A Tapestry of Nations: Understanding the Tribal Map of North America
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Nations: Understanding the Tribal Map of North America
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Nations: Understanding the Tribal Map of North America. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Nations: Understanding the Tribal Map of North America
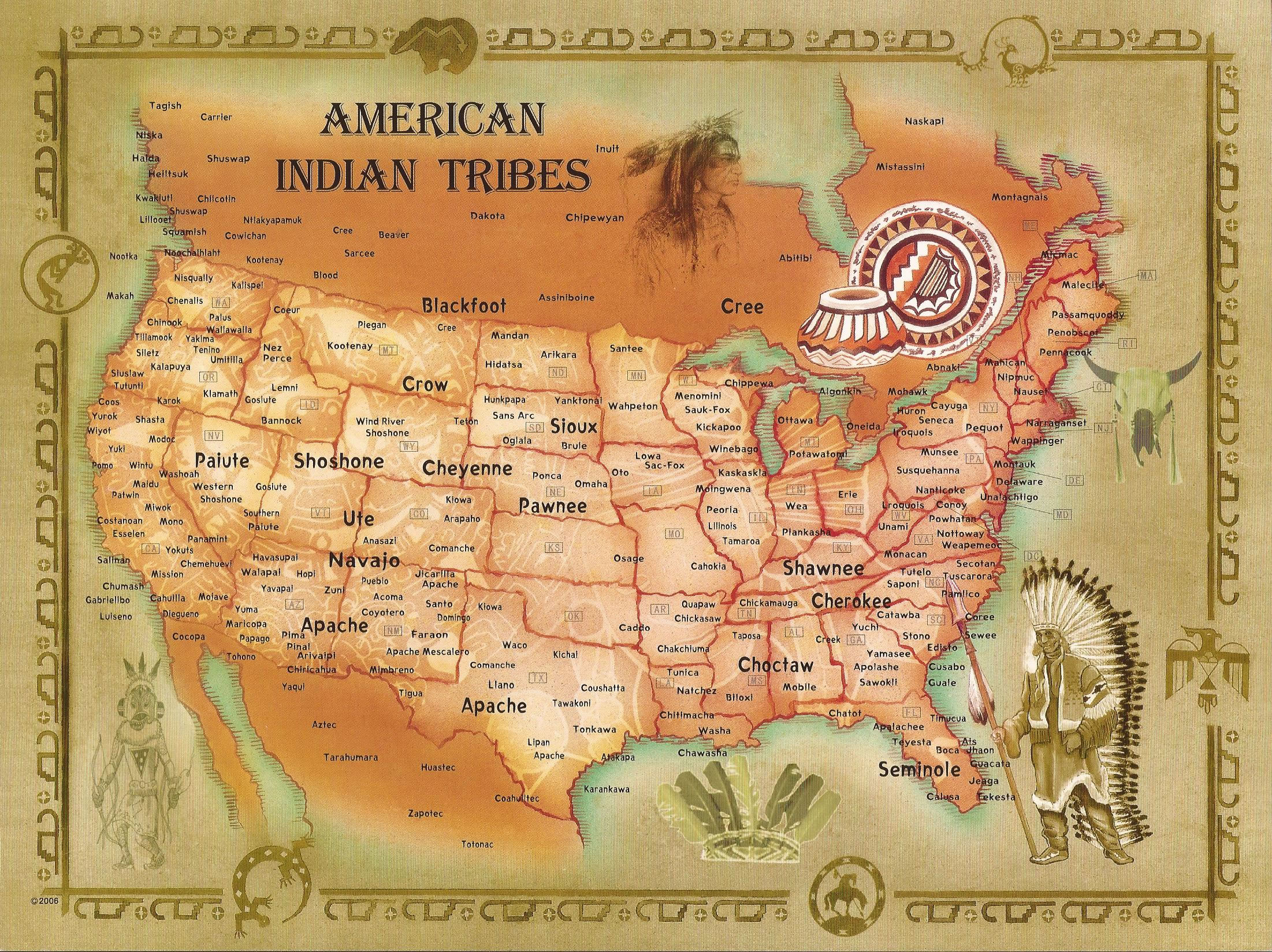
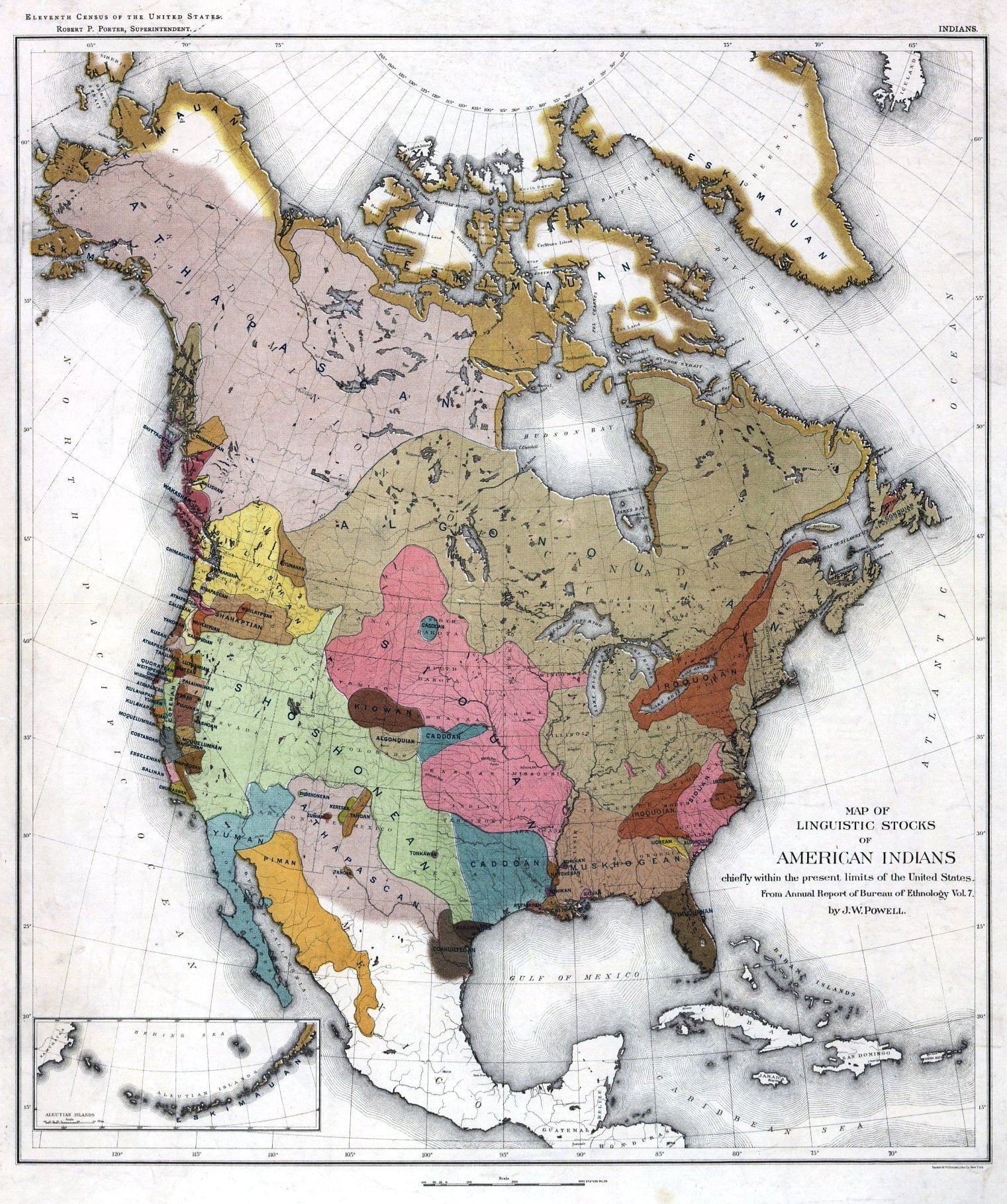
The vibrant tapestry of indigenous cultures that once spanned the entirety of North America is reflected in the intricate mosaic of tribal territories, a landscape of distinct nations, languages, and traditions. The Tribal Map of North America, a visual representation of these indigenous lands, is a powerful tool for understanding the continent’s history, the enduring impact of colonization, and the ongoing struggle for sovereignty and self-determination.
Historical Context and Significance:
The map is a testament to the long and complex history of indigenous peoples in North America, dating back thousands of years. Prior to European colonization, the continent was home to hundreds of distinct indigenous nations, each with its own unique language, culture, and governance system. These nations were not static entities but rather dynamic communities that interacted and traded with one another, forming complex networks across vast distances.
The arrival of European colonists in the 15th century marked a dramatic shift in the landscape of North America. The introduction of European diseases, warfare, and forced displacement resulted in the decimation of indigenous populations and the dispossession of their lands. The process of colonization, often characterized by violence and cultural suppression, dramatically altered the map of indigenous territories, leaving a legacy of trauma and dispossession that continues to impact indigenous communities today.
Interpreting the Tribal Map:
The Tribal Map of North America is not a static or definitive representation of indigenous territories. It is a dynamic and evolving tool that reflects the ongoing efforts of indigenous communities to reclaim their history, culture, and sovereignty. Interpreting the map requires an understanding of its historical context and the complexities of indigenous land claims.
