Deciphering the French Political Landscape: A Guide to the Nation’s Administrative Divisions
Related Articles: Deciphering the French Political Landscape: A Guide to the Nation’s Administrative Divisions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the French Political Landscape: A Guide to the Nation’s Administrative Divisions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the French Political Landscape: A Guide to the Nation’s Administrative Divisions

The French political map, a complex tapestry woven from administrative regions, departments, and municipalities, reflects a long history of political evolution and administrative organization. Understanding this intricate system is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate the French political landscape, from analyzing election results to comprehending the nuances of local governance. This article delves into the key components of the French political map, shedding light on its historical development, current structure, and significance.
Historical Roots of the French Political Map:
The French political map has undergone significant transformations throughout history, mirroring shifts in power dynamics and societal structures. The country’s current administrative divisions are rooted in the French Revolution of 1789, which dismantled the feudal system and established a centralized state. This period saw the creation of departments, replacing the former provinces, as a means of decentralizing power and fostering a sense of national unity.
The 19th century witnessed further adjustments to the political map, with the establishment of communes (municipalities) and the creation of regions, initially with limited administrative power. The 20th century brought about a gradual shift towards regionalization, with the creation of regional councils and the transfer of certain powers from the central government to regional authorities.
Current Structure of the French Political Map:
The French political map today comprises three main tiers of administrative divisions:
-
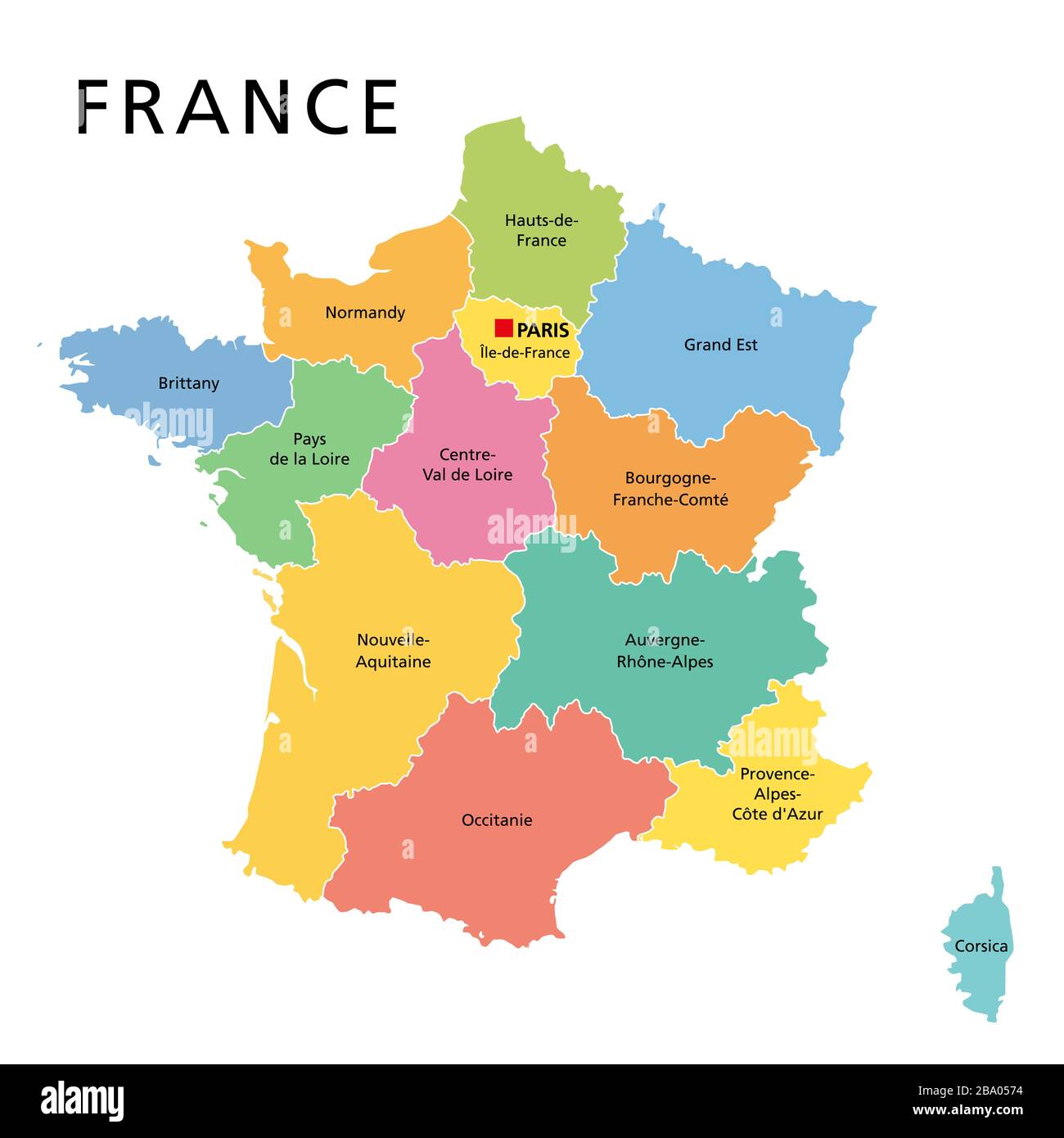
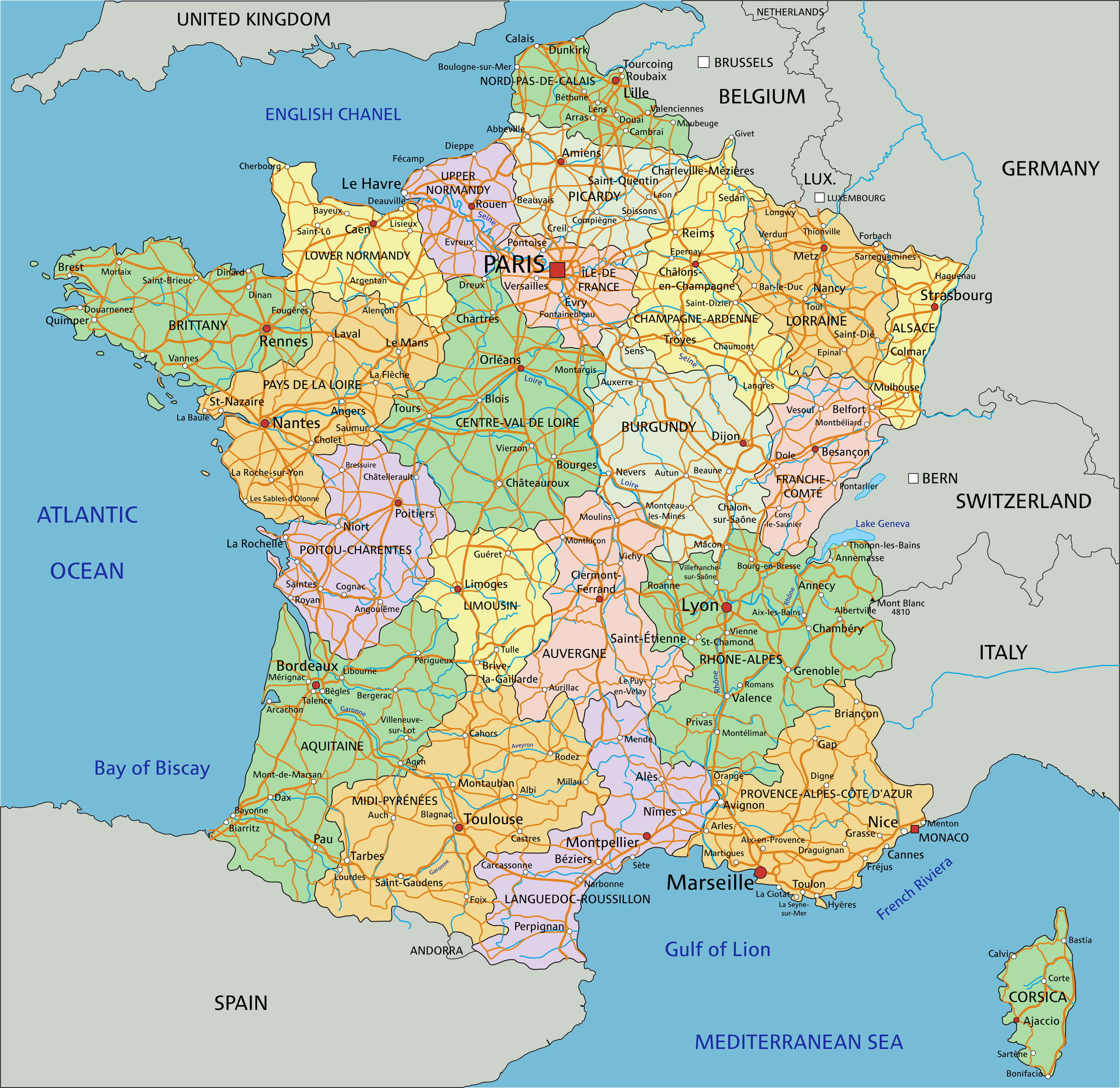
