A Comprehensive Exploration of Canada’s Geographical Map
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of Canada’s Geographical Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of Canada’s Geographical Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Exploration of Canada’s Geographical Map

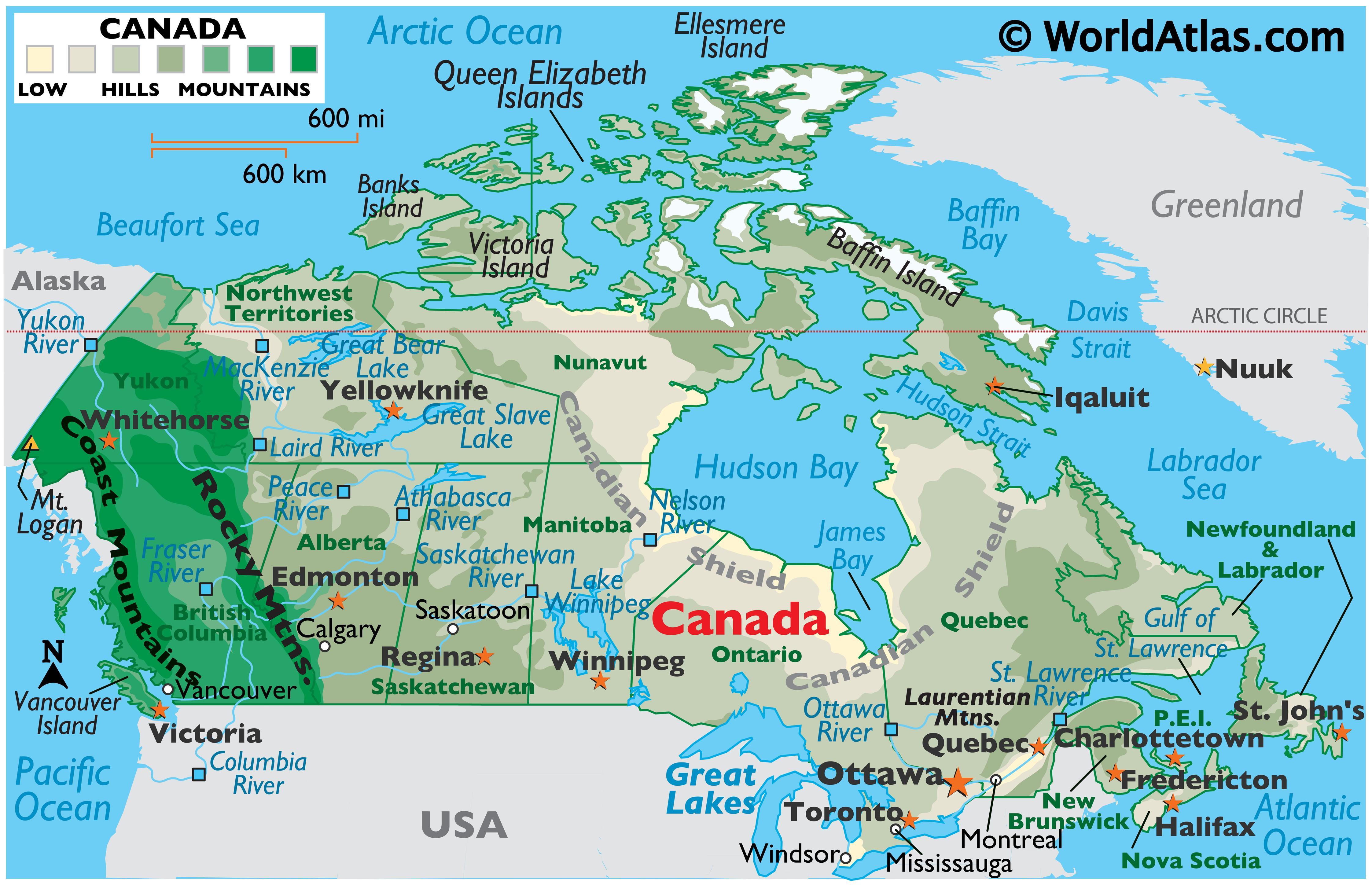
Canada, the second-largest country in the world by land area, boasts a diverse and captivating landscape sculpted by geological forces and shaped by climatic extremes. Understanding the country’s geographical map is essential for appreciating its natural wonders, diverse cultures, and unique challenges. This exploration delves into the key elements of Canada’s geography, highlighting its significance in shaping the nation’s history, economy, and identity.
