Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to Understanding Weather Maps of North America
Related Articles: Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to Understanding Weather Maps of North America
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to Understanding Weather Maps of North America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to Understanding Weather Maps of North America

Weather maps are essential tools for understanding and predicting the atmospheric conditions that shape our lives. North America, with its vast and diverse landscape, experiences a wide range of weather phenomena, making the interpretation of its weather maps particularly crucial. This article delves into the intricacies of North American weather maps, explaining their components, analyzing their significance, and highlighting their crucial role in informing decision-making across various sectors.
Understanding the Elements of a Weather Map
A typical North American weather map presents a wealth of information through a combination of symbols, lines, and colors. The most common elements include:
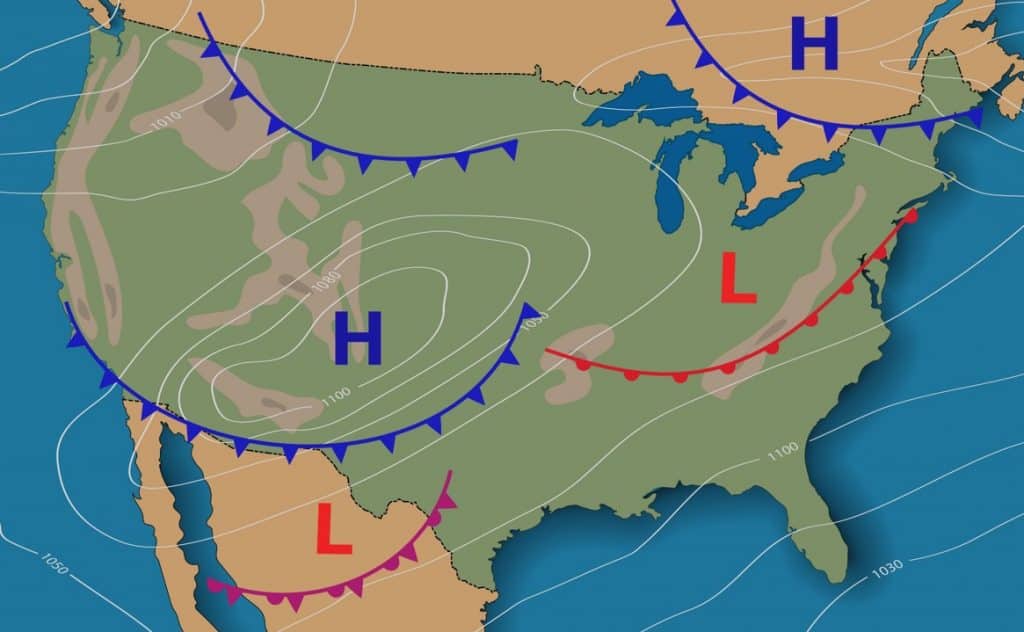
- Isobars: These are lines connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. Closely spaced isobars indicate a steep pressure gradient, often associated with strong winds.
- Fronts: These are boundaries between air masses of different temperatures and densities.
- Cold fronts: Represented by blue lines with triangles pointing in the direction of movement, cold fronts bring cooler temperatures, gusty winds, and often heavy precipitation.
- Warm fronts: Represented by red lines with semicircles pointing in the direction of movement, warm fronts bring milder temperatures and often light to moderate precipitation.
- Stationary fronts: Represented by alternating blue triangles and red semicircles, stationary fronts are relatively slow-moving, often bringing persistent precipitation.
- Occluded fronts: Represented by purple lines with alternating triangles and semicircles, occluded fronts occur when a cold front overtakes a warm front, bringing complex weather patterns.
- Temperature: Temperature is typically displayed using color gradients, with warmer temperatures represented by reds and oranges and cooler temperatures by blues and purples.
- Wind: Wind direction and speed are usually depicted using arrows. The arrow’s direction indicates wind direction, and its length or color intensity represents wind speed.
- Precipitation: Precipitation is often indicated by symbols. Different symbols represent various types of precipitation, such as rain, snow, sleet, or hail. The intensity of precipitation is often indicated by the size or color of the symbol.
- Cloud cover: The amount of cloud cover is often displayed using symbols or shading.
- Other data: Weather maps may also include additional information, such as dew point temperature, humidity, visibility, and even satellite imagery.
The Importance of Weather Maps in North America
Weather maps play a crucial role in various aspects of life across North America, impacting:
- Public safety: Accurate weather forecasts are vital for public safety. They allow authorities to issue timely warnings for severe weather events such as hurricanes, tornadoes, blizzards, and heatwaves, enabling people to take necessary precautions and minimize potential risks.
- Agriculture: Farmers rely heavily on weather maps to make critical decisions about planting, harvesting, and irrigation. Accurate forecasts help farmers optimize crop yields, manage resources efficiently, and minimize potential losses due to adverse weather conditions.
- Transportation: Weather maps are essential for the transportation sector, including aviation, maritime, and road travel. They help pilots, ship captains, and drivers make informed decisions about routes, scheduling, and safety precautions, ensuring smooth and efficient operations.
- Energy production: Weather maps are crucial for energy production companies, especially those relying on renewable sources like solar and wind power. Accurate forecasts help optimize energy generation and distribution, ensuring reliable power supply.
- Tourism: Weather maps are vital for tourism, helping individuals plan trips, choose appropriate destinations, and prepare for potential weather challenges.