Regions: The largest administrative units, France is currently divided into 18 regions, including the overseas territories. These regions are responsible for a wide range of policy areas, including education, transportation, and economic development. Each region is governed by a regional council, elected by universal suffrage.
-
Departments: France is further subdivided into 101 departments, including five overseas departments. Departments are responsible for social services, public works, and cultural affairs. Each department is governed by a departmental council, also elected by universal suffrage.
-
Communes: The smallest administrative units, France has over 36,000 communes, each with its own elected council and mayor. Communes are responsible for local services such as waste management, public safety, and cultural activities.
Significance of the French Political Map:
The French political map serves as a fundamental framework for governing the country, distributing power, and facilitating local decision-making. Its structure enables:
-
Decentralization: The division of power between national, regional, and local levels fosters a more balanced distribution of authority, allowing for greater responsiveness to local needs and priorities.
-
Representation: The elected councils at each level of government provide a platform for citizens to participate in the decision-making process and voice their concerns.
-
Local Autonomy: The structure of the political map empowers local communities to manage their own affairs, promoting a sense of ownership and fostering local development initiatives.
-
Efficient Governance: By dividing administrative responsibilities across different levels of government, the French political map promotes efficiency and effectiveness in public service delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions about the French Political Map:
Q: What are the main differences between regions and departments?
A: Regions are larger and have broader responsibilities than departments. Regions focus on strategic planning and policy implementation, while departments handle more localized services and administration.
Q: How are the boundaries of the different administrative units determined?
