A Geographic Exploration of Russia: Unraveling the Immensity
Related Articles: A Geographic Exploration of Russia: Unraveling the Immensity
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Exploration of Russia: Unraveling the Immensity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Exploration of Russia: Unraveling the Immensity
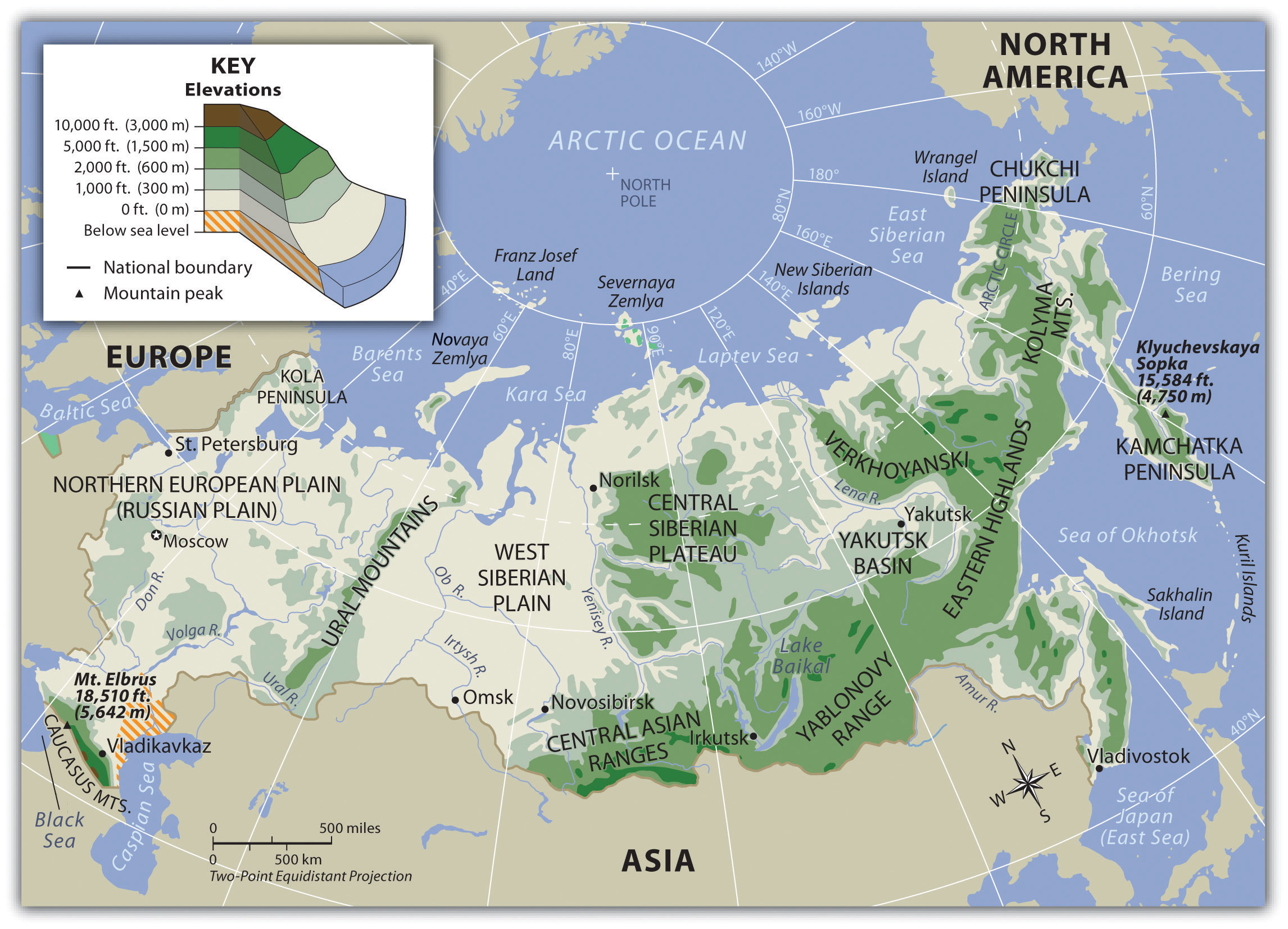
Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, spans eleven time zones and encompasses a vast and diverse tapestry of landscapes, cultures, and natural resources. Its geographic expanse, stretching from the Baltic Sea in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east, presents a unique challenge and opportunity for understanding its complexity. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Russia’s geography, highlighting its defining characteristics and the significance of its vastness.
A Land of Extremes: The Geographic Features of Russia
Russia’s geographic profile is marked by a range of extremes. Its northernmost point, Cape Chelyuskin, sits within the Arctic Circle, while its southernmost point, Mount Bazardüzü, lies within the Caucasus Mountains. This vast north-south expanse results in a wide variation in climate, ranging from the frigid tundra of the Arctic to the subtropical Black Sea coast.
