A Geographical Exploration: China and its Surrounding Countries
Related Articles: A Geographical Exploration: China and its Surrounding Countries
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Exploration: China and its Surrounding Countries. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Exploration: China and its Surrounding Countries

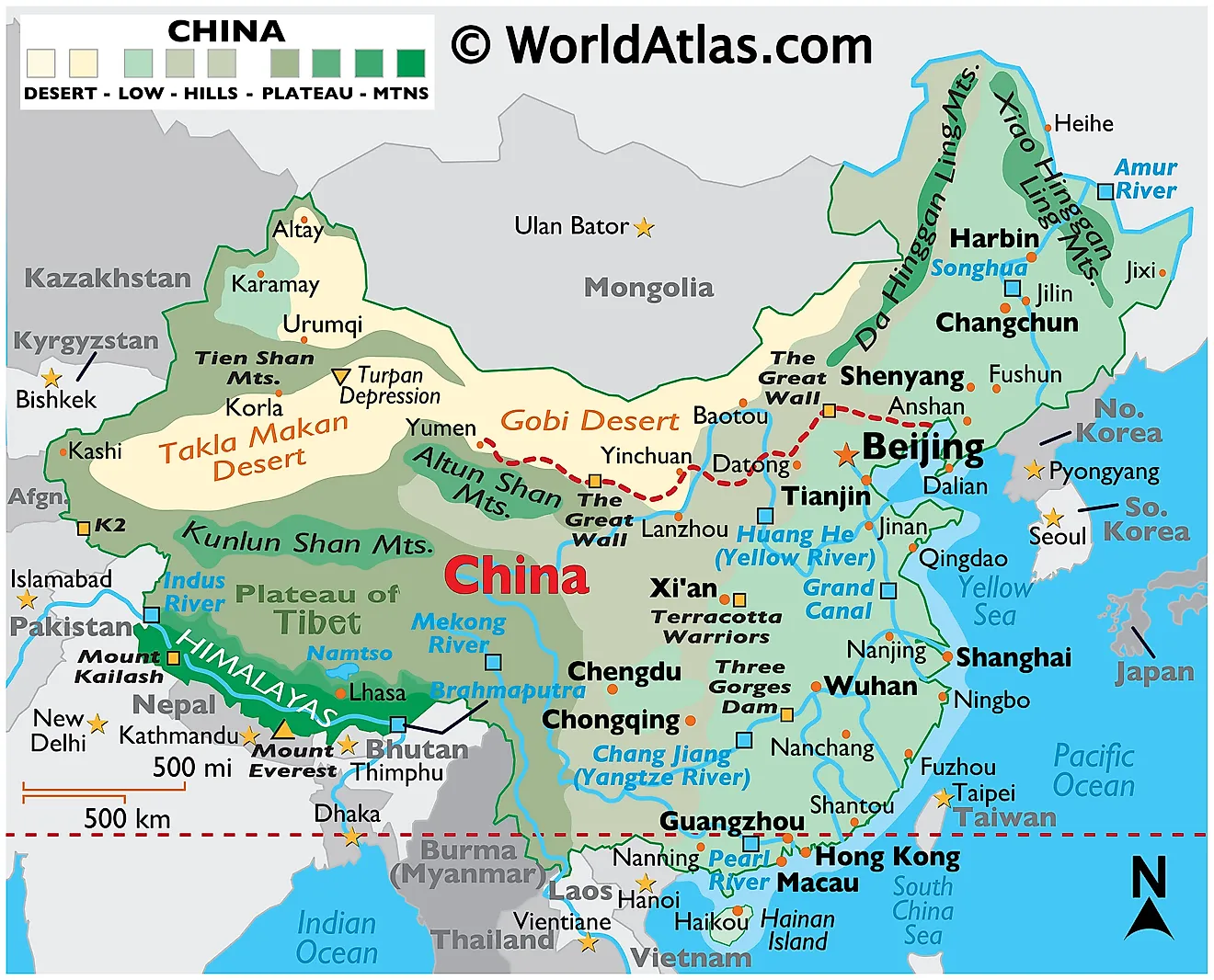
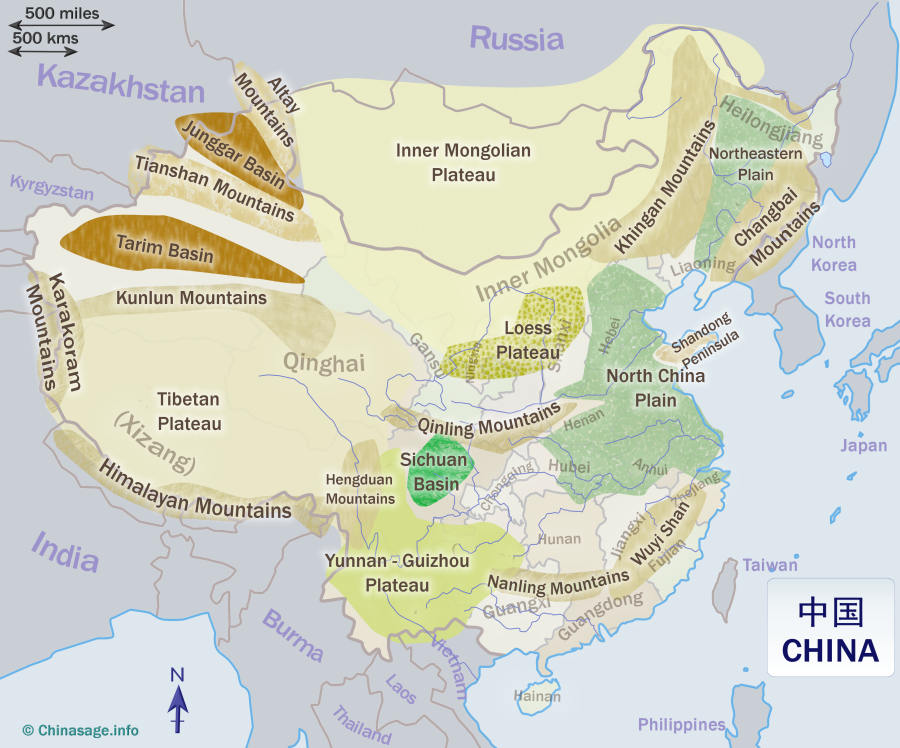
China, the world’s most populous nation, occupies a vast and diverse geographical region in East Asia. Its sprawling landscape, encompassing mountains, deserts, plateaus, and fertile plains, has shaped the nation’s history, culture, and economy. Understanding China’s geographical