The map often depicts traditional territories, which may differ from present-day jurisdictional boundaries. These traditional territories are not merely geographical spaces but rather represent the ancestral homelands and cultural landscapes of indigenous nations. The map also highlights the ongoing struggle for recognition of indigenous sovereignty and the right to self-determination.
Benefits and Importance:
The Tribal Map of North America offers a valuable framework for understanding the complexities of indigenous history, culture, and contemporary issues. It serves as a vital resource for:
- Educational purposes: The map provides a visual representation of the diversity of indigenous cultures and the historical impact of colonization. It can be used to educate students and the general public about the rich heritage of indigenous peoples and the ongoing struggle for self-determination.
- Reconciliation and healing: The map can facilitate dialogue and understanding between indigenous communities and non-indigenous populations. It can help to foster a more accurate and nuanced understanding of indigenous history and the ongoing process of reconciliation.
- Land rights and sovereignty: The map serves as a powerful tool for advocating for indigenous land rights and self-determination. It highlights the historical and cultural significance of indigenous territories and the importance of recognizing indigenous sovereignty.
- Preservation of culture and language: The map can help to raise awareness of the diversity of indigenous languages and cultures and the importance of preserving these traditions for future generations.
FAQs About the Tribal Map of North America:
1. What is the difference between a traditional territory and a present-day reservation?
Traditional territories represent the ancestral homelands of indigenous nations, often encompassing vast areas that extend beyond the boundaries of present-day reservations. Reservations are designated areas of land set aside for indigenous communities by the federal government.
2. Why are there so many different tribal nations?
The diversity of indigenous cultures in North America reflects the long history of adaptation to different environments and the development of unique social, cultural, and linguistic practices.
3. How does the Tribal Map of North America help to address issues of indigenous sovereignty?
