A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation: Exploring the 13 Colonies Map with Cities
Related Articles: A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation: Exploring the 13 Colonies Map with Cities
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation: Exploring the 13 Colonies Map with Cities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation: Exploring the 13 Colonies Map with Cities

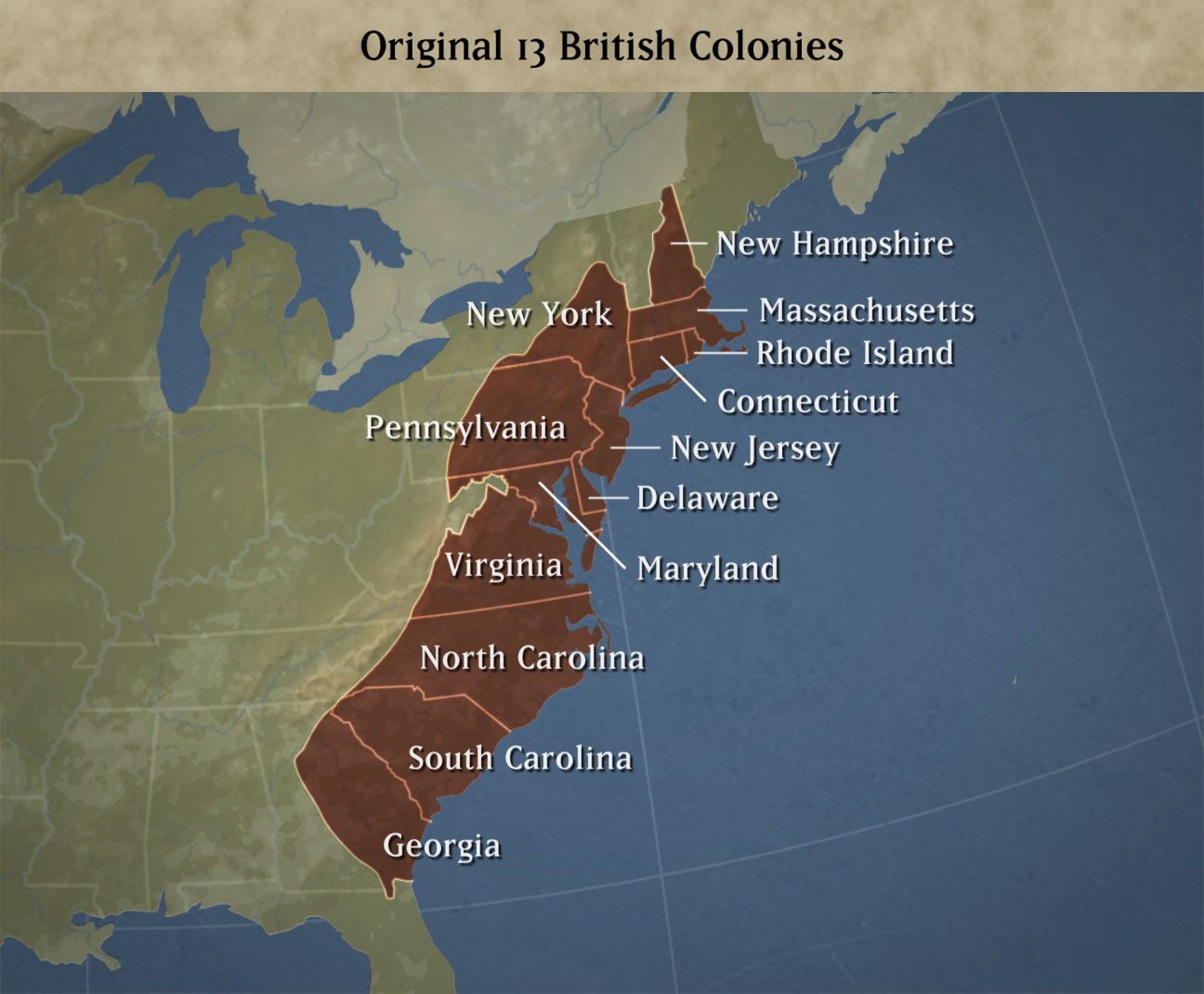
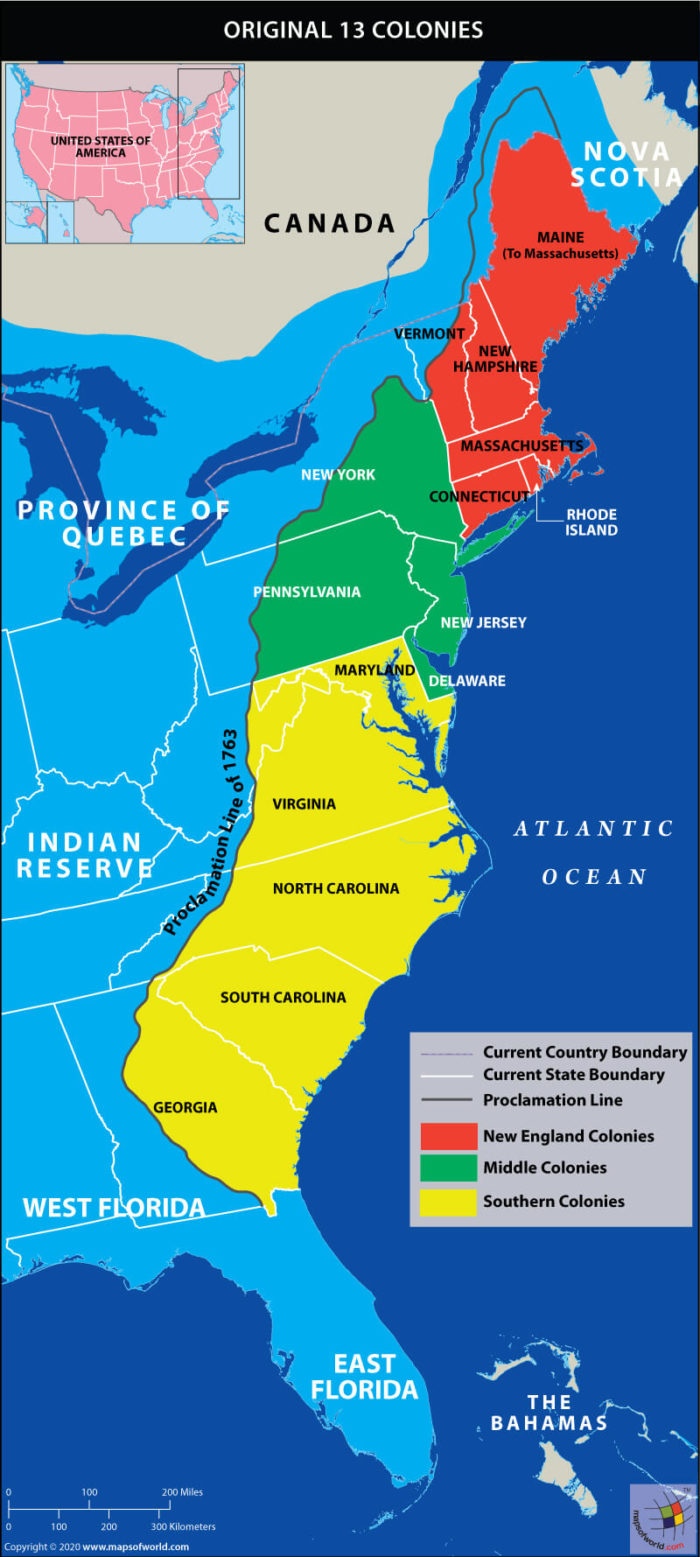
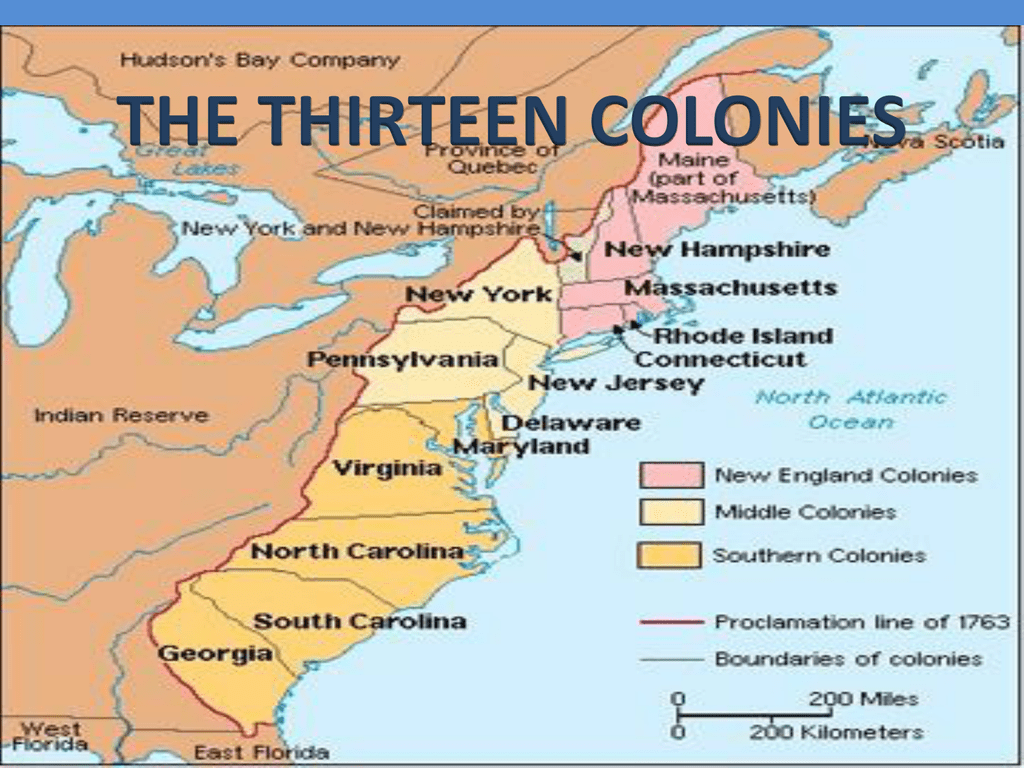
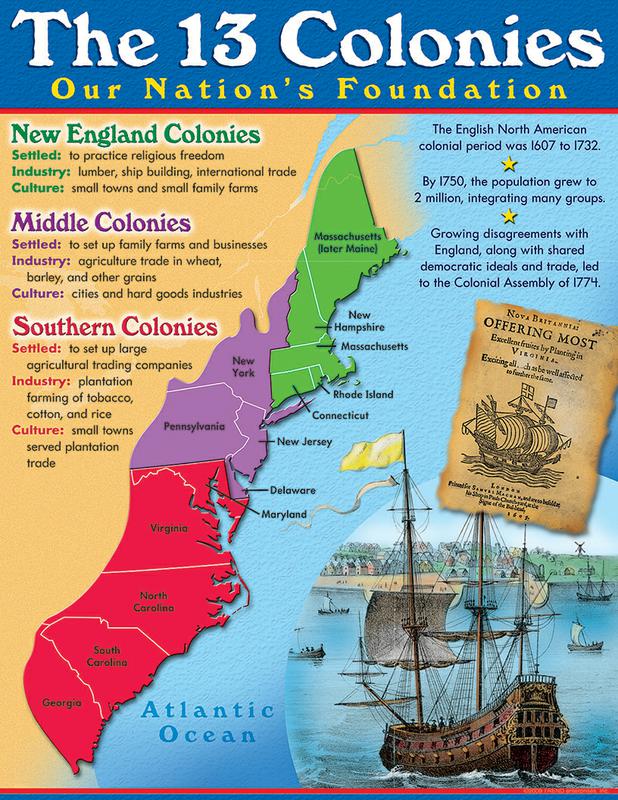
The 13 Colonies map, a visual representation of the original British settlements that formed the foundation of the United States, holds immense historical and cultural significance. This map, dotted with bustling cities and sprawling landscapes, tells a story of resilience, ambition, and the birth of a nation.
