A Journey Through Japan’s Physical Landscape: Unveiling the Islands’ Diverse Topography
Related Articles: A Journey Through Japan’s Physical Landscape: Unveiling the Islands’ Diverse Topography
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Japan’s Physical Landscape: Unveiling the Islands’ Diverse Topography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Japan’s Physical Landscape: Unveiling the Islands’ Diverse Topography
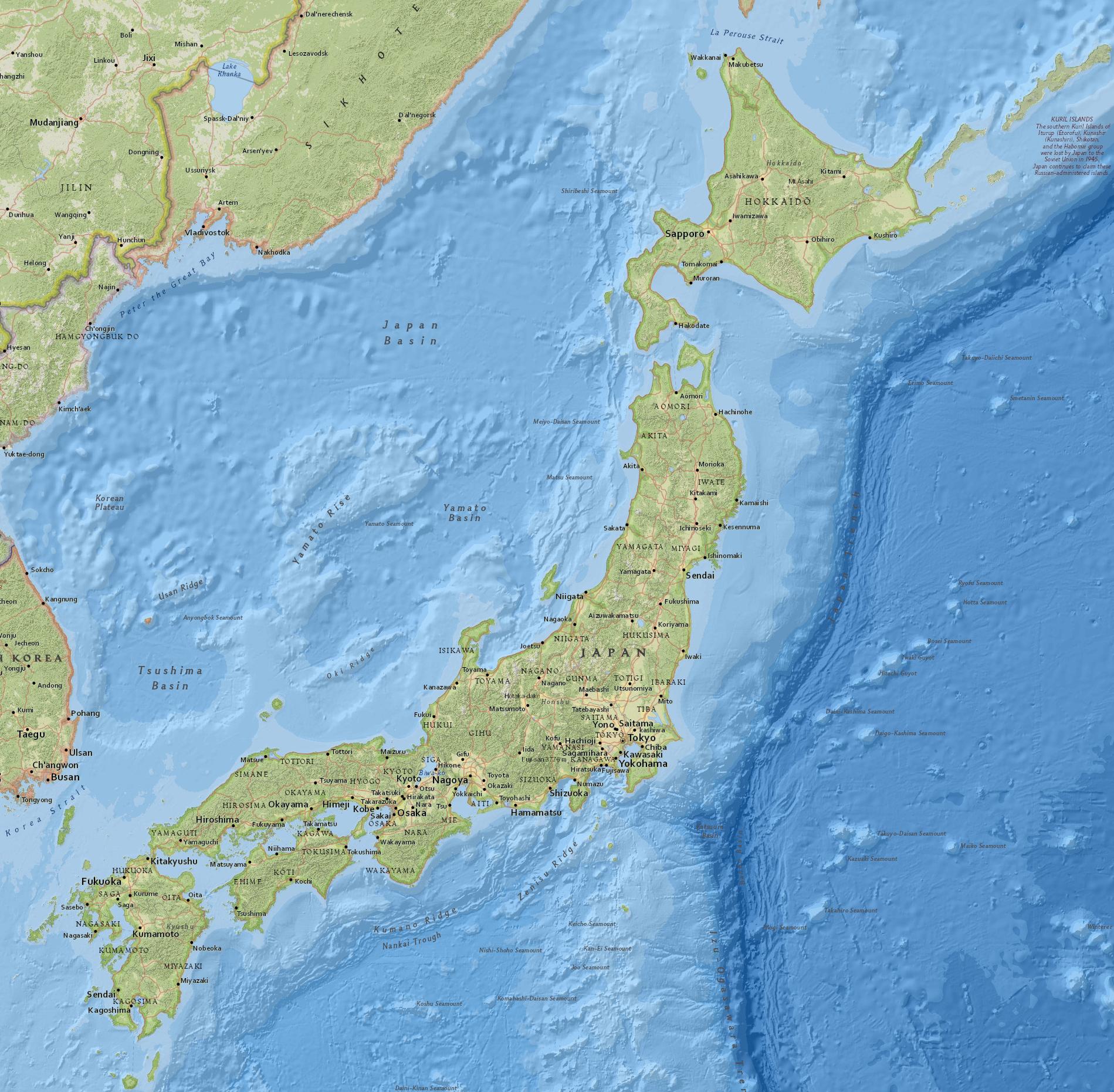
Japan, an archipelago nation in East Asia, is renowned for its vibrant culture, technological prowess, and captivating beauty. However, beyond the bustling cities and serene temples lies a diverse and fascinating physical landscape shaped by tectonic forces, volcanic activity, and centuries of weathering. Understanding the physical map of Japan is crucial for appreciating its natural wonders, understanding its unique challenges, and appreciating the intricate relationship between its people and the environment.