context requires examining not only its internal features but also its relationship with its neighboring countries. This exploration delves into the complexities of China’s map, analyzing its surrounding countries, and highlighting the significance of these interactions.
China’s Enormous Landscape:
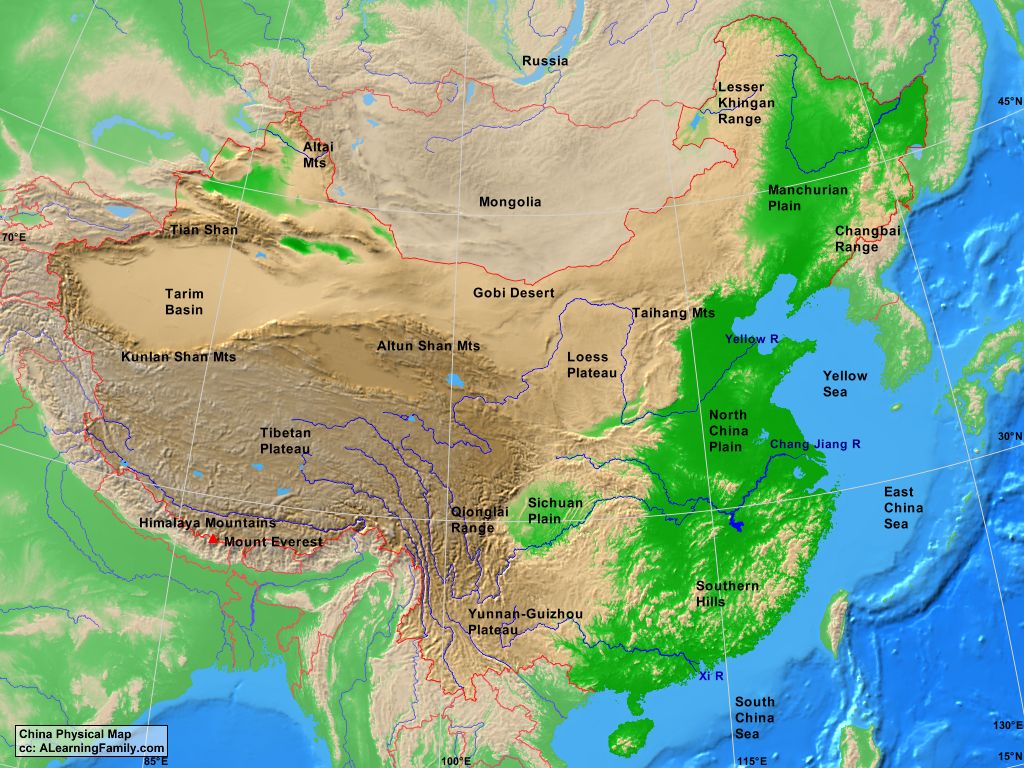
China’s landmass, stretching over 9.59 million square kilometers, is a testament to its geographical diversity. The towering Himalayas, forming a natural barrier in the southwest, give rise to the vast Tibetan Plateau, the world’s highest and largest plateau. This region, known for its harsh climate and unique culture, holds immense ecological and strategic importance.