By visually representing the historical and cultural significance of indigenous territories, the map helps to raise awareness of the ongoing struggle for indigenous self-determination and the right to govern their own affairs.
4. What are some of the challenges faced by indigenous communities in reclaiming their lands and asserting their sovereignty?
Indigenous communities continue to face challenges related to land rights, treaty violations, and the ongoing effects of colonization, including poverty, lack of access to education and healthcare, and environmental degradation.
5. How can I learn more about the history and culture of specific indigenous nations?
There are a wealth of resources available online and in libraries, including books, documentaries, and websites dedicated to the history and culture of specific indigenous nations.
Tips for Understanding and Engaging with the Tribal Map of North America:
- Engage with indigenous communities: Reach out to local indigenous organizations and leaders to learn more about their history, culture, and perspectives.
- Support indigenous-led initiatives: Support organizations that are working to preserve indigenous languages and cultures, protect indigenous rights, and promote economic development in indigenous communities.
- Educate yourself: Read books, watch documentaries, and visit museums to learn about the history and culture of indigenous peoples.
- Be respectful: When discussing indigenous issues, use respectful language and avoid perpetuating stereotypes.
Conclusion:
The Tribal Map of North America is a powerful tool for understanding the complex history of indigenous peoples in North America and the ongoing struggle for recognition and self-determination. It serves as a reminder of the rich diversity of indigenous cultures and the importance of preserving their heritage for future generations. By engaging with the map and its historical context, we can foster a deeper understanding of the past and contribute to a more just and equitable future for indigenous communities.


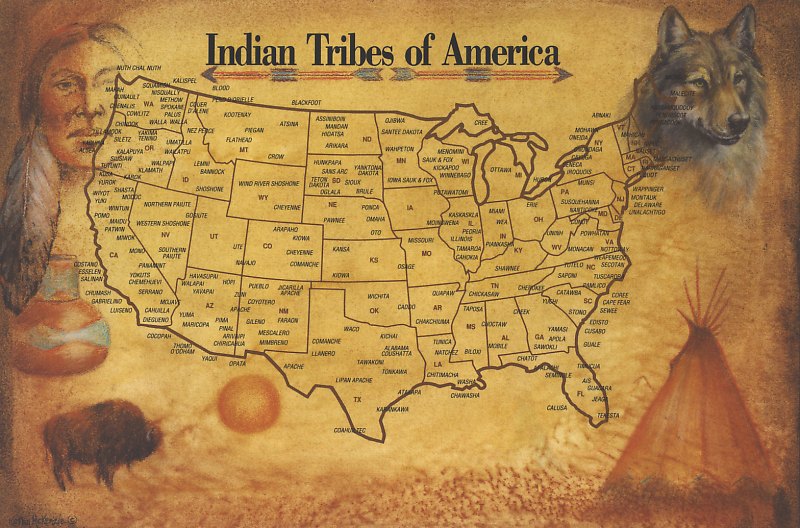

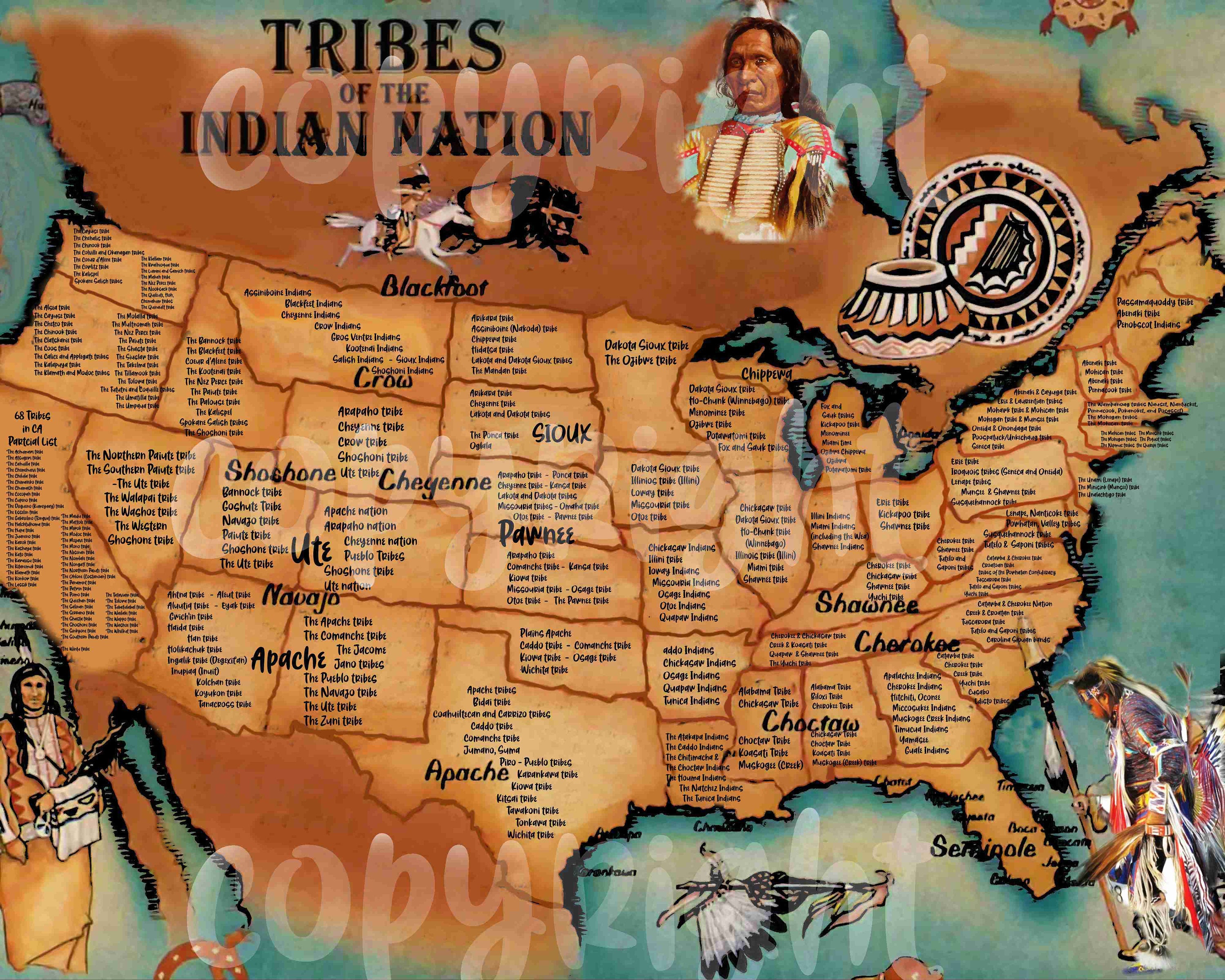
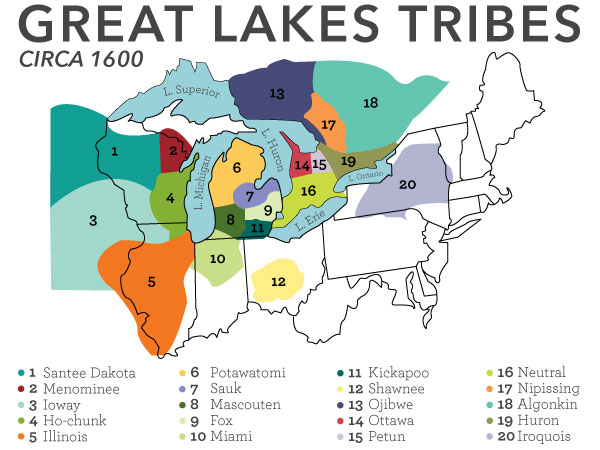

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Nations: Understanding the Tribal Map of North America. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!