The Russian Plain: A Foundation for History and Development
At the heart of Russia lies the vast East European Plain, a fertile and historically significant region that has played a crucial role in the country’s development. The plain, stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Ural Mountains, provides fertile land for agriculture and has historically served as a conduit for trade and migration. Major cities like Moscow and St. Petersburg, both located on the plain, have been centers of political and cultural power for centuries.
Ural Mountains: A Natural Divide
The Ural Mountains, stretching for over 2,000 kilometers, serve as a natural boundary between Europe and Asia, separating the East European Plain from the vast Siberian lowlands. The Urals are rich in mineral resources, including iron ore, copper, and precious metals, which have been crucial to Russia’s industrial development.
Siberia: A Land of Untamed Beauty and Resources
Beyond the Urals lies Siberia, a vast region encompassing over 77% of Russia’s total land area. Characterized by its taiga forests, frozen tundras, and vast expanses of permafrost, Siberia is home to a diverse array of natural resources, including timber, oil, gas, and minerals. The region also boasts a unique ecosystem, harboring a rich variety of flora and fauna, including the endangered Siberian tiger.
The Far East: A Bridge to the Pacific
Russia’s Far East, located along the Pacific coast, is a region of immense strategic importance. It borders China, North Korea, and Japan, making it a crucial link between Russia and the Asia-Pacific region. The region is rich in natural resources, including timber, fish, and minerals, and plays a key role in Russia’s economic development.
The Caucasus Mountains: A Region of Diverse Cultures and Landscapes
The Caucasus Mountains, located in the southwest of Russia, are a region of breathtaking beauty and cultural diversity. Home to a multitude of ethnic groups, the Caucasus region boasts a rich history and a unique cultural heritage. The mountains are also a source of important natural resources, including oil, gas, and minerals.
The Significance of Russia’s Geography
Russia’s vast geographic expanse has had a profound impact on its history, culture, and development. The country’s diverse landscapes and climate zones have shaped its economic activities, its social structures, and its cultural traditions. The vastness of the country has also presented challenges, particularly in terms of infrastructure development, resource management, and maintaining national unity.
Challenges and Opportunities: The Impact of Russia’s Geography
1. Infrastructure Development: The vast distances and challenging terrain in Russia have presented significant challenges for infrastructure development. Building roads, railways, and pipelines across such a vast and diverse landscape requires significant investment and engineering expertise.
2. Resource Management: Russia’s abundant natural resources have been a source of both wealth and challenges. The country’s vast forests, mineral deposits, and energy reserves require careful management to ensure sustainable development and environmental protection.
3. National Unity: Maintaining national unity across such a vast and diverse territory has been a recurring challenge for Russia. Regional differences in culture, language, and economic development can sometimes create tensions.
4. Climate Change: Russia’s vast and diverse geography makes it particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Rising temperatures, melting permafrost, and extreme weather events pose significant threats to the country’s infrastructure, ecosystems, and economic activities.
5. Geopolitical Significance: Russia’s strategic location, bordering numerous countries and spanning two continents, makes it a key player in global politics. Its vast territory and natural resources have historically been a source of both conflict and cooperation.
FAQs about Russia’s Geography
Q: What is the largest city in Russia?
A: Moscow, with a population of over 12.5 million, is the largest city in Russia.
Q: What are the main rivers in Russia?
A: Some of the major rivers in Russia include the Volga, Ob, Yenisei, Lena, and Amur.
Q: What are the major natural resources found in Russia?
A: Russia is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, coal, timber, iron ore, copper, gold, and diamonds.
Q: What are the main climate zones in Russia?
A: Russia experiences a wide range of climates, including tundra, taiga, steppe, and subtropical.
Q: What are the major ethnic groups in Russia?
A: Russia is home to a diverse range of ethnic groups, including Russians, Ukrainians, Tatars, Bashkirs, and Chechens.
Tips for Understanding Russia’s Geography
1. Use a Detailed Map: A detailed map of Russia is essential for understanding its vastness and the location of its major cities, rivers, and mountains.
2. Explore Online Resources: Numerous online resources, such as Google Maps, Wikipedia, and government websites, offer detailed information about Russia’s geography, including maps, satellite images, and historical data.
3. Read Books and Articles: Books and articles about Russian history, culture, and geography can provide valuable insights into the country’s unique geographic features and their impact on its development.
4. Watch Documentaries: Documentaries about Russia, its people, and its landscapes can offer a visually engaging and informative way to learn about the country’s geography.
5. Travel to Russia: If possible, traveling to Russia is the best way to experience its diverse landscapes and cultures firsthand.
Conclusion: A Land of Endless Possibilities
Russia’s vast geography is a defining characteristic of the country, shaping its history, culture, and development. Its diverse landscapes, abundant resources, and strategic location have made it a significant player on the global stage. While its size presents challenges, it also offers immense opportunities for economic growth, scientific exploration, and cultural exchange. Understanding Russia’s geography is crucial for comprehending its past, present, and future.