Moving eastward, the terrain gradually descends, transitioning into the fertile plains of the Yellow River and the Yangtze River basins. These river systems, crucial for agriculture and transportation, have been the cradle of Chinese civilization for centuries.
Further east, the country stretches towards the Pacific Ocean, where coastal provinces experience a humid subtropical climate. This region, known for its bustling cities and thriving industries, is a key driver of China’s economic growth.
Surrounding Countries: A Mosaic of Cultures and Connections:
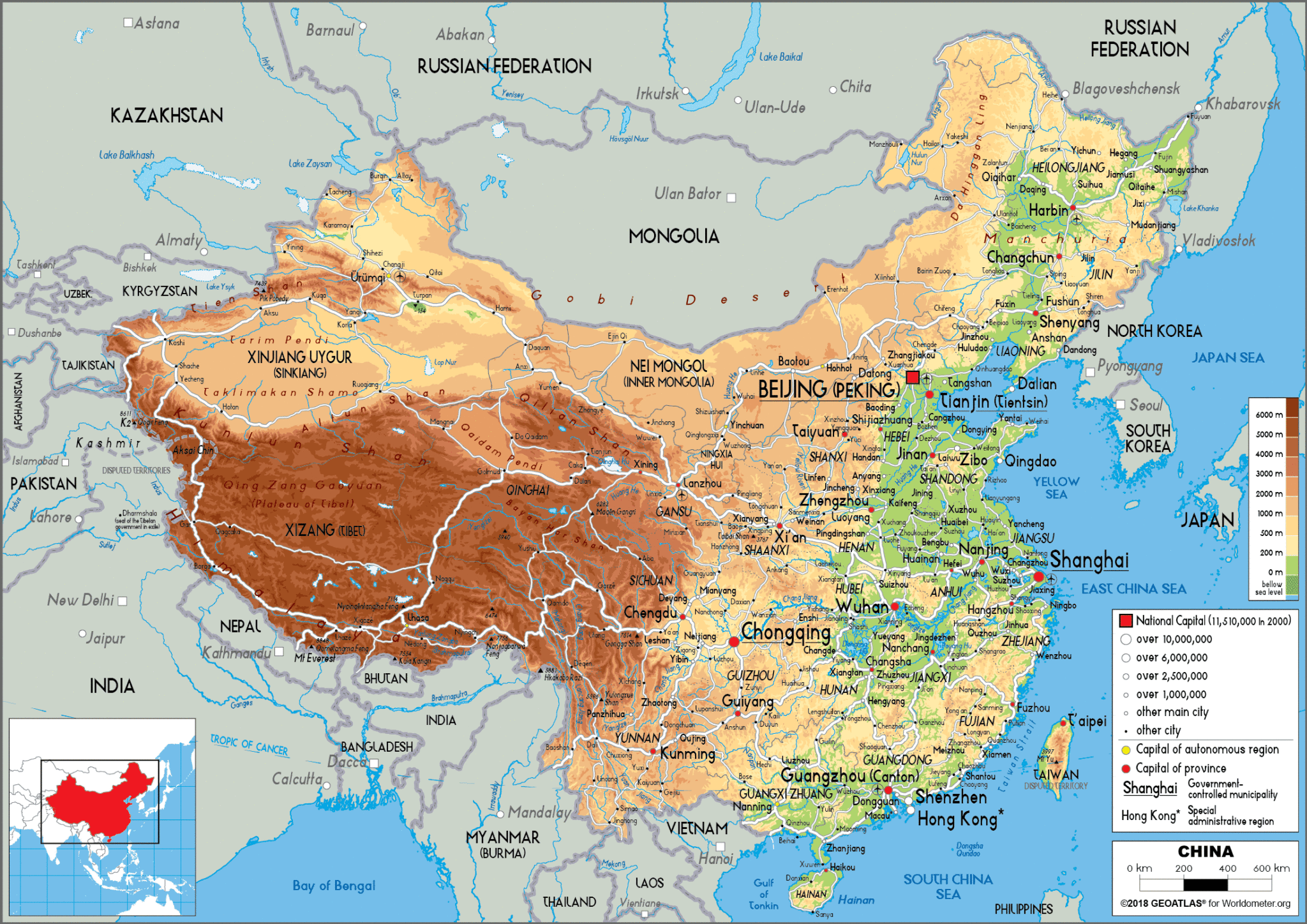
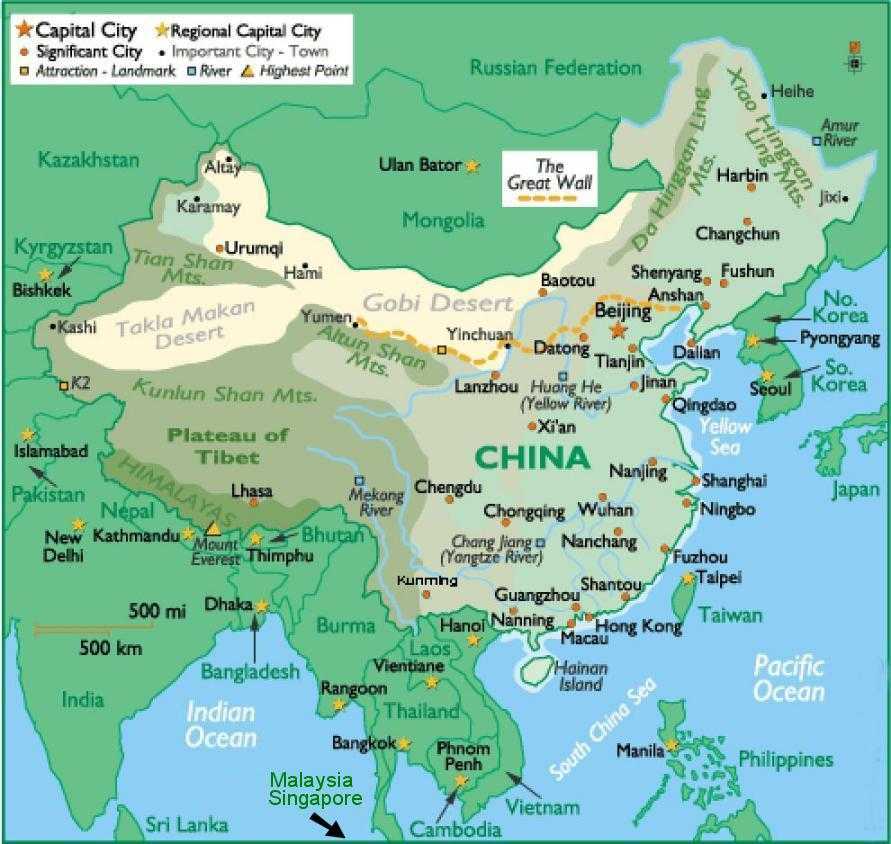
China shares land borders with 14 countries, each contributing to a complex tapestry of cultural, economic, and political interactions.
To the north:
- Mongolia: A landlocked country known for its steppes and nomadic traditions, Mongolia shares a long history with China, marked by both cooperation and conflict.
- Russia: The world’s largest country, Russia shares a vast border with China, encompassing the Amur River and the mountainous region of the Altai Mountains. The relationship between the two nations is characterized by a mix of cooperation and competition, driven by economic interests and geopolitical considerations.
