A Comprehensive Look at North America’s Diverse Landscape: Unveiling the Physical Feature Map
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at North America’s Diverse Landscape: Unveiling the Physical Feature Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at North America’s Diverse Landscape: Unveiling the Physical Feature Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at North America’s Diverse Landscape: Unveiling the Physical Feature Map

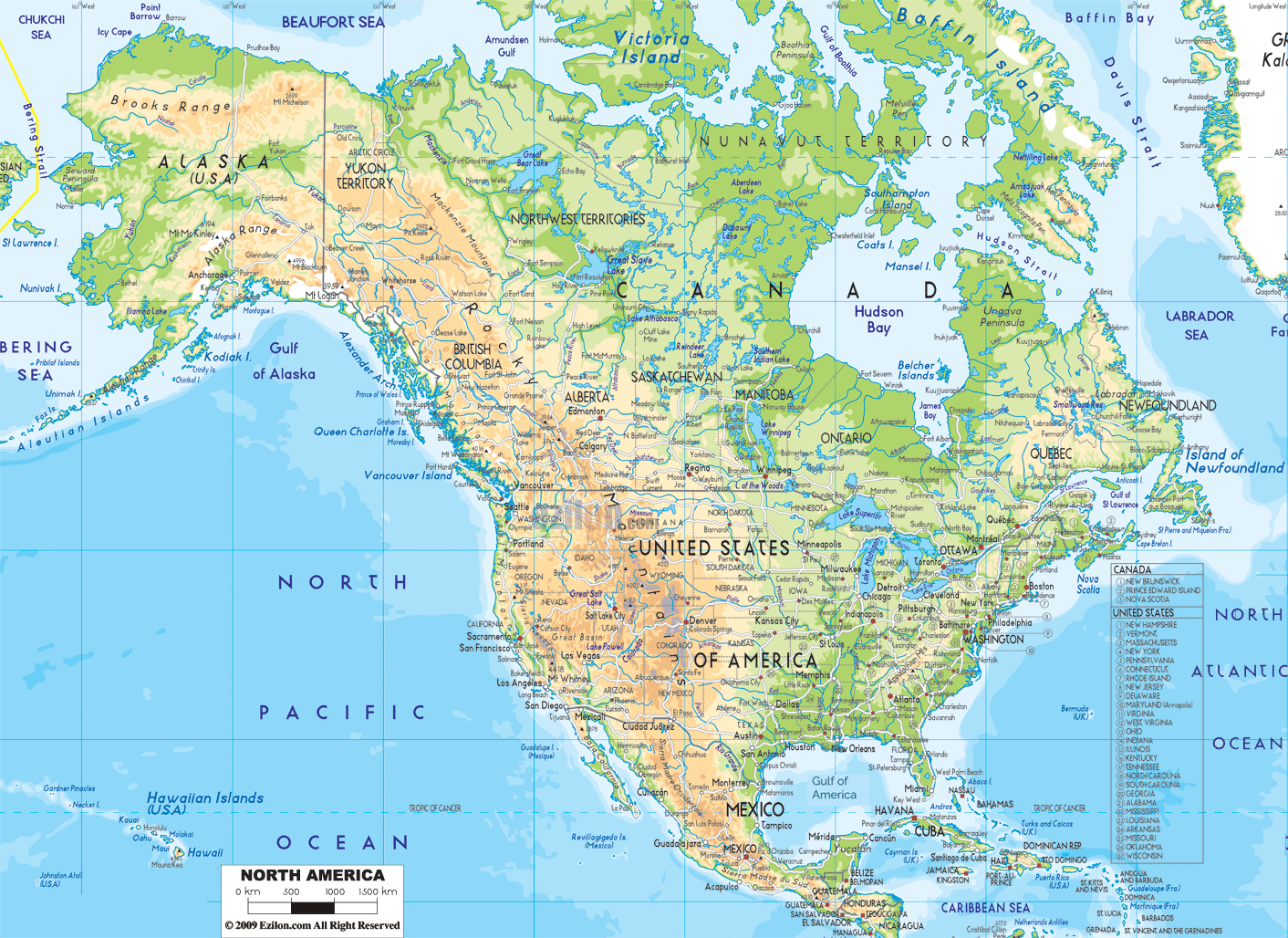
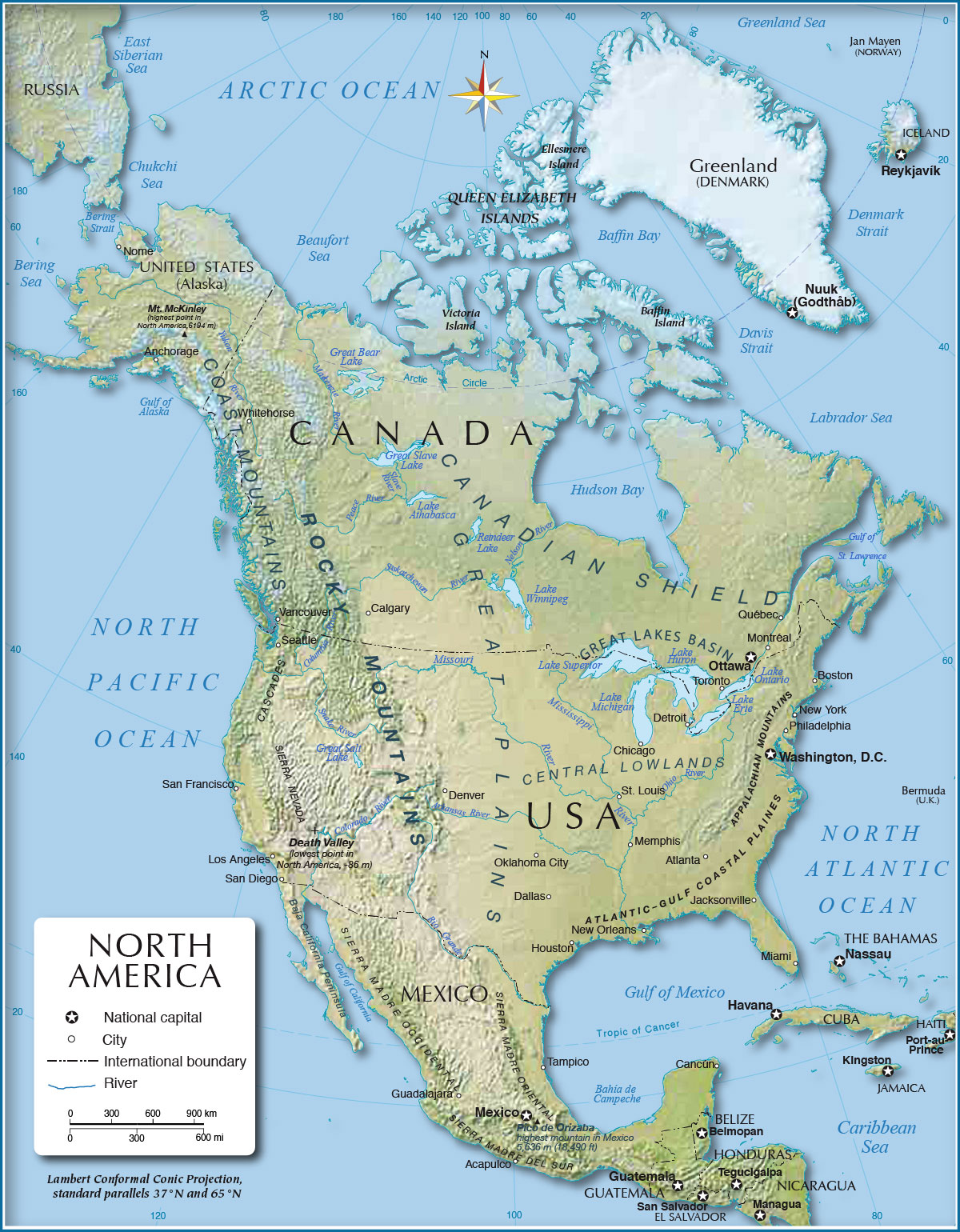
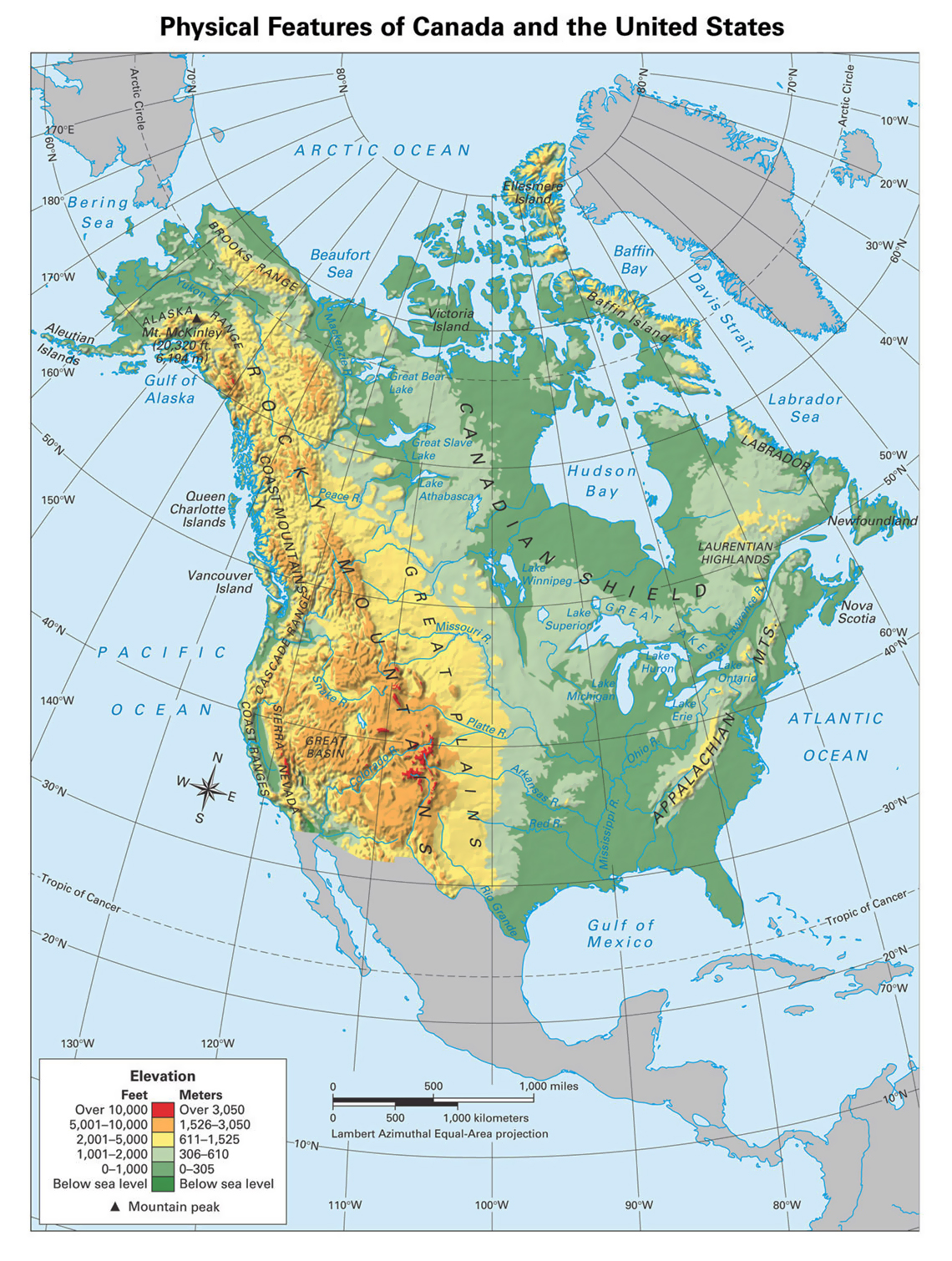
North America, a continent of vast and varied landscapes, boasts a remarkable tapestry of physical features that have shaped its history, culture, and environment. A physical feature map of North America provides a visual representation of this diverse terrain, highlighting the intricate interplay of mountains, plains, plateaus, rivers, and coastlines that define its character. Understanding these features is crucial for comprehending the continent’s unique ecosystems, resource distribution, and human settlements.
A Visual Guide to North America’s Geography
A physical feature map of North America serves as a visual key to understanding the continent’s geographical makeup. It presents a clear and concise overview of the major landforms, water bodies, and elevation changes that characterize the region. These maps typically employ color variations, contour lines, and symbols to depict:
- Mountains: The continent’s backbone is formed by the towering Rocky Mountains, stretching from Canada to Mexico. The Appalachian Mountains, a much older range, run along the eastern coast. Other notable mountain ranges include the Sierra Nevada, the Cascade Range, and the Coast Mountains.