A: The boundaries of regions and departments are defined by law, often reflecting historical, geographical, or cultural considerations. Commune boundaries can be adjusted through local referendums or administrative decisions.
Q: What are the roles of the elected councils at each level of government?
A: Elected councils at the regional, departmental, and communal levels have legislative and budgetary powers. They set policies, approve budgets, and oversee the execution of local services.
Q: How does the French political map influence elections?
A: The structure of the political map impacts electoral strategies and outcomes. Political parties often target specific regions or departments, tailoring their campaigns to local concerns and demographics.
Tips for Understanding the French Political Map:
-
Consult maps and resources: Utilize online maps and government websites to visualize the different administrative units and their boundaries.
-
Explore local news and media: Stay informed about local issues and political developments by following news sources in specific regions or departments.
-
Attend local events: Participate in community meetings and public forums to engage with local officials and understand local priorities.
-
Learn about the history of the French political map: Understanding the historical evolution of the administrative divisions provides context for current political dynamics.
Conclusion:
The French political map is a complex and dynamic system that underpins the country’s administrative structure and political landscape. Its intricate network of regions, departments, and communes reflects a long history of political evolution and societal change. Understanding this system is crucial for appreciating the nuances of French governance, the distribution of power, and the role of local communities in national decision-making. By navigating the intricacies of the French political map, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the country’s political dynamics and the diverse perspectives shaping its future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the French Political Landscape: A Guide to the Nation’s Administrative Divisions. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!