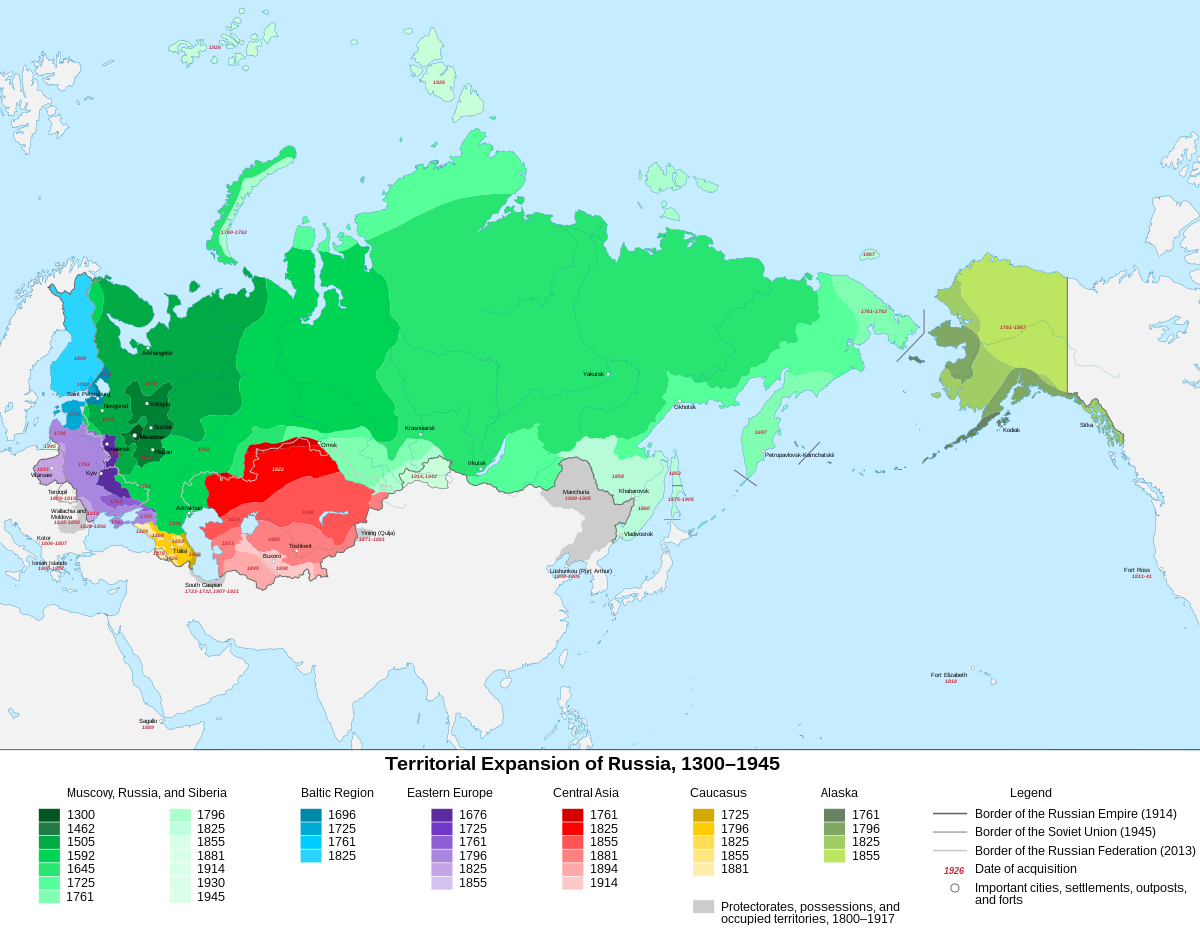
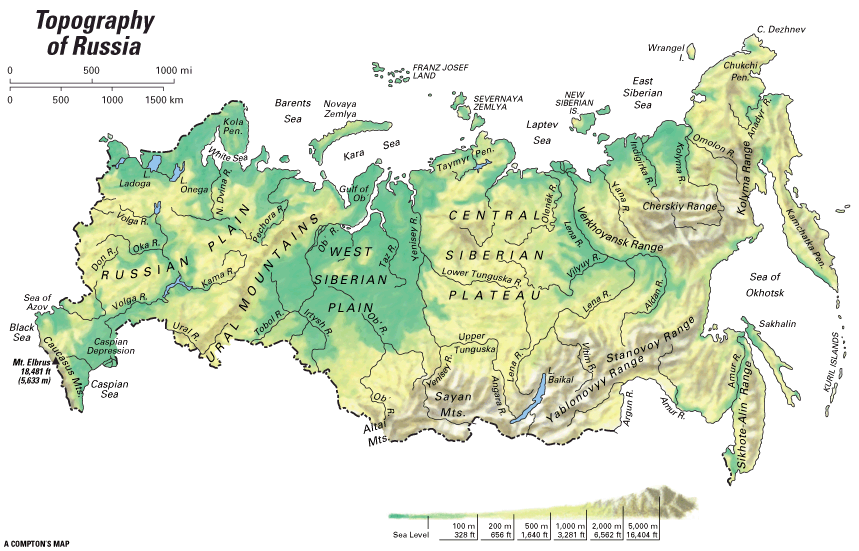





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Exploration of Russia: Unraveling the Immensity. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!