The Archipelago’s Formation: A Symphony of Tectonic Forces
Japan’s physical landscape is a testament to the dynamic forces of plate tectonics. The country sits at the juncture of four major tectonic plates: the Eurasian, North American, Pacific, and Philippine Sea plates. This convergence zone is characterized by intense seismic activity, volcanic eruptions, and mountain formation. The Japanese archipelago itself emerged from the collision of these plates, with the Pacific Plate subducting beneath the Eurasian Plate, creating a chain of volcanic islands.
Mountain Ranges: The Backbone of Japan
The Japanese archipelago is dominated by a series of mountain ranges that run its length, forming the country’s dramatic backbone. The Japanese Alps, a series of high peaks in central Honshu, are a testament to the country’s mountainous terrain. Mount Fuji, Japan’s iconic volcano and highest peak, is a symbol of national pride and a testament to the country’s volcanic heritage. These mountain ranges, with their rugged slopes and deep valleys, have played a significant role in shaping Japan’s history, culture, and development.
Volcanoes: A Force of Creation and Destruction
Volcanoes are an integral part of Japan’s physical landscape, a consequence of the country’s tectonic setting. Mount Fuji, Mount Asama, and Mount Sakurajima are just a few of the many active volcanoes that dot the archipelago. While volcanic eruptions can pose a threat, they also contribute to the fertility of the surrounding land, creating fertile soil for agriculture and providing geothermal energy resources.
Rivers and Lakes: Lifeblood of the Nation
Japan’s numerous rivers and lakes are essential to its water resources, agriculture, and transportation systems. The longest river, the Shinano River, flows through the mountainous heartland of Honshu, while Lake Biwa, the largest freshwater lake, is a vital source of water for the surrounding region. These waterways have served as vital trade routes throughout history, connecting communities and facilitating the movement of goods and people.
Coastal Landscapes: A Tapestry of Beaches and Cliffs
Japan’s coastline is a diverse tapestry of beaches, cliffs, and inlets, shaped by the relentless forces of the sea. The Pacific Ocean, to the east, is characterized by its deep waters and powerful waves, while the Sea of Japan, to the west, is calmer and shallower. Coastal areas have historically played a crucial role in Japan’s economy, supporting fishing communities and providing access to trade routes.
The Importance of Understanding Japan’s Physical Map
Understanding Japan’s physical landscape is crucial for several reasons:
- Appreciating Natural Wonders: The physical map reveals the breathtaking beauty of Japan’s mountains, volcanoes, rivers, and coastlines, offering insights into the country’s unique natural heritage.
- Understanding Environmental Challenges: The physical map highlights the vulnerability of Japan to natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions, emphasizing the importance of disaster preparedness and mitigation efforts.
- Analyzing Economic Development: The physical map reveals the distribution of resources, including fertile land, water, and mineral deposits, influencing economic development and agricultural practices.
- Exploring Cultural Significance: The physical map sheds light on the influence of the landscape on traditional Japanese culture, art, and literature, demonstrating the deep connection between the people and their environment.
FAQs
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in Japan?
A: The major mountain ranges in Japan include the Japanese Alps, the Chubu Mountains, the Kii Mountains, and the Hida Mountains.
Q: How many active volcanoes are there in Japan?
A: Japan has over 100 active volcanoes, making it one of the most volcanically active countries in the world.
Q: What is the significance of Mount Fuji?
A: Mount Fuji is a dormant volcano and Japan’s highest peak. It holds significant cultural and religious importance, often depicted in art and literature.
Q: How do Japan’s rivers contribute to its economy?
A: Japan’s rivers provide essential water resources for agriculture, industry, and household use. They also serve as vital transportation routes and sources of hydroelectric power.
Q: What are the challenges posed by Japan’s coastal landscapes?
A: Japan’s coastal landscapes are susceptible to tsunamis, storm surges, and coastal erosion, posing challenges for coastal communities and infrastructure.
