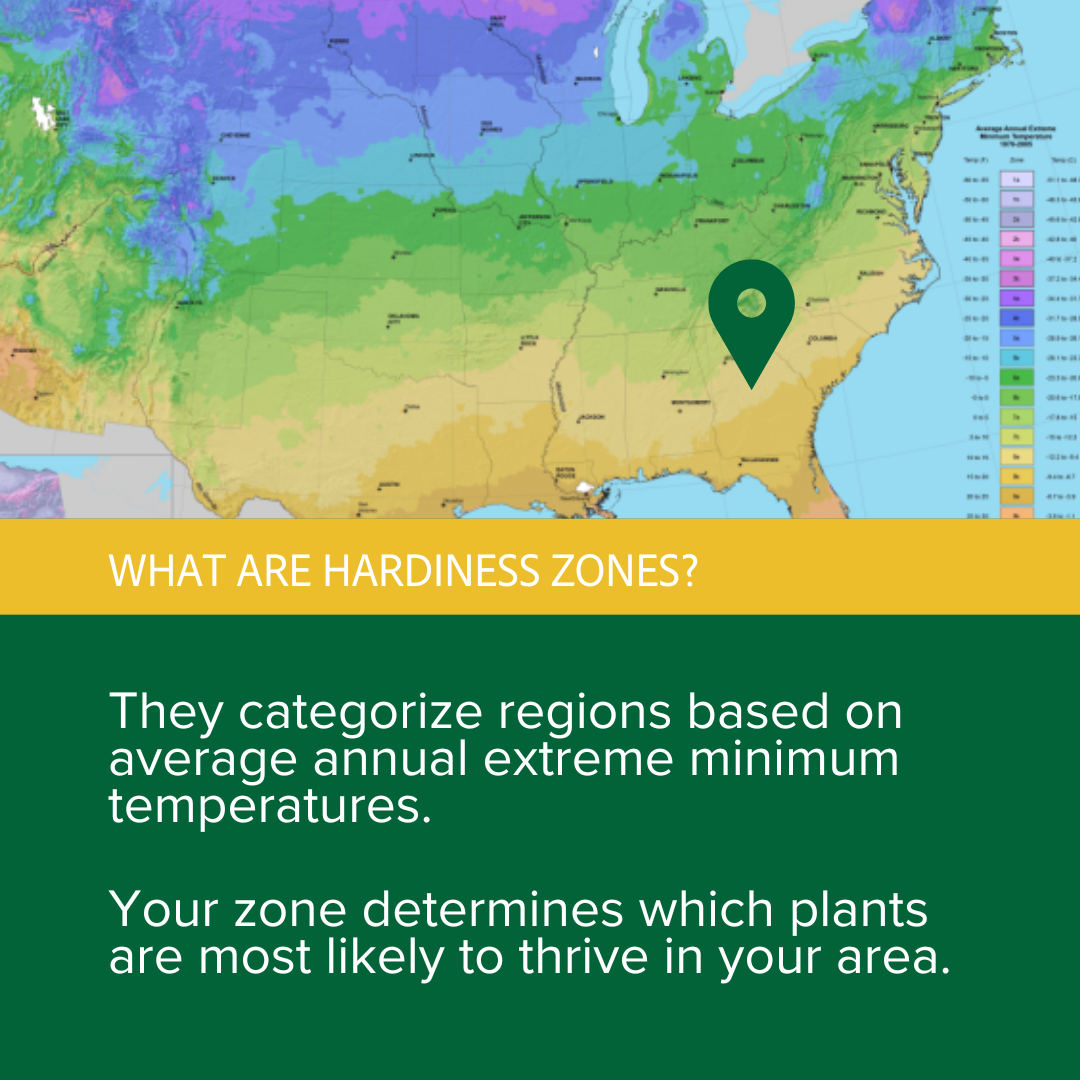
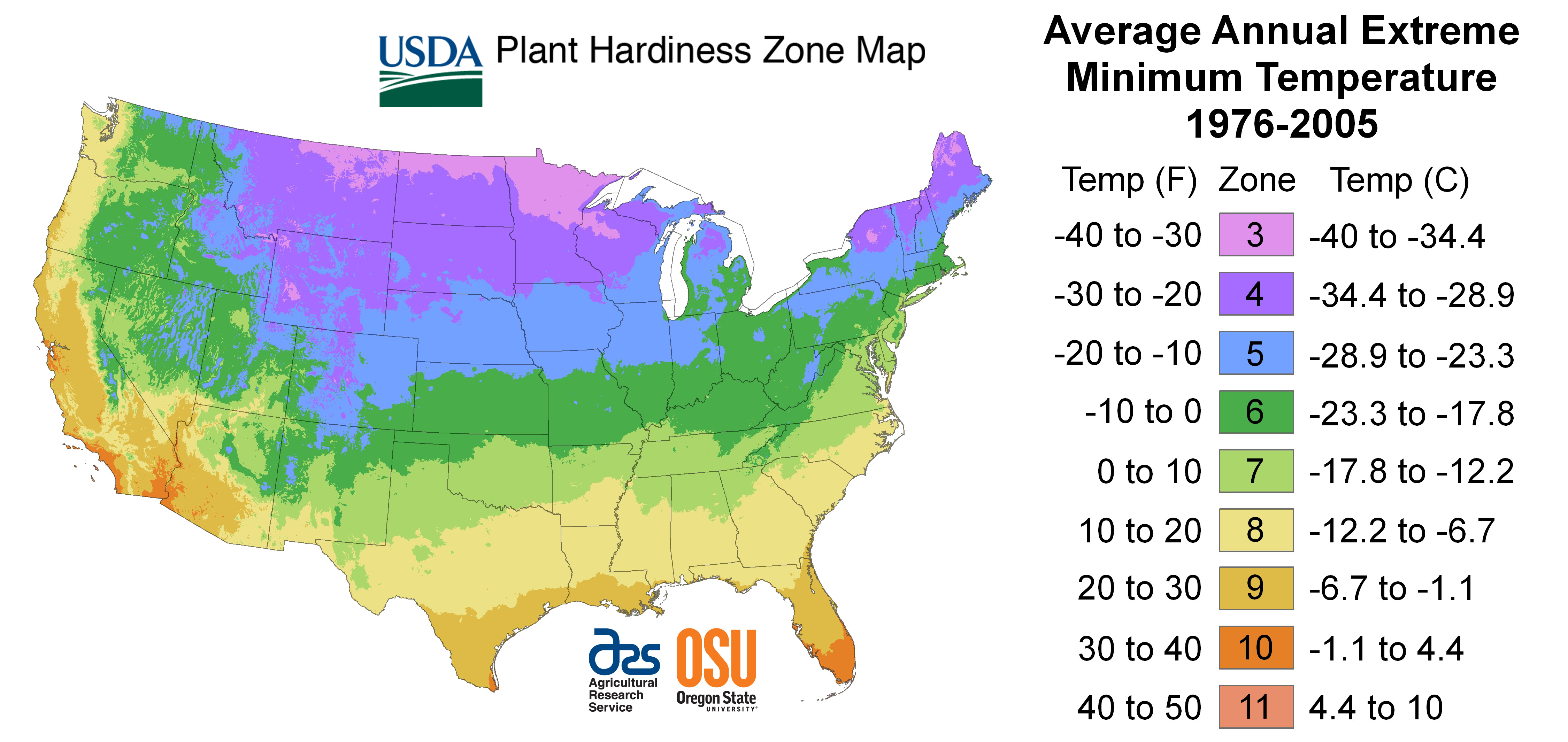
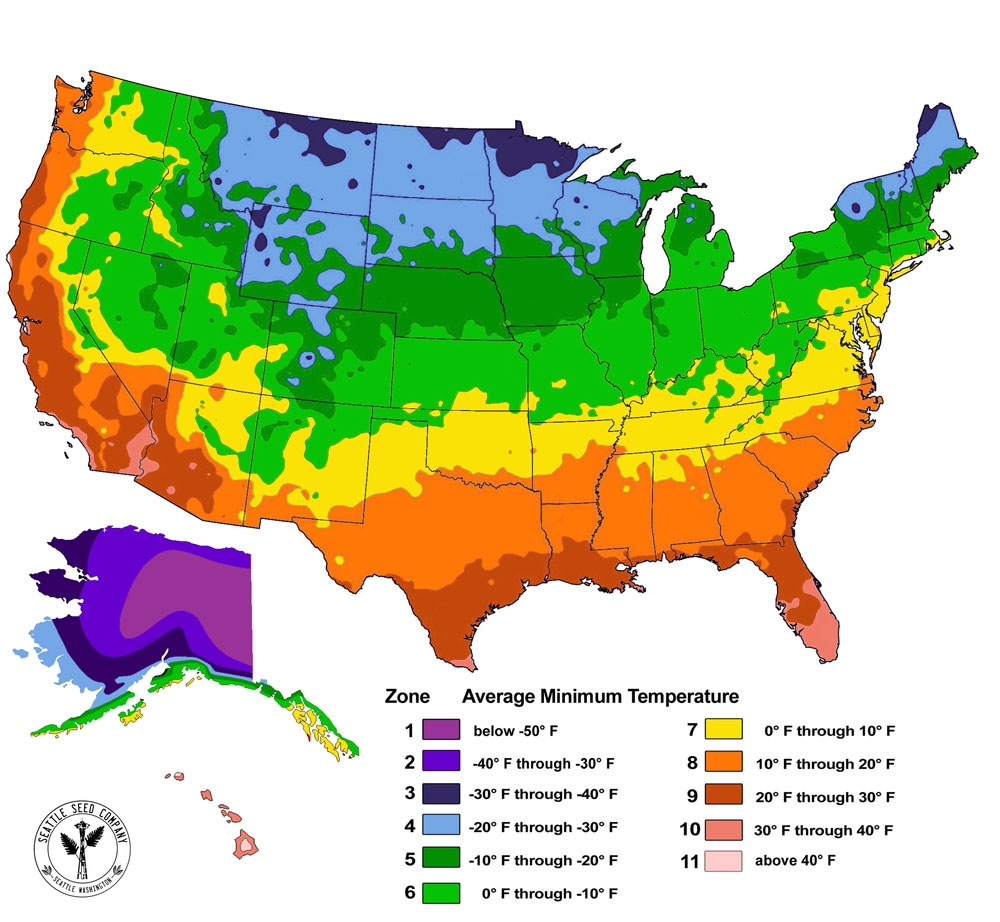
The world’s diverse climates create a mosaic of environments, each with unique conditions that influence plant growth. To navigate this complex tapestry, gardeners and horticulturists rely on a powerful