Unveiling India’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Topographical Map
Related Articles: Unveiling India’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Topographical Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling India’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Topographical Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling India’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Topographical Map
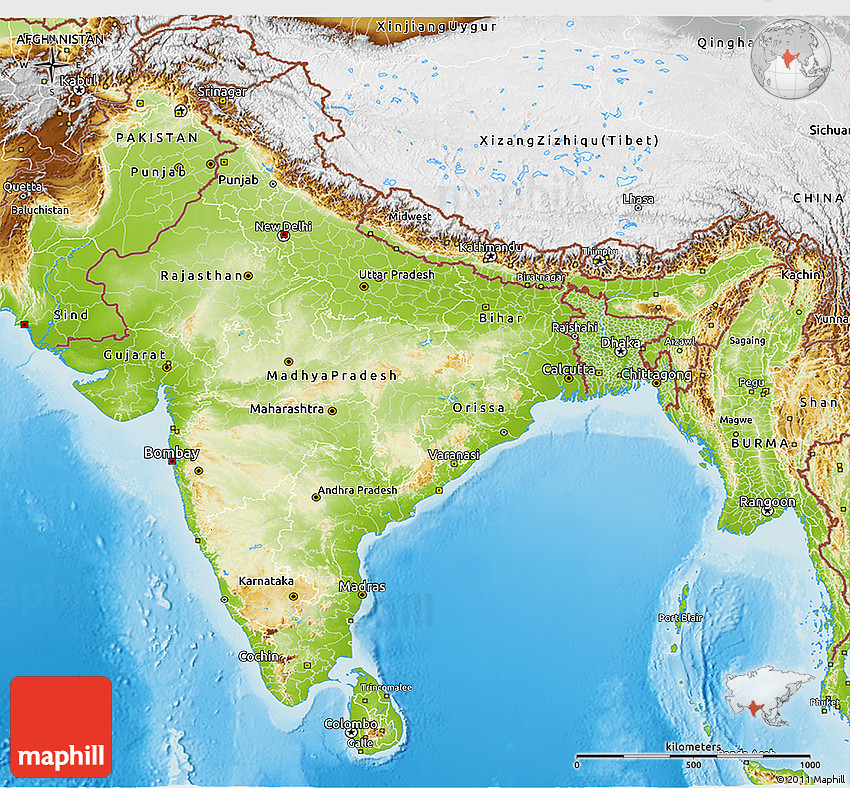
India, a land of unparalleled diversity, is a tapestry woven with vibrant cultures, languages, and landscapes. Understanding the intricate interplay of these elements requires a visual representation of its physical geography. This is where the topographical map of India steps in, offering a detailed and insightful perspective on the country’s diverse topography.
Deciphering the Terrain: A Visual Guide to India’s Topography
A topographical map is a specialized map that showcases the elevation and shape of the land. It utilizes contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation, to depict the terrain’s undulations. These lines create a visual representation of valleys, hills, mountains, and plateaus, providing a three-dimensional understanding of the landscape.
