A Geographic Overview of North Africa: Unveiling the Region’s Diversity
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview of North Africa: Unveiling the Region’s Diversity
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview of North Africa: Unveiling the Region’s Diversity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview of North Africa: Unveiling the Region’s Diversity
North Africa, a geographically distinct and culturally rich region, extends across the northernmost portion of the African continent. Bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Red Sea to the east, it encompasses a vast expanse of land characterized by diverse landscapes, from the Sahara Desert’s arid expanse to the fertile Nile River Valley. This article delves into the geographical and political divisions of North Africa, providing a comprehensive understanding of its unique characteristics.
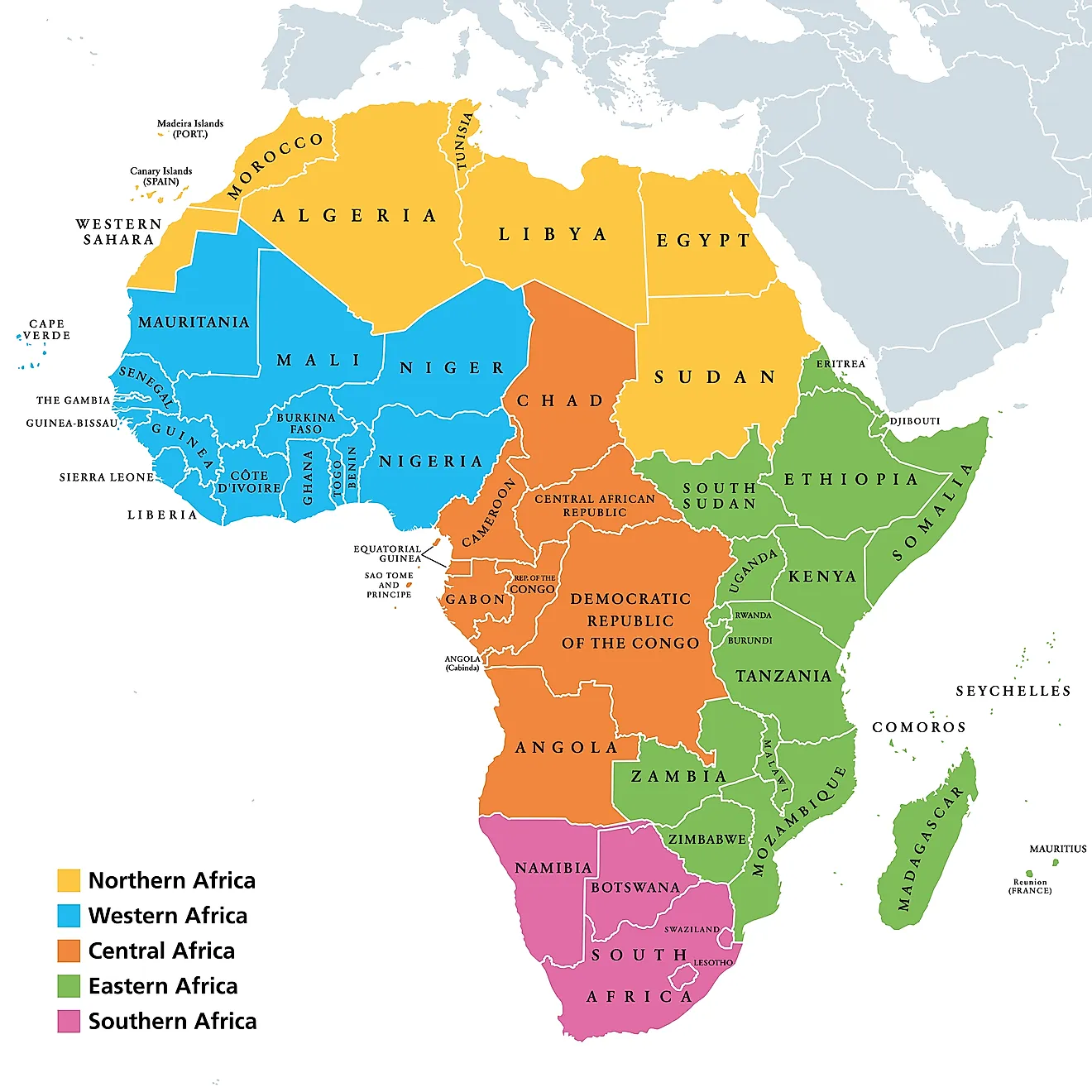