A Tapestry of Colonial Life:
The 13 Colonies map is more than just a geographical outline; it’s a window into the diverse tapestry of colonial life. Each colony, with its unique geographical features, economic activities, and social structures, contributed to the rich mosaic that eventually became the United States.
The Northern Colonies:
- New Hampshire: Founded in 1623, New Hampshire was a haven for shipbuilding and fishing, with Portsmouth emerging as a prominent port city.
- Massachusetts: The heart of Puritanism, Massachusetts witnessed the establishment of Boston, a thriving center for commerce and intellectual pursuits.
- Rhode Island: Founded on principles of religious freedom, Rhode Island’s capital, Providence, became a hub for trade and industry.
- Connecticut: Known for its fertile agricultural lands, Connecticut saw the growth of Hartford, a center for trade and government.
The Middle Colonies:
- New York: Originally New Netherland, New York City became a cosmopolitan hub under British rule, attracting diverse populations and fostering trade.
- New Jersey: A diverse colony with a mix of agricultural and commercial activities, New Jersey saw the rise of cities like Newark and Trenton, playing a significant role in the American Revolution.
- Pennsylvania: Founded by William Penn as a haven for religious tolerance, Philadelphia emerged as a major center for commerce and culture, becoming the nation’s first capital.
- Delaware: A small colony with a strong agricultural economy, Delaware’s capital, Dover, served as a vital link between the northern and southern colonies.