Key Topographical Features of India
The topographical map of India reveals a fascinating array of features that define the country’s landscape:
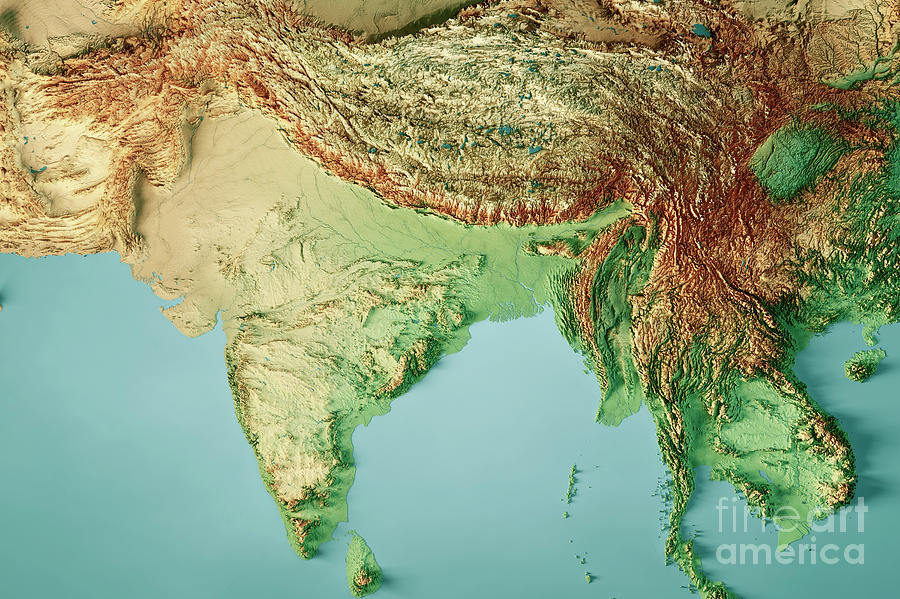
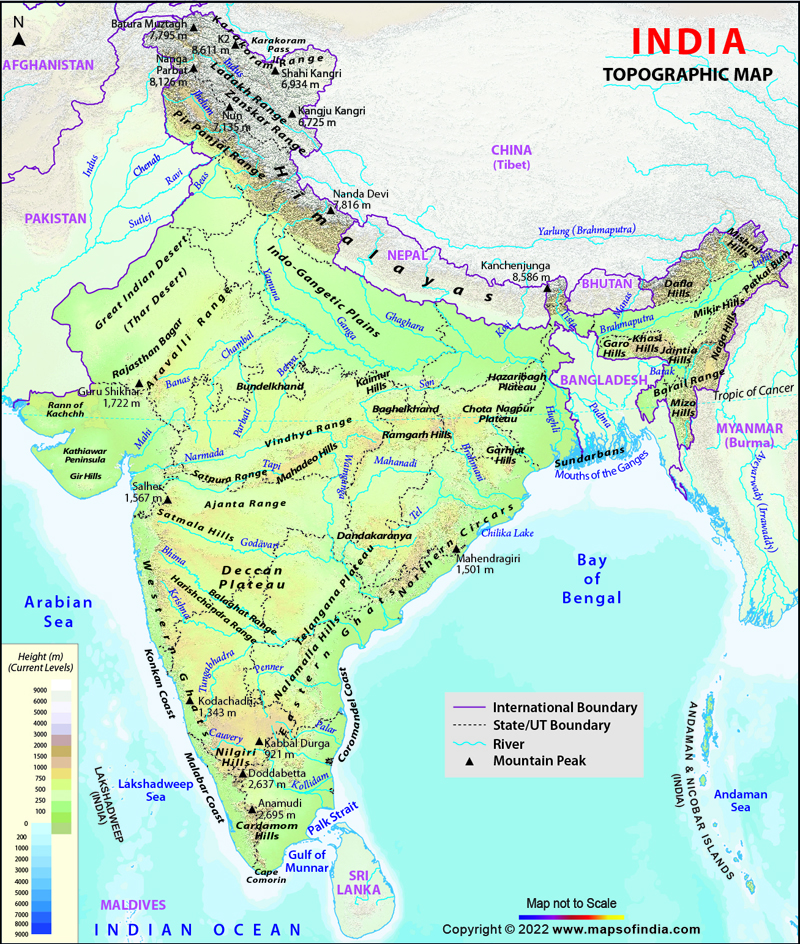
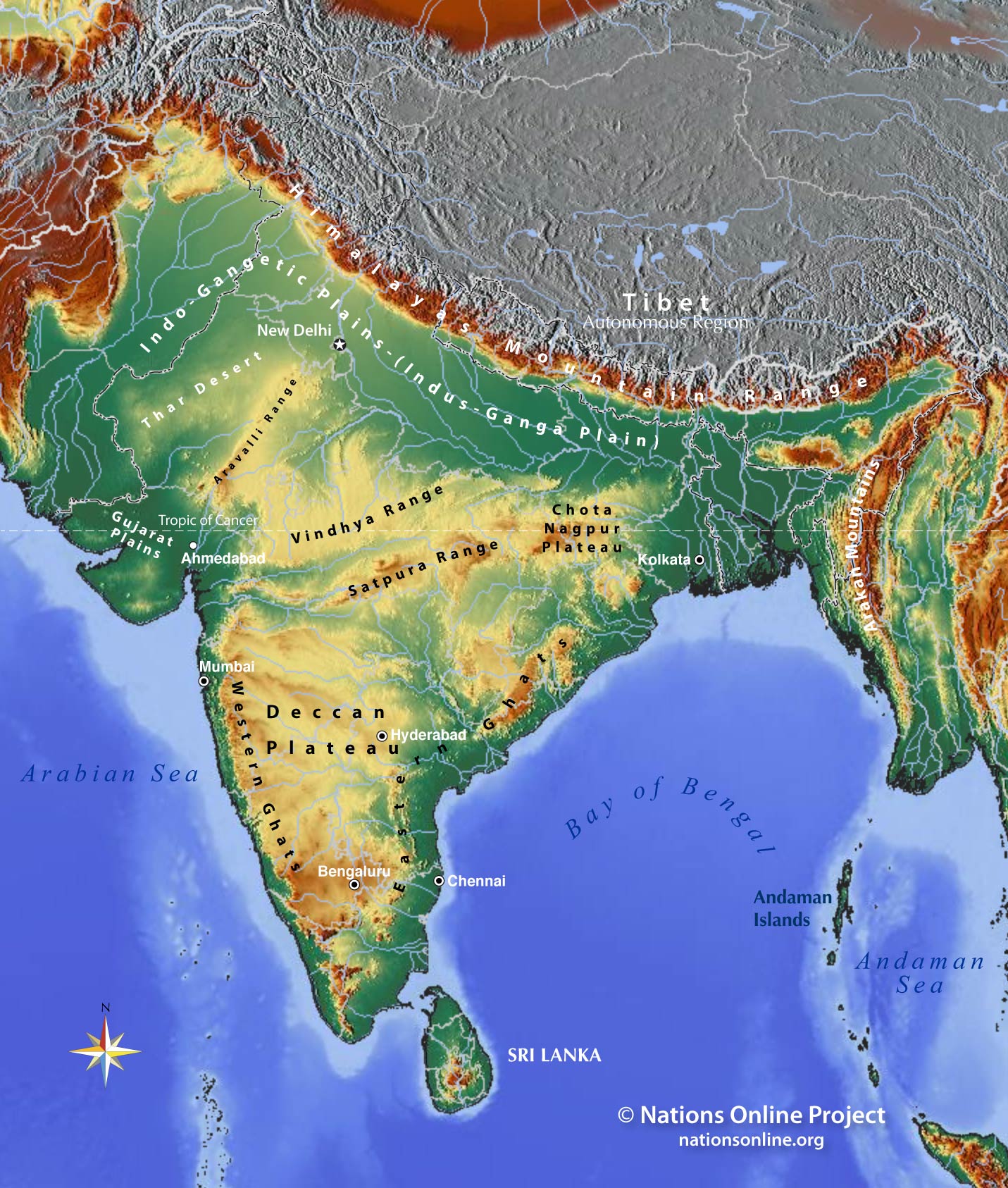
1. The Mighty Himalayas: The towering Himalayan mountain range, forming India’s northern frontier, is a defining feature of the topographical map. This grand geological marvel houses the world’s highest peaks, including Mount Everest, and plays a pivotal role in shaping India’s climate and river systems.
2. The Northern Plains: The vast expanse of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, stretching across northern India, is a product of the deposition of sediments carried by the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra rivers. This fertile region, marked by its flat topography, is the heartland of Indian agriculture and civilization.
3. The Deccan Plateau: Located in the south, the Deccan Plateau is a vast, triangular-shaped plateau formed by volcanic activity. Characterized by its elevated terrain and rugged hills, the Deccan Plateau is home to diverse flora and fauna, including the iconic Deccan thorn scrub forests.