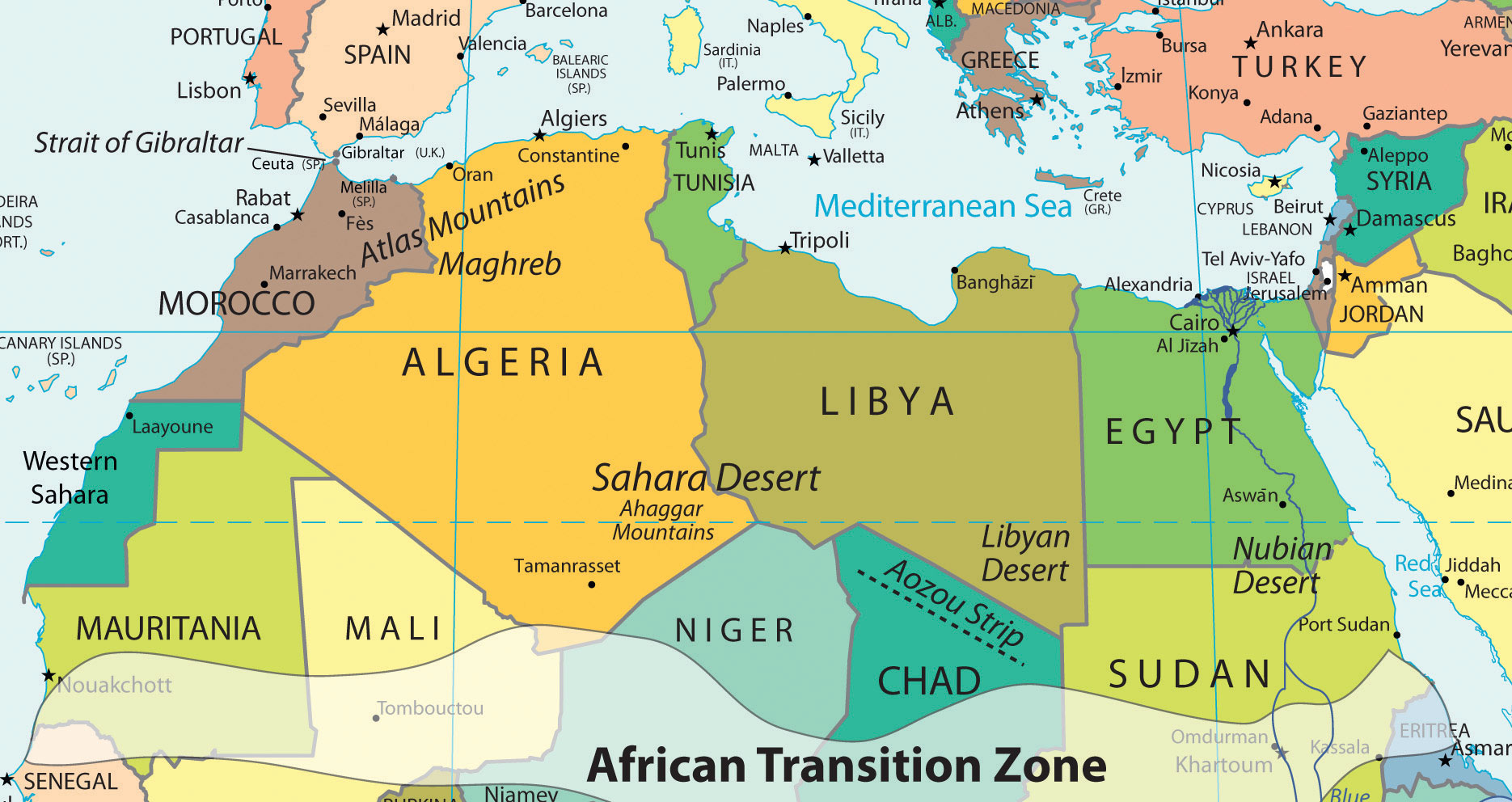
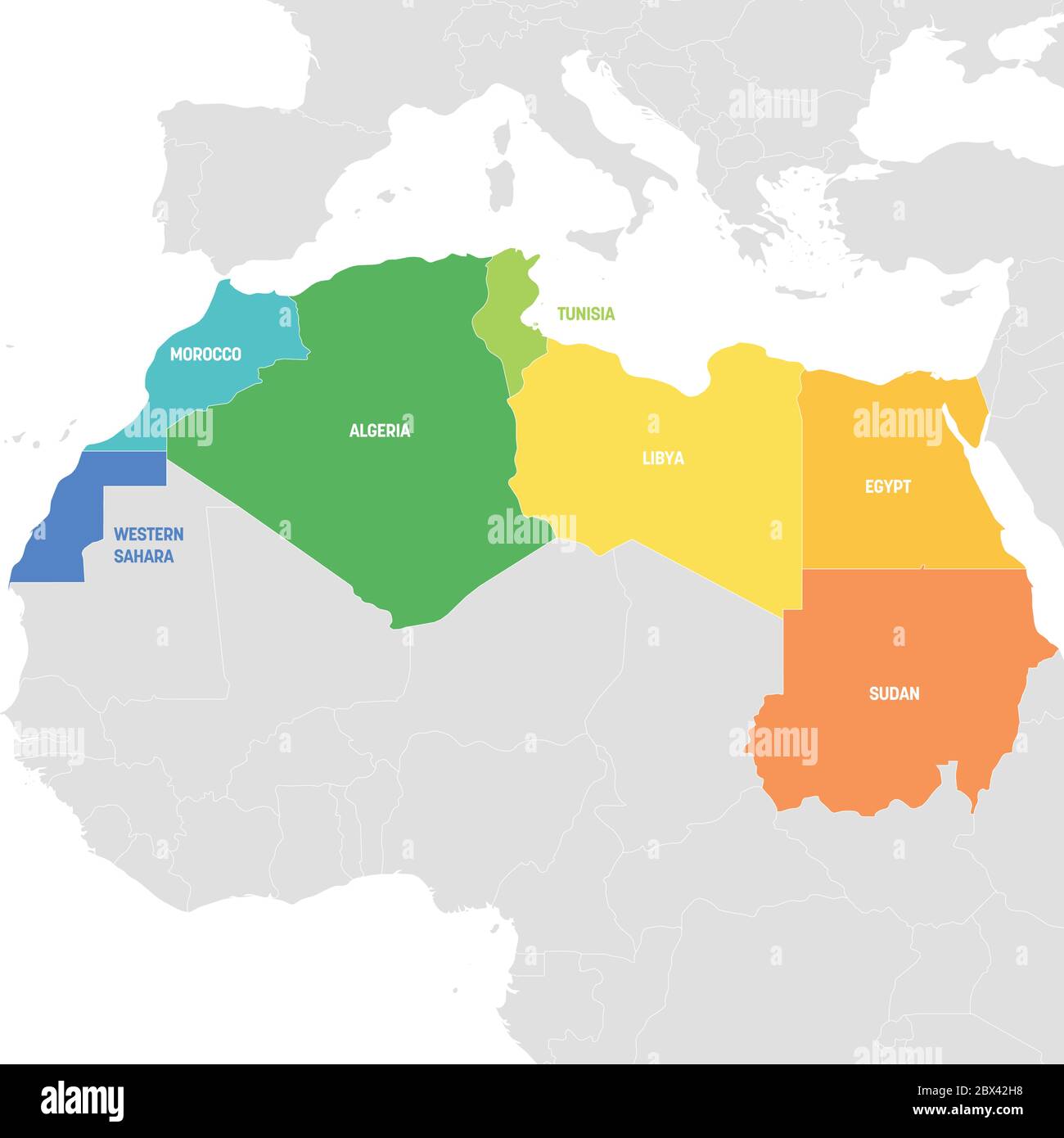
The Countries of North Africa:
North Africa is home to seven distinct countries, each with its own unique history, culture, and political landscape. These countries, listed from west to east, are:
-
Morocco: Situated on the northwestern edge of Africa, Morocco boasts a diverse geography, encompassing the Atlas Mountains, fertile plains, and a long coastline. Its strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Africa has shaped its history and cultural identity.
-
Algeria: The largest country in Africa and the Arab world, Algeria is dominated by the Sahara Desert, which covers the majority of its territory. Its coastline along the Mediterranean Sea provides access to vital shipping routes and resources.
-
Tunisia: Located on the northern coast of Africa, Tunisia is a relatively small country known for its vibrant culture, beautiful beaches, and ancient Roman ruins. Its strategic location has historically made it a significant trading hub.
-
Libya: Situated in the northeastern part of North Africa, Libya is characterized by its vast desert landscape and abundant oil reserves. Its strategic location along the Mediterranean Sea has made it a crucial player in regional politics.
-
Egypt: Straddling the northeastern corner of Africa, Egypt is renowned for its ancient civilization, the Nile River, and the Suez Canal, a vital waterway connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea. Its rich history and cultural heritage make it a major tourist destination.
-
Sudan: Situated in the eastern part of North Africa, Sudan is the third-largest country in Africa. It is characterized by a diverse geography, including the Sahara Desert, the Nile River, and fertile plains. Its cultural and ethnic diversity is reflected in its rich history and traditions.