The Southern Colonies:
- Maryland: Founded as a haven for Catholics, Maryland’s capital, Annapolis, became a center for trade and government, with a thriving tobacco industry.
- Virginia: The first permanent English settlement in North America, Virginia witnessed the rise of Jamestown and later, Williamsburg, which became a hub of colonial society and government.
- North Carolina: Known for its fertile farmland and abundant natural resources, North Carolina saw the growth of cities like Wilmington and New Bern, important centers for trade.
- South Carolina: A center for rice and indigo production, South Carolina’s capital, Charleston, emerged as a bustling port city with a significant slave population.
- Georgia: Founded as a buffer colony against Spanish Florida, Georgia’s capital, Savannah, became a center for trade and agriculture, with a diverse population including debtors and refugees.
The Importance of Cities:
The cities on the 13 Colonies map were not merely points on a grid; they were the engines of colonial growth and development. They served as centers for commerce, trade, government, and cultural exchange. These cities fostered a spirit of innovation, entrepreneurship, and intellectual discourse that would ultimately pave the way for the American Revolution and the birth of a new nation.
Key Cities and Their Significance:
- Boston (Massachusetts): A hub for commerce, shipbuilding, and intellectual pursuits, Boston played a pivotal role in the American Revolution, serving as the cradle of the movement for independence.
- New York City (New York): A cosmopolitan center for trade, finance, and culture, New York City became the largest and most diverse city in the colonies, playing a crucial role in the nation’s economic development.
- Philadelphia (Pennsylvania): A center for commerce, government, and culture, Philadelphia served as the nation’s first capital and played a vital role in the American Revolution.
- Charleston (South Carolina): A major port city and center for trade, Charleston served as a vital link between the colonies and the rest of the world, but also reflected the harsh realities of slavery and its impact on the region.
Beyond the Map: The Legacy of the 13 Colonies
The 13 Colonies map is more than just a historical artifact; it’s a testament to the enduring legacy of the early American settlements. The cities, towns, and landscapes depicted on the map continue to shape the American landscape, culture, and identity. The spirit of innovation, resilience, and self-governance that characterized the 13 Colonies remains a cornerstone of American values and ideals.
FAQs:
Q: What are the major geographical features of the 13 Colonies?
A: The 13 Colonies spanned a diverse range of geographical features, from the rugged coastline of New England to the fertile farmland of the Middle Colonies and the vast, coastal plains of the South. These features significantly influenced the economic activities and cultural development of the colonies.
Q: What were the major economic activities of the 13 Colonies?
A: The economic activities of the 13 Colonies varied significantly. The Northern Colonies focused on shipbuilding, fishing, and trade, while the Middle Colonies were known for their agriculture and commerce. The Southern Colonies relied heavily on plantation agriculture, particularly tobacco, rice, and indigo.
Q: What was the role of slavery in the 13 Colonies?
A: Slavery played a significant role in the economic development of the Southern Colonies, particularly in the production of cash crops like tobacco and rice. The institution of slavery had a profound impact on the social, political, and cultural landscape of the colonies, ultimately leading to the Civil War.
Q: What was the impact of the American Revolution on the 13 Colonies?
A: The American Revolution resulted in the establishment of the United States of America, transforming the 13 Colonies from British settlements into a new nation. The revolution also led to significant changes in the political, social, and economic landscape of the colonies.
Tips for Studying the 13 Colonies Map:
- Focus on the key cities and their significance: Understand the role of cities like Boston, New York City, Philadelphia, and Charleston in the development of the colonies and the nation.
- Consider the geographical features and their impact on colonial life: Explore the relationship between the environment and the economic activities, culture, and social structures of the colonies.
- Study the historical context: Understand the events and influences that shaped the development of the 13 Colonies, including the arrival of Europeans, the establishment of settlements, and the rise of conflicts with Native Americans and other European powers.
- Examine the legacy of the 13 Colonies: Explore how the institutions, values, and ideas developed in the 13 Colonies continue to shape American society today.
Conclusion:
The 13 Colonies map is a powerful reminder of the origins of the United States, a nation born from the ambition, resilience, and diverse experiences of its early settlers. By studying this map, we gain a deeper understanding of the historical forces that shaped the nation, the challenges faced by its founders, and the enduring legacy of the 13 Colonies in the American experience. The map serves as a visual testament to the power of human ingenuity, the pursuit of freedom, and the enduring quest for a better future, all of which continue to shape the United States today.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Visual Journey Through the Birthplace of a Nation: Exploring the 13 Colonies Map with Cities. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!