1. The Vast and Diverse Landscape:
Canada’s geographical map is a testament to its vastness and diversity. Stretching from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, the country encompasses an array of distinct geographical features:
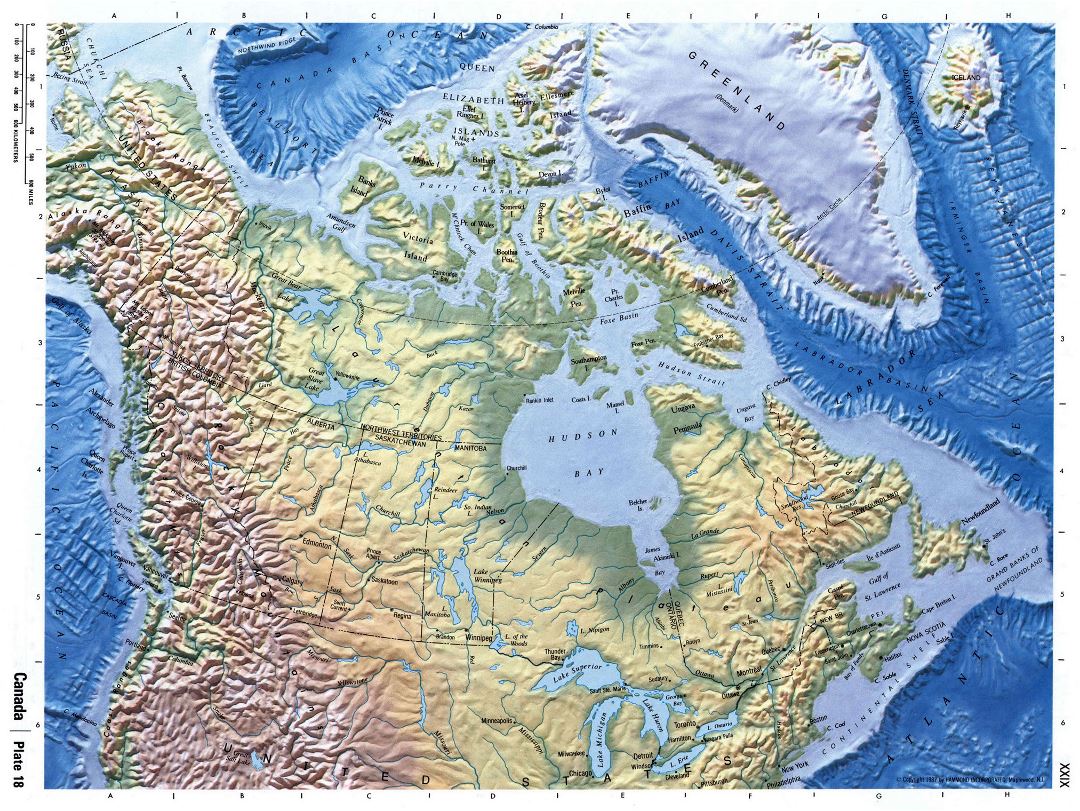
- The Canadian Shield: This ancient geological formation, covering nearly half of Canada’s landmass, is characterized by rugged terrain, numerous lakes, and vast boreal forests. Its rich mineral deposits have played a pivotal role in Canada’s economic development.
- The Rocky Mountains: Rising dramatically along the western border, the Rockies offer breathtaking scenery, abundant wildlife, and world-renowned ski resorts. They also serve as a natural barrier, influencing weather patterns and shaping the distribution of plant and animal life.
- The Great Plains: Stretching east from the Rockies, the plains are a vast expanse of fertile land, ideal for agriculture. This region has historically been the heartland of Canada’s agricultural industry and remains crucial for food production.
- The St. Lawrence Lowlands: Situated in southeastern Canada, this region features fertile soils, abundant water resources, and a temperate climate, making it a major center of population and economic activity.
- The Arctic Archipelago: This vast and remote region comprises numerous islands north of the mainland, characterized by icy landscapes, permafrost, and unique wildlife. Its strategic location and potential for resource extraction have garnered increasing attention in recent years.
2. The Importance of Water:
Canada’s geographical map is intimately linked to water. The country possesses an abundance of freshwater resources, including vast lakes, rivers, and glaciers:
- The Great Lakes: Five interconnected freshwater lakes, shared with the United States, form a vital waterway for transportation, recreation, and economic activity.
- The St. Lawrence River: This major waterway connects the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean, playing a critical role in trade and transportation since the early days of European settlement.
- The Mackenzie River: The longest river in Canada, the Mackenzie flows through the Northwest Territories, connecting the Arctic Ocean to the interior. Its importance lies in its role in transportation, resource extraction, and as a habitat for diverse wildlife.
3. The Influence of Climate:
Canada’s climate varies significantly across its vast geographical expanse. The country experiences a range of climates, from the temperate maritime climate of the Atlantic coast to the frigid Arctic climate in the north:
- The Maritime Climate: Characterized by warm summers, mild winters, and abundant rainfall, this climate prevails along the Atlantic coast, supporting diverse forests and a rich agricultural sector.
- The Continental Climate: Predominating in the interior, this climate features hot summers, cold winters, and moderate rainfall, influencing the growth of grasslands and boreal forests.