tool: the plant hardiness zone map. This map, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), divides North America into zones based on average minimum winter temperatures. Each zone represents a range of temperatures that plants can tolerate, offering crucial information for successful gardening.
A Framework for Success: Understanding Plant Hardiness Zones
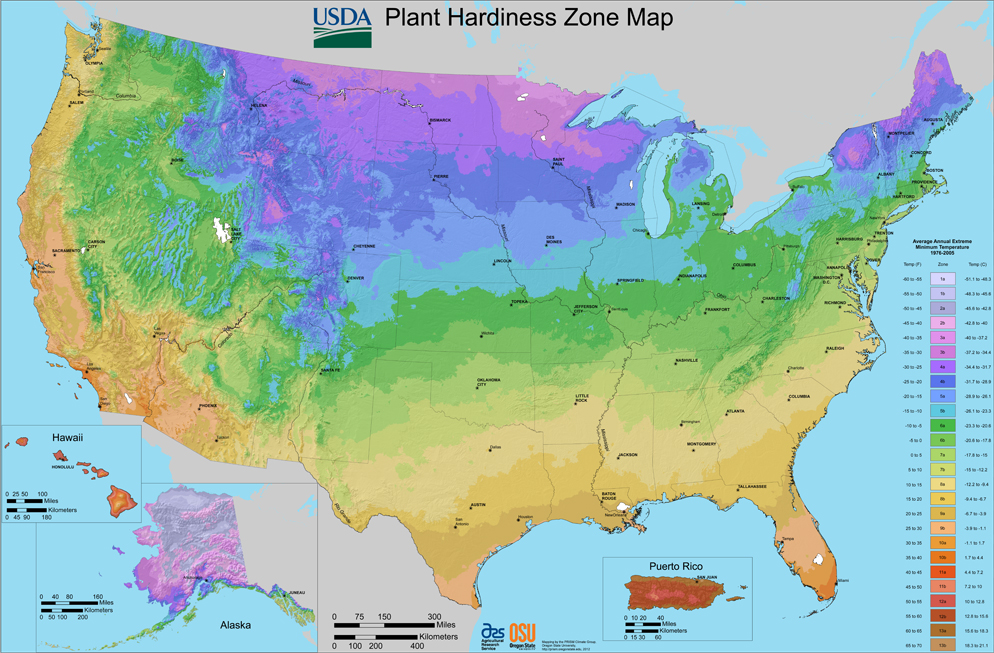
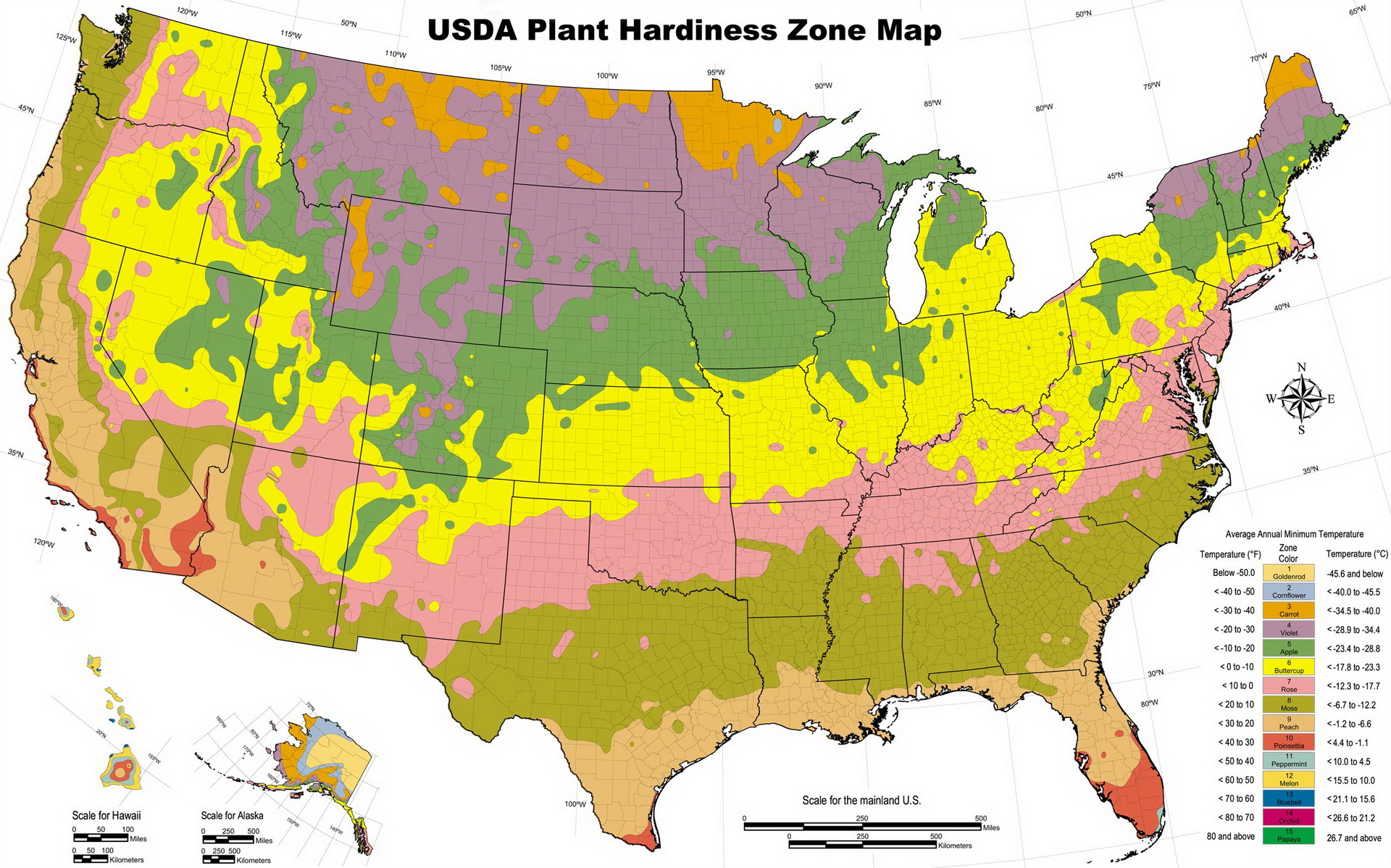
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable resource for gardeners, landscape architects, and plant enthusiasts. It provides a standardized system for understanding the climatic conditions suitable for different plant species. Each zone is defined by a number, ranging from Zone 1, the coldest, to Zone 13, the warmest. Within each zone, the average minimum winter temperature falls within a specific range. For example, Zone 5 encompasses areas with average minimum winter temperatures between -20°F and -10°F.