-
Western Sahara: A disputed territory located on the western edge of North Africa, Western Sahara is largely controlled by Morocco. Its future remains uncertain, with ongoing territorial disputes and political complexities.
The Importance of Geography:
The geography of North Africa plays a crucial role in shaping its history, culture, and economic development. The vast expanse of the Sahara Desert has historically presented challenges to communication, trade, and settlement, influencing the distribution of population and the development of unique adaptations to its harsh environment. The fertile Nile River Valley, in contrast, has been a center of civilization for millennia, providing vital resources and fostering agricultural development.
The Mediterranean Sea, a vital maritime route, has connected North Africa to Europe for centuries, facilitating trade, cultural exchange, and political interaction. This strategic location has also made the region a focal point of historical events and international relations.
Understanding the Diverse Cultures:
North Africa is a melting pot of cultures, influenced by centuries of interaction between indigenous Berber populations, Arab invaders, and European colonizers. The region’s cultural diversity is reflected in its languages, religions, traditions, and arts.
-
Arabic: The dominant language in North Africa, Arabic is spoken by the majority of the population. However, various dialects exist, reflecting the region’s diverse cultural heritage.
-
Berber: A group of indigenous languages spoken by Berber communities in North Africa, Berber languages have survived despite centuries of Arab influence.
-
Islam: The predominant religion in North Africa, Islam has deeply influenced the region’s culture, social norms, and legal systems.
-
Traditional Arts: North African art forms, such as pottery, textiles, jewelry, and music, reflect the region’s rich cultural heritage and diverse artistic traditions.
Economic Development and Challenges:
North Africa faces a range of economic challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and uneven distribution of resources. However, the region also boasts significant potential for growth, driven by its rich natural resources, strategic location, and growing population.
-
Oil and Gas: Significant oil and gas reserves in Libya, Algeria, and Egypt contribute significantly to their economies, but also pose challenges related to resource management and environmental sustainability.
-
Tourism: The region’s rich history, cultural heritage, and stunning landscapes attract millions of tourists annually, contributing to economic growth and employment.
-
Agriculture: While the Sahara Desert dominates the landscape, fertile areas along the Nile River Valley and coastal regions support significant agricultural production, providing food security and employment.
FAQs about the Countries of North Africa:
1. What are the most common languages spoken in North Africa?
The most common languages spoken in North Africa are Arabic and Berber. Arabic is the official language of all North African countries, while Berber languages are spoken by indigenous communities in Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. French is also widely spoken in many countries due to their colonial history.
2. What are the major religions practiced in North Africa?
Islam is the dominant religion in North Africa, practiced by the majority of the population. However, other religions, such as Christianity and Judaism, are also present in smaller communities.
3. What are the major economic activities in North Africa?
Major economic activities in North Africa include oil and gas extraction, tourism, agriculture, and fishing. The region also boasts significant mineral resources, including phosphates and iron ore.
4. What are the key challenges facing North Africa?
Key challenges facing North Africa include poverty, unemployment, political instability, environmental degradation, and climate change. These challenges are interconnected and require multifaceted solutions.
5. What are the opportunities for development in North Africa?
Opportunities for development in North Africa include harnessing its natural resources, promoting tourism, investing in education and infrastructure, and fostering regional cooperation.
Tips for Exploring North Africa:
-
Research your destination: Each country in North Africa has its own unique culture, history, and attractions. Researching your destination beforehand will enhance your travel experience.
-
Respect local customs: North Africa is a region with strong cultural traditions. Respecting local customs and traditions will ensure a positive and enriching experience.
-
Learn basic Arabic phrases: While English is spoken in tourist areas, learning basic Arabic phrases will enhance your interactions with locals.
-
Embrace the diversity: North Africa is a melting pot of cultures, religions, and traditions. Embrace the region’s diversity and immerse yourself in its unique experiences.
-
Consider visiting during the shoulder seasons: To avoid the peak tourist season and experience more favorable weather conditions, consider traveling during the shoulder seasons (spring and fall).
Conclusion:
North Africa is a region of immense diversity, encompassing vibrant cultures, rich history, stunning landscapes, and significant economic potential. Understanding its geographical, political, and cultural complexities is crucial for appreciating its unique character and navigating its challenges. By promoting regional cooperation, investing in education and infrastructure, and fostering sustainable development, North Africa can unlock its full potential and contribute to a more prosperous and peaceful future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview of North Africa: Unveiling the Region’s Diversity. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!