Analyzing Weather Patterns with North American Weather Maps
North American weather maps reveal intricate patterns influenced by several key factors:
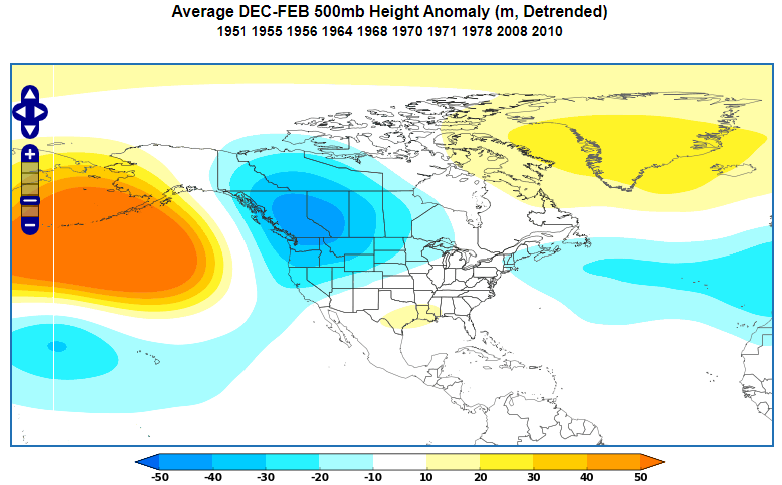
- Jet streams: Powerful air currents high in the atmosphere, known as jet streams, significantly impact weather patterns. Their position and strength can influence the movement of weather systems and the severity of weather events.
- Air masses: North America experiences the interaction of various air masses, including cold, dry Arctic air, warm, moist tropical air, and maritime air from the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. These air masses, with their distinct characteristics, shape the weather patterns across the continent.
- Mountain ranges: The Rocky Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains act as barriers, influencing precipitation patterns and creating distinct microclimates.
- Ocean currents: Warm ocean currents like the Gulf Stream and the California Current influence the temperature and humidity of coastal regions.
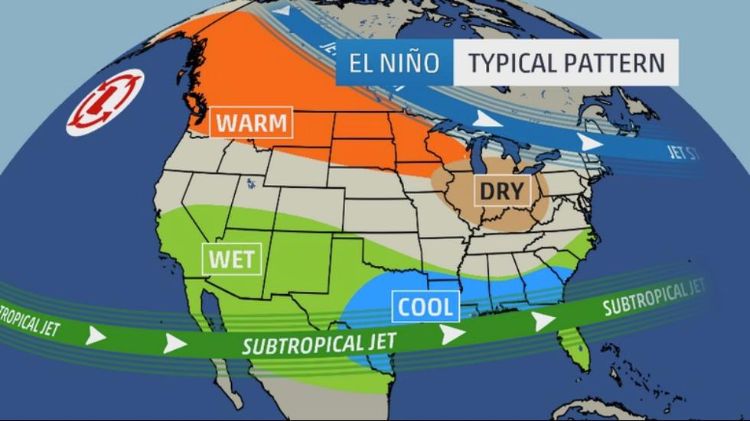
- El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO): This climate pattern, with its alternating phases of El Niño and La Niña, significantly impacts North American weather, influencing precipitation patterns, temperatures, and the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events.
Interpreting Weather Maps: A Step-by-Step Guide
To effectively interpret North American weather maps, follow these steps:
- Identify the time and date: Ensure you are looking at the most up-to-date weather map.
- Observe the pressure patterns: Examine the isobars to identify areas of high and low pressure. High-pressure systems are associated with clear skies and calm weather, while low-pressure systems often bring clouds, precipitation, and wind.
- Analyze the fronts: Identify the types of fronts and their direction of movement. This will give you an idea of the anticipated weather changes.
- Assess temperature patterns: Observe the color gradients to understand the temperature distribution across the continent.
- Interpret wind patterns: Examine the wind arrows to understand wind direction and speed. This can help predict the movement of weather systems.
- Pay attention to precipitation: Look for precipitation symbols and their intensity.
- Consider additional information: Analyze other data on the map, such as cloud cover, humidity, and visibility, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the weather conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the best source for North American weather maps?
A: Several reliable sources provide accurate and up-to-date weather maps for North America, including the National Weather Service (NWS), Environment Canada, and various private weather forecasting websites.
Q: How often are weather maps updated?
A: Weather maps are typically updated several times a day, with some services offering hourly updates.
Q: What are the limitations of weather maps?
A: Weather maps are based on complex models and data analysis, and while they provide valuable insights, they are not always perfect. Weather forecasts can be influenced by unexpected events and can be less accurate for localized weather conditions.
Q: Can I use weather maps to predict future weather events?
A: Weather maps can provide a general outlook on weather patterns, but they do not offer precise predictions for future events. Long-range forecasts are less reliable than short-term forecasts.
Tips for Using Weather Maps
- Familiarize yourself with the symbols and conventions: Spend time understanding the different symbols and lines used on weather maps.
- Look at multiple sources: Compare different weather maps from various sources to get a broader perspective on weather patterns.
- Consider local factors: Be aware of local factors that might influence weather conditions, such as topography, elevation, and proximity to bodies of water.
- Stay informed: Regularly check weather updates and be prepared for potential weather changes.
Conclusion
Weather maps are vital tools for understanding and predicting the weather patterns that shape our lives in North America. By understanding the components, analyzing the patterns, and interpreting the information presented, individuals, businesses, and governments can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and adapt to the ever-changing atmospheric conditions that define our continent. From ensuring public safety to optimizing agricultural practices and facilitating efficient transportation, weather maps play a crucial role in shaping our daily lives and contributing to the well-being of our society.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Patterns: A Guide to Understanding Weather Maps of North America. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!