- The Arctic Climate: This harsh climate, characterized by extremely low temperatures, long winters, and limited precipitation, prevails in the northern territories, shaping the unique ecosystem and challenging human settlements.
4. The Human Impact:
Canada’s geographical map is not merely a static representation of its landforms and features. It is also a reflection of human activity, shaping the distribution of population, the development of infrastructure, and the impact on the environment:
- Urbanization: Canada’s population is concentrated in major cities along its southern border, with vast areas of the country remaining sparsely populated. This uneven distribution has implications for resource management, infrastructure development, and the preservation of natural landscapes.
- Resource Extraction: Canada’s vast natural resources, including forests, minerals, and oil and gas, have fueled its economic development. However, resource extraction has also raised concerns about environmental sustainability and the impact on Indigenous communities.
- Climate Change: Canada’s geographical map is being reshaped by climate change, with rising temperatures, melting glaciers, and shifting weather patterns. These changes pose significant challenges for infrastructure, agriculture, and the well-being of communities.
5. The Importance of Geographical Knowledge:
Understanding Canada’s geographical map is crucial for various reasons:
- Informed Decision-Making: Knowledge of the country’s diverse landscape, climate, and resources is essential for making informed decisions in areas such as infrastructure development, resource management, and environmental protection.
- Understanding Cultural Diversity: Canada’s diverse geography has played a role in shaping its cultural mosaic. Different regions have developed unique traditions, languages, and ways of life, influenced by their specific geographical characteristics.
- Appreciating Natural Beauty: The geographical map reveals Canada’s breathtaking natural wonders, from the majestic Rocky Mountains to the vast boreal forests. This understanding fosters appreciation for the country’s unique and irreplaceable natural heritage.
FAQs about Canada’s Geographical Map:
1. What is the highest point in Canada?
The highest point in Canada is Mount Logan, located in the Yukon Territory, with an elevation of 5,959 meters (19,551 feet).
2. What is the longest river in Canada?
The longest river in Canada is the Mackenzie River, flowing through the Northwest Territories and measuring 4,241 kilometers (2,639 miles) in length.
3. What is the largest lake in Canada?
The largest lake in Canada is Great Bear Lake, located in the Northwest Territories, covering an area of 31,150 square kilometers (12,027 square miles).
4. What is the most populous province in Canada?
The most populous province in Canada is Ontario, with a population of over 14 million people.
5. What are the major geographical features of Canada’s East Coast?
The East Coast of Canada is characterized by the Atlantic Provinces, featuring rolling hills, coastal plains, and numerous bays and inlets. The region is also known for its rich maritime history and fishing industry.
6. What are the major geographical features of Canada’s West Coast?
The West Coast of Canada is defined by the Rocky Mountains, the Pacific Ocean, and the coastal rainforest. This region is renowned for its stunning scenery, diverse wildlife, and thriving tourism industry.
7. What are the major geographical features of Canada’s North?
Canada’s North encompasses the vast Arctic Archipelago, characterized by icy landscapes, permafrost, and unique wildlife. This region is sparsely populated, but its strategic location and potential for resource extraction have attracted increasing attention in recent years.
8. What are the main challenges facing Canada due to its geography?
Canada’s vast size and diverse geography present both opportunities and challenges. Some of the key challenges include:
- Infrastructure Development: Building and maintaining infrastructure across such a vast and diverse landscape can be costly and complex.
- Resource Management: Balancing resource extraction with environmental sustainability is a major challenge, particularly in regions with sensitive ecosystems.
- Climate Change: The impacts of climate change, such as rising temperatures, melting glaciers, and shifting weather patterns, pose significant challenges for infrastructure, agriculture, and the well-being of communities.
- Transportation: The vast distances and challenging terrain can make transportation difficult and expensive, particularly in remote regions.
Tips for Understanding Canada’s Geographical Map:
- Use a variety of resources: Explore maps, atlases, online resources, and documentaries to gain a comprehensive understanding of Canada’s geography.
- Focus on key features: Identify the major geographical features, such as the Canadian Shield, the Rocky Mountains, and the Great Lakes, and understand their significance.
- Consider the human impact: Explore how human activity has shaped Canada’s geography, including urbanization, resource extraction, and climate change.
- Travel and experience: Visiting different regions of Canada provides firsthand experience of the country’s diverse landscapes and cultures.
Conclusion:
Canada’s geographical map is a testament to its vastness, diversity, and unique character. From the rugged Canadian Shield to the majestic Rocky Mountains, from the fertile Great Plains to the icy Arctic Archipelago, the country’s landscape is a captivating tapestry of natural wonders. Understanding this map is essential for appreciating Canada’s history, culture, economy, and the challenges it faces in a changing world. By recognizing the significance of its geography, we can foster a deeper appreciation for this remarkable nation and its irreplaceable natural heritage.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of Canada’s Geographical Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!