4. The Coastal Plains: India’s coastline is fringed by a network of narrow coastal plains, formed by the deposition of sediments carried by rivers. These plains, characterized by their low elevation and fertile soils, are important centers of agriculture, fishing, and trade.
5. The Western Ghats: Rising along India’s western coast, the Western Ghats are a series of mountain ranges that run parallel to the Arabian Sea. These mountains are characterized by their steep slopes, lush forests, and abundant waterfalls, making them a biodiversity hotspot.
6. The Eastern Ghats: Stretching along India’s eastern coast, the Eastern Ghats are a series of discontinuous ranges, less elevated than the Western Ghats. They are characterized by their gentle slopes, fertile valleys, and numerous rivers.
7. The Thar Desert: Located in northwestern India, the Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is a vast expanse of arid land. Its low rainfall, sandy terrain, and extreme temperatures create a unique ecological environment.
Understanding the Significance of the Topographical Map
The topographical map of India serves as a vital tool for various purposes:
1. Resource Management: Understanding the terrain allows for effective resource management, including water resource allocation, land use planning, and the development of infrastructure projects.
2. Disaster Preparedness: The topographical map provides crucial information for disaster preparedness, enabling authorities to identify areas vulnerable to natural hazards such as floods, earthquakes, and landslides.
3. Transportation and Communication: The map helps plan efficient transportation networks, including roads, railways, and airways, taking into account the terrain’s challenges and opportunities.
4. Environmental Conservation: Understanding the distribution of different ecosystems, such as forests, grasslands, and wetlands, is crucial for environmental conservation efforts.
5. Tourism and Recreation: The topographical map plays a vital role in promoting tourism and recreation, highlighting the diverse landscapes and attractions across the country.
6. Educational and Research Purposes: The map is an invaluable tool for educational institutions and research organizations, providing a visual representation of India’s physical geography for study and analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the major landforms depicted on the topographical map of India?
The topographical map of India depicts various landforms, including the Himalayas, the Northern Plains, the Deccan Plateau, the Coastal Plains, the Western Ghats, the Eastern Ghats, and the Thar Desert.
2. How does the topographical map help in understanding India’s climate?
The topographical map provides insights into the distribution of different climatic zones. For example, the Himalayas act as a barrier, blocking cold winds from Central Asia and creating a distinct climatic zone in the northern plains.
3. What are contour lines, and how are they used on the topographical map?
Contour lines connect points of equal elevation on the map, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s undulations. They help visualize valleys, hills, mountains, and plateaus.
4. How does the topographical map contribute to disaster preparedness?
The map helps identify areas prone to natural hazards like floods, earthquakes, and landslides. This information is crucial for planning evacuation routes, establishing early warning systems, and developing disaster management strategies.
5. Are there different types of topographical maps of India?
Yes, different types of topographical maps exist, including those focusing on specific regions, elevation ranges, or specific aspects like land use or vegetation.
Tips for Understanding the Topographical Map
- Start with the legend: The legend explains the symbols and colors used on the map, providing a key to interpreting the information.
- Focus on contour lines: Pay attention to the spacing and direction of contour lines to understand the terrain’s slope and elevation changes.
- Use the scale: The scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground, allowing for accurate measurements.
- Consult multiple maps: Combining topographical maps with other maps, such as political maps or thematic maps, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the region.
- Utilize online resources: Numerous online platforms offer interactive topographical maps, allowing for exploration and analysis.
Conclusion
The topographical map of India is a powerful tool for understanding the country’s diverse landscape and its intricate relationship with human activities. It provides a visual representation of the terrain, highlighting its unique features and their implications for resource management, disaster preparedness, transportation, environmental conservation, tourism, and education. As a vital resource for various disciplines, the topographical map plays a crucial role in shaping our understanding of India’s physical geography and its influence on the lives of its people.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling India’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at the Topographical Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!