To the east:
- North Korea: A communist state bordering China in the northeast, North Korea’s relationship with China is marked by a strong historical and political alliance.
- South Korea: Separated from North Korea by a heavily fortified border, South Korea has developed a complex and dynamic relationship with China, driven by economic interdependence and cultural exchange.
To the south:
- Vietnam: A Southeast Asian country with a long coastline, Vietnam shares a border with China in the southwest. The relationship between the two countries is marked by a complex history of conflicts and cooperation.
- Laos: A landlocked country in Southeast Asia, Laos borders China in the west. The relationship between the two countries is characterized by growing economic cooperation and infrastructure development.
- Myanmar: A Southeast Asian country with a diverse landscape, Myanmar shares a border with China in the southwest. The relationship between the two countries is characterized by economic cooperation and political influence.
- India: The world’s second most populous country, India shares a long and complex border with China in the southwest. The relationship between the two nations is marked by territorial disputes, economic competition, and strategic rivalry.
To the west:
- Pakistan: A South Asian country with a diverse landscape, Pakistan shares a border with China in the west. The relationship between the two countries is characterized by a close strategic partnership, driven by shared interests in countering regional threats and promoting economic development.
- Afghanistan: A landlocked country in Central Asia, Afghanistan shares a border with China in the northwest. The relationship between the two countries is marked by a complex history of political instability and cooperation in counterterrorism efforts.
- Tajikistan: A Central Asian country known for its mountainous terrain, Tajikistan shares a border with China in the west. The relationship between the two countries is characterized by growing economic cooperation and infrastructure development.
- Kyrgyzstan: A Central Asian country known for its mountainous terrain, Kyrgyzstan shares a border with China in the west. The relationship between the two countries is characterized by growing economic cooperation and infrastructure development.
- Kazakhstan: A vast Central Asian country, Kazakhstan shares a border with China in the northwest. The relationship between the two countries is characterized by strong economic ties and cooperation in energy and infrastructure development.
The Significance of China’s Surrounding Countries:
The surrounding countries play a crucial role in China’s national security, economic development, and global influence.
- Economic Growth: China’s economic growth has been driven by its vast resources, skilled workforce, and strategic location. The surrounding countries offer access to markets, resources, and investment opportunities, contributing to China’s economic expansion.
- Regional Stability: China’s relationship with its neighbors is crucial for maintaining regional stability. Cooperation in areas such as trade, infrastructure development, and security ensures a peaceful and prosperous environment for all.
- Global Influence: China’s growing economic and military power has increased its global influence. Its interactions with its surrounding countries, including its involvement in regional organizations and initiatives, shape the regional and global order.
FAQs about China and its Surrounding Countries:
Q: What are the major geographical features of China?
A: China’s geography is diverse, encompassing the Himalayas, the Tibetan Plateau, the Yellow River and Yangtze River basins, and coastal regions. These features have shaped China’s history, culture, and economy.
Q: How does China’s relationship with its surrounding countries impact its economy?
A: China’s surrounding countries offer access to markets, resources, and investment opportunities, contributing to its economic growth.
Q: What are the major geopolitical challenges facing China in its relations with its neighbors?
A: China faces geopolitical challenges in its relations with its neighbors, including territorial disputes, economic competition, and strategic rivalry.
Q: How does China’s relationship with its surrounding countries affect its global influence?
A: China’s interactions with its neighbors, including its involvement in regional organizations and initiatives, shape the regional and global order.
Tips for Understanding China and its Surrounding Countries:
- Study the history of the region: Understanding the historical interactions between China and its neighbors provides context for contemporary relationships.
- Analyze the economic and political landscape: Understanding the economic and political dynamics between China and its neighbors provides insights into their current and future interactions.
- Follow developments in regional organizations: China’s involvement in regional organizations, such as the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, provides insight into its regional policies and priorities.
Conclusion:
China’s map and its surrounding countries are interconnected in a complex and dynamic way. Understanding this relationship is crucial for comprehending the nation’s history, culture, and current affairs. The interactions between China and its neighbors shape the regional and global landscape, influencing economic development, geopolitical stability, and global influence. As China continues to play an increasingly important role in the world, its relationships with its surrounding countries will continue to evolve and shape the future of the region.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Exploration: China and its Surrounding Countries. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!