Tips
- Use a Physical Map: A physical map of Japan is essential for visualizing the country’s diverse topography and understanding the spatial relationships between different geographic features.
- Explore Online Resources: Numerous online resources, including Google Earth and interactive maps, offer detailed information about Japan’s physical landscape.
- Engage with Local Communities: Visiting Japan and interacting with local communities can provide insights into the cultural and economic impact of the country’s physical landscape.
- Consider the Impact of Climate Change: Climate change is affecting Japan’s physical landscape, leading to increased sea levels, more frequent extreme weather events, and changes in plant and animal life.
Conclusion
The physical map of Japan is a window into a dynamic and captivating landscape shaped by tectonic forces, volcanic activity, and centuries of weathering. It reveals the country’s unique natural heritage, its vulnerabilities to natural disasters, and the intricate relationship between its people and the environment. Understanding this physical map is essential for appreciating Japan’s cultural richness, understanding its challenges, and appreciating the beauty of its diverse topography.

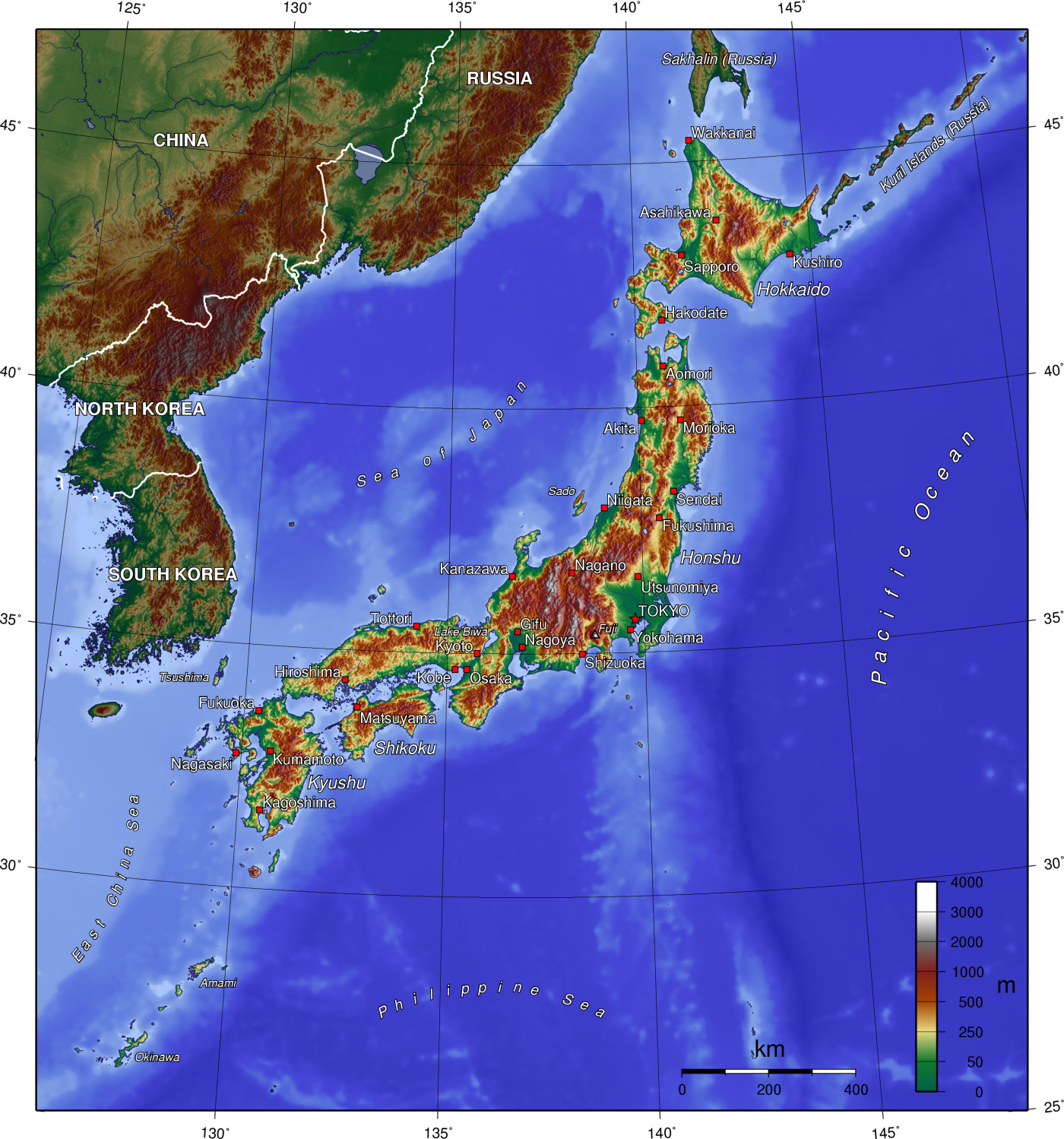
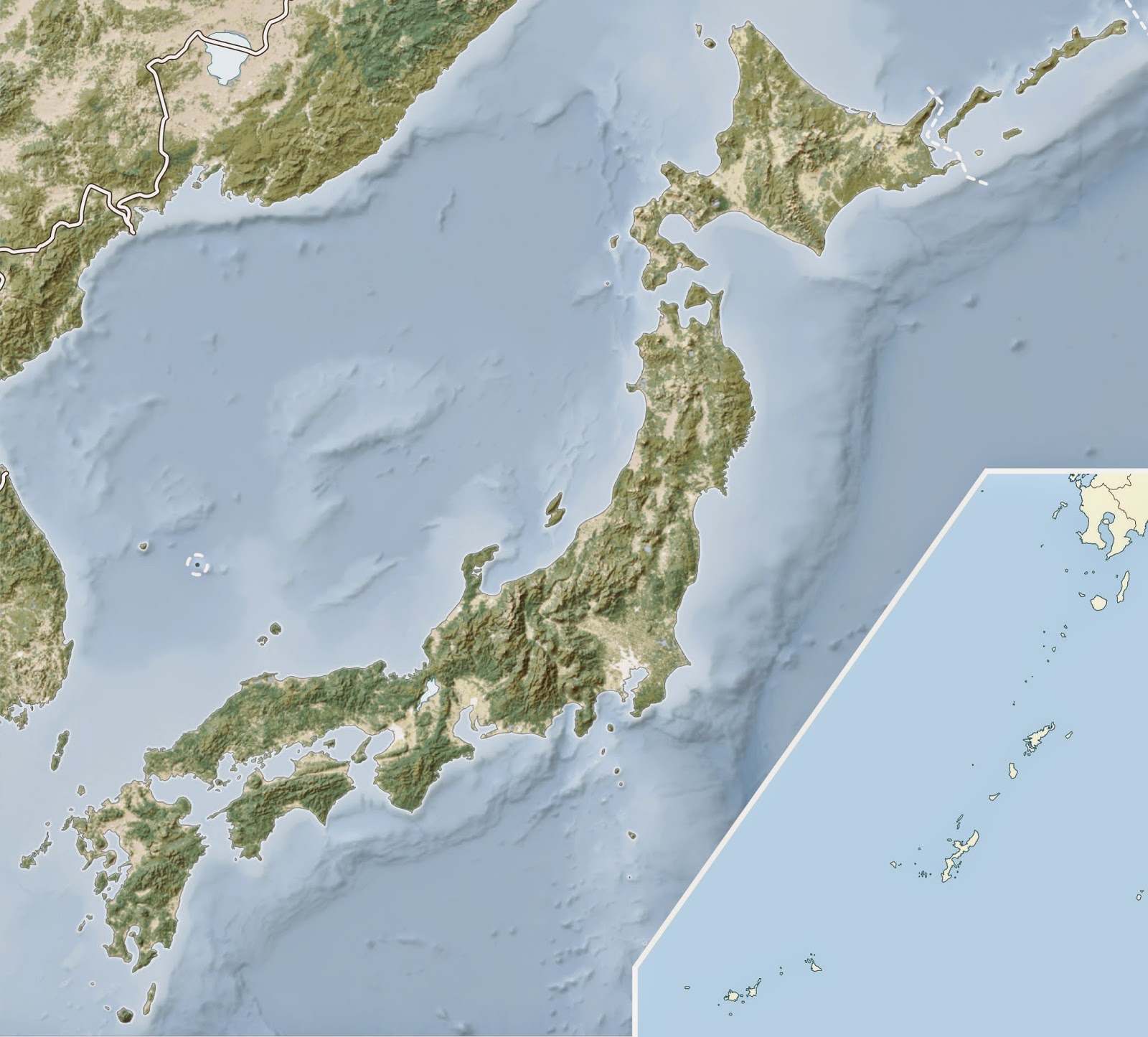


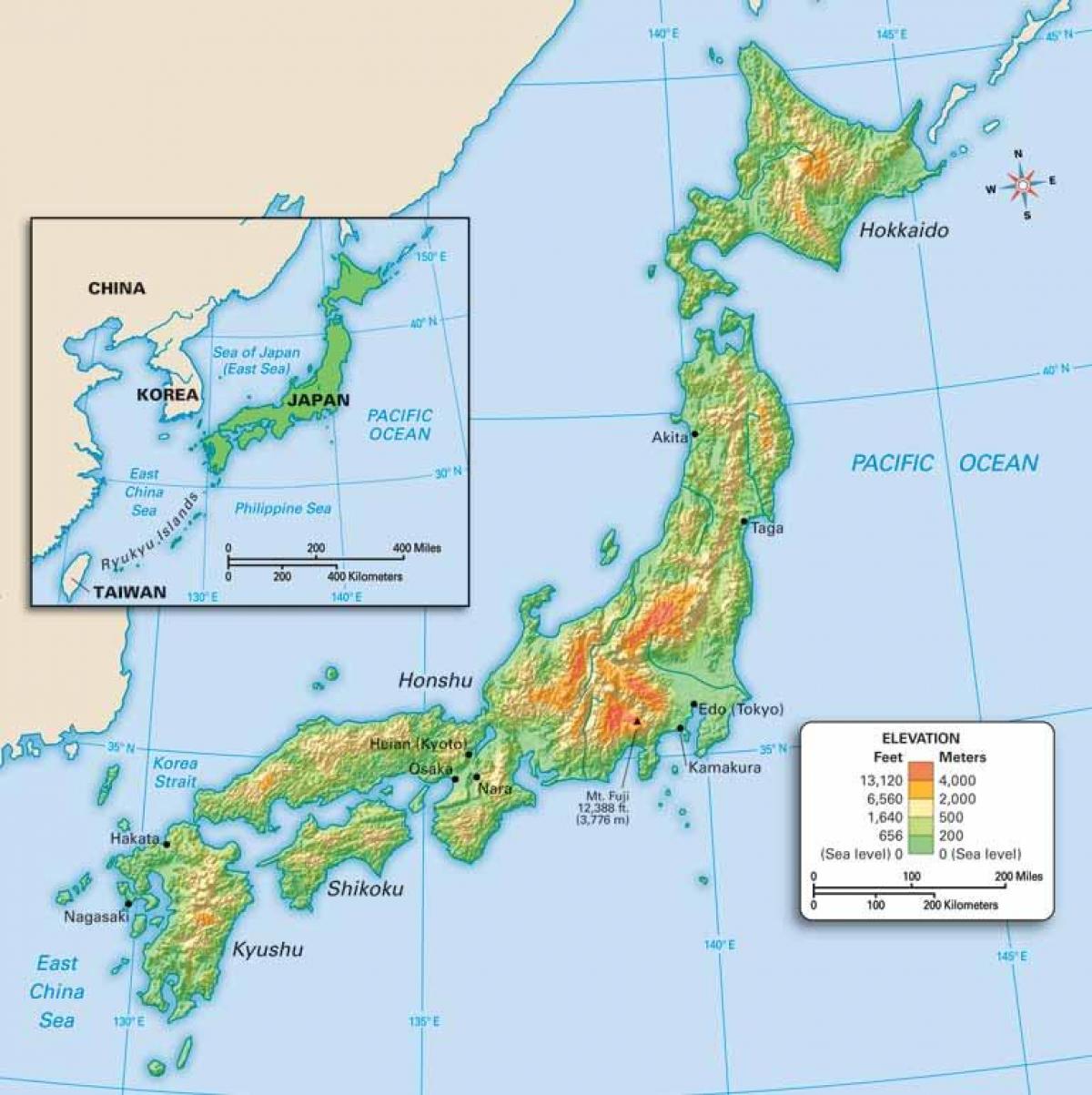


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Japan’s Physical Landscape: Unveiling the Islands’ Diverse Topography. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!