- Plains: Vast, flat expanses of land dominate the central and eastern regions of North America. The Great Plains, stretching from the Rocky Mountains to the Mississippi River, are characterized by fertile soils and a relatively flat topography. The Coastal Plains, bordering the Atlantic and Gulf coasts, are lower-lying and often feature wetlands and estuaries.
- Plateaus: Elevated, relatively flat areas, plateaus are prominent features in North America. The Colorado Plateau, renowned for its canyons and mesas, is a striking example. The Canadian Shield, a vast expanse of ancient rock, is another significant plateau covering much of northern Canada.
- Rivers: North America is crisscrossed by a network of major rivers, shaping its landscape and providing crucial transportation routes. The Mississippi River, the continent’s longest, flows southward through the heartland. Other notable rivers include the Missouri, the Rio Grande, the St. Lawrence, and the Yukon.
- Coastlines: North America boasts diverse coastlines, ranging from the rugged cliffs of the Pacific coast to the sandy shores of the Atlantic and Gulf coasts. These coastlines are shaped by various geological processes, including tectonic activity, erosion, and sedimentation.
The Importance of Understanding North America’s Physical Features
Beyond its aesthetic appeal, a physical feature map of North America holds immense value for a variety of disciplines and pursuits:
- Environmental Studies: The map provides a foundation for understanding the continent’s diverse ecosystems, from the boreal forests of Canada to the deserts of the southwestern United States. It helps identify areas of ecological sensitivity, resource distribution, and potential threats to biodiversity.
- Resource Management: By highlighting the location of natural resources such as minerals, oil, gas, and forests, the map guides resource extraction and management practices. It aids in identifying areas suitable for agriculture, forestry, and energy production.
- Infrastructure Development: Understanding the terrain is crucial for planning and constructing transportation networks, pipelines, and other infrastructure projects. The map helps identify challenges and opportunities related to terrain, elevation, and water bodies.
- Climate Analysis: The map provides insights into the continent’s climate patterns, influenced by factors such as elevation, proximity to water bodies, and prevailing wind patterns. This understanding is crucial for predicting weather events, managing water resources, and adapting to climate change.
- Historical Context: The physical features of North America have played a pivotal role in shaping its history and culture. Understanding the terrain helps explain the migration patterns of indigenous peoples, the development of trade routes, and the establishment of settlements.
Frequently Asked Questions about North America’s Physical Feature Map
Q: What are the most prominent features on a North America physical feature map?
A: The most prominent features are the Rocky Mountains, the Great Plains, the Mississippi River, the Appalachian Mountains, and the various coastlines.
Q: What are the main differences between the eastern and western regions of North America?
A: The eastern region is characterized by older, rounded mountains (Appalachians), vast plains, and a network of navigable rivers. The western region, on the other hand, features towering mountain ranges (Rockies, Sierra Nevada), plateaus, and a drier climate.
Q: How do physical features influence the climate of North America?
A: Mountains create rain shadows, leading to drier conditions on their leeward sides. Coastal areas experience more moderate climates due to the moderating influence of the ocean. Elevation also plays a significant role, with higher altitudes generally experiencing colder temperatures.
Q: What are some of the environmental challenges facing North America?
A: North America faces challenges such as deforestation, pollution, climate change, and habitat loss. Understanding the continent’s physical features is crucial for addressing these challenges and implementing sustainable management practices.
Tips for Using a North America Physical Feature Map
- Study the legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols, colors, and other conventions used on the map.
- Focus on specific regions: Explore the map in detail to understand the unique features of different areas.
- Compare and contrast: Analyze the differences in topography, elevation, and vegetation between different regions.
- Relate to other maps: Combine the physical feature map with other maps, such as climate maps or population density maps, to gain a more comprehensive understanding.
- Engage in hands-on activities: Use the map to plan virtual or real-life expeditions, explore historical events, or design hypothetical infrastructure projects.
Conclusion
A physical feature map of North America is an indispensable tool for understanding the continent’s remarkable landscape. By visually representing its diverse terrain, the map provides a foundation for comprehending its ecosystems, resources, history, and cultural development. From its towering mountains to its vast plains, North America’s physical features continue to shape its present and influence its future. By engaging with this map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate interplay of nature and human activity that defines this vast and dynamic continent.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at North America’s Diverse Landscape: Unveiling the Physical Feature Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!