Beyond Temperature: Factors Influencing Plant Hardiness
While the USDA map focuses on average minimum winter temperatures, other factors also influence plant hardiness. These include:
- Microclimates: Localized variations in temperature, humidity, and wind patterns can significantly affect plant growth. For instance, a south-facing slope might experience warmer temperatures than a shaded area, creating a microclimate suitable for plants requiring warmer conditions.
- Soil Type and Drainage: Soil composition and drainage influence water retention and nutrient availability, impacting plant growth. For example, well-drained sandy soil might support plants that thrive in drier conditions, while clay soils retain moisture, favoring plants adapted to wetter environments.
- Elevation and Latitude: Altitude and distance from the equator influence temperature and sunlight exposure. Higher elevations and northern latitudes tend to experience colder temperatures and shorter growing seasons.
- Precipitation: Rainfall patterns influence plant growth and water availability. Regions with abundant rainfall may support lush vegetation, while arid areas require plants adapted to drought conditions.
Navigating the Map: Choosing Plants for Your Zone
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides a starting point for selecting plants suitable for your location. By identifying your zone, you can narrow down your choices to species that can withstand the local climate. However, it is crucial to consider other factors, such as:
- Sunlight Exposure: Plants require varying amounts of sunlight. Some thrive in full sun, while others prefer shade. Understanding your site’s sunlight exposure is crucial for choosing appropriate plants.
- Soil Conditions: Different plants have specific soil requirements. Consider your soil’s pH, texture, and drainage to select plants that will flourish in your garden.
- Plant Size and Growth Habit: Ensure that the chosen plants will fit comfortably in their designated space and won’t outgrow their surroundings.
Beyond the Map: Utilizing Additional Resources
While the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides a valuable framework, it is not a definitive guide. Several additional resources can help you refine your plant selection:
- Local Botanical Gardens and Nurseries: Local experts can provide insights into plants that perform well in your specific region.
- Online Plant Databases: Websites dedicated to plant information offer detailed descriptions, including hardiness zones, growing conditions, and care requirements.
- Regional Horticultural Societies: These organizations offer valuable resources, including plant lists, gardening tips, and community forums for sharing knowledge.
FAQs About Plant Hardiness Zones
Q: Can I grow plants outside their designated zone?
A: While it is generally recommended to choose plants within your hardiness zone, it is possible to grow plants outside their designated range. However, it requires careful planning and additional care. For example, providing winter protection, such as mulch or burlap wraps, can help plants survive colder temperatures.
Q: How often is the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map updated?
A: The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is updated periodically to reflect changes in climate patterns. The most recent update was in 2012.
Q: What is the difference between a hardiness zone and a growing zone?
A: A hardiness zone focuses on the minimum winter temperatures a plant can tolerate, while a growing zone considers the length of the growing season. The growing season is the period between the last frost in spring and the first frost in autumn.
Q: How can I determine my microclimate?
A: Observing your garden throughout the year can help you understand your microclimate. Consider factors such as sunlight exposure, wind patterns, and soil drainage. You can also consult with local gardening experts or use online tools to assess your microclimate.
Tips for Utilizing Plant Hardiness Zones
- Start with a Plan: Before selecting plants, identify your hardiness zone and consider your site’s specific conditions, such as sunlight exposure, soil type, and drainage.
- Consult with Experts: Seek advice from local garden centers, nurseries, or horticultural societies to gain insights into plants well-suited for your region.
- Consider the Long Term: Choose plants that will thrive in your climate and provide long-lasting beauty.
- Embrace Diversity: Plant a variety of species to create a resilient and visually appealing garden.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Successful Gardening
Understanding plant hardiness zones is crucial for successful gardening. This knowledge provides a framework for choosing plants that thrive in your climate, maximizing your chances of success. By utilizing the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map and other resources, gardeners can create thriving gardens that enhance their landscapes and provide enjoyment for years to come. Remember, a well-informed approach to plant selection ensures a flourishing garden, reflecting the beauty and resilience of the natural world.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding the Landscape: Understanding Plant Hardiness Zones. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!