The Power of the Map Hub: Navigating Data, Connecting Insights
Related Articles: The Power of the Map Hub: Navigating Data, Connecting Insights
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Power of the Map Hub: Navigating Data, Connecting Insights. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of the Map Hub: Navigating Data, Connecting Insights

In the digital age, where information flows relentlessly, the ability to organize, visualize, and understand data is paramount. Enter the map hub, a central platform that serves as a navigational beacon for diverse data sets, enabling users to unlock hidden insights and make informed decisions.
Understanding the Concept
A map hub is not simply a collection of maps; it’s a dynamic ecosystem that integrates diverse data sources, mapping tools, and analytical capabilities. Imagine a central repository where data from various departments, projects, or even external sources converge, ready to be analyzed and visualized through interactive maps. This unified platform empowers users to:
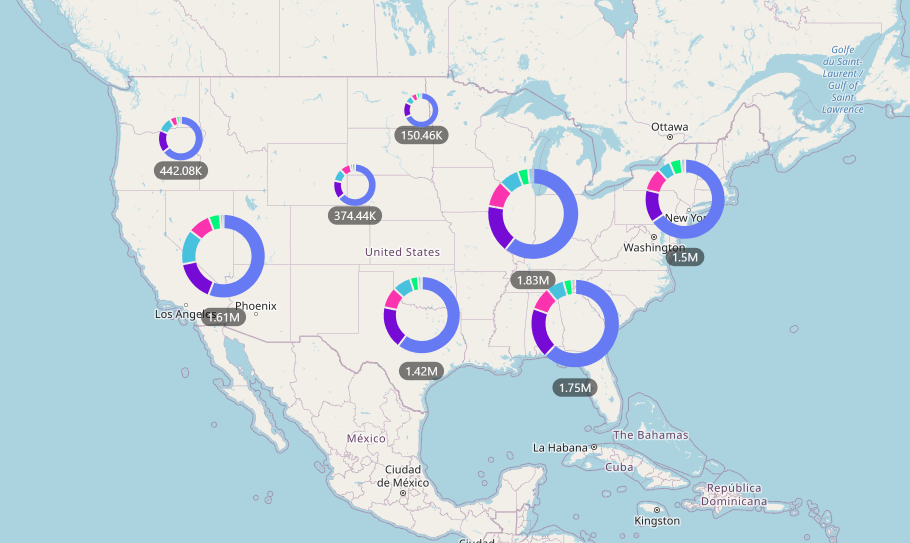
- Visualize Complex Data: Map hubs transform raw data into compelling visual representations, revealing trends, patterns, and anomalies that might otherwise remain hidden.
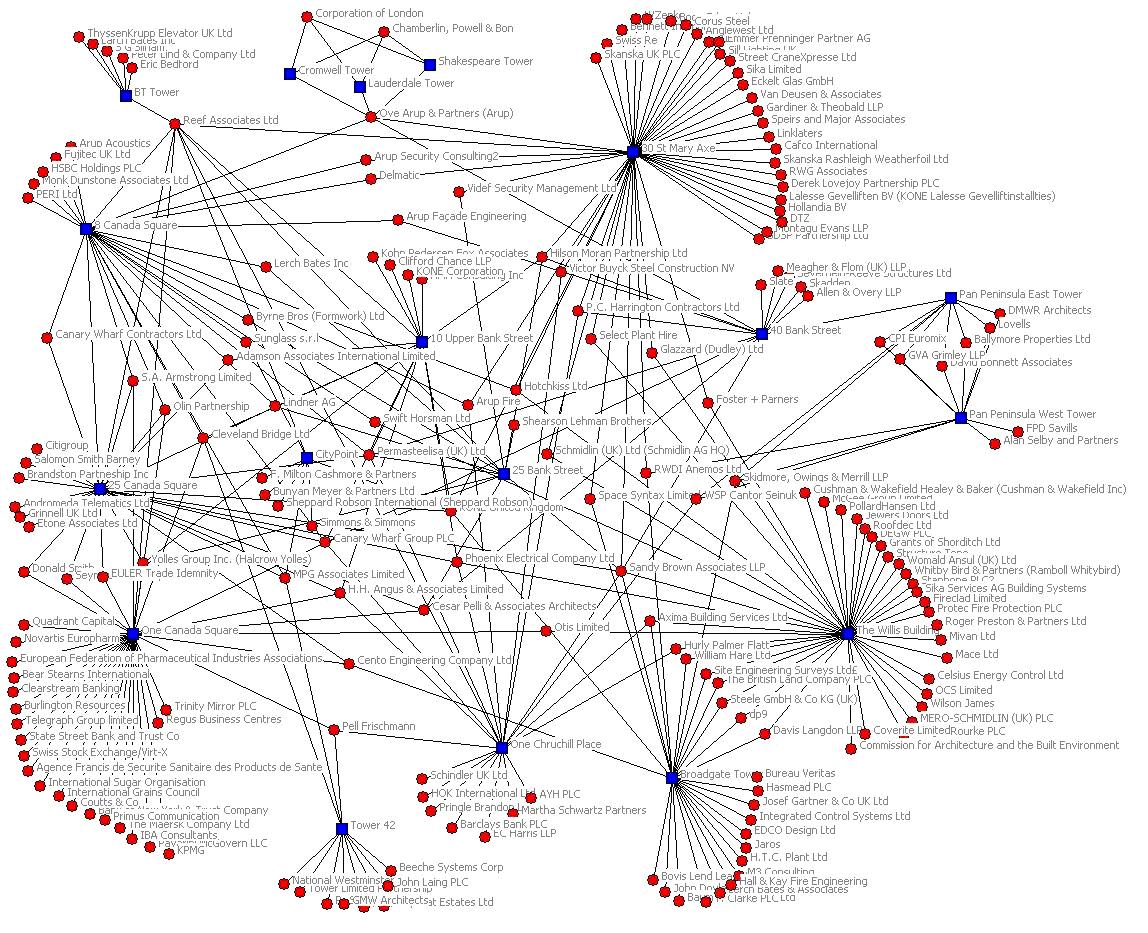
- Connect the Dots: By overlaying different data layers, users can identify relationships and correlations between seemingly disparate information, fostering a deeper understanding of the data landscape.
- Gain Contextual Insights: Maps provide a powerful spatial context, allowing users to analyze data within its geographical setting, enabling them to understand the impact of location, proximity, and environmental factors.
- Collaborate Effectively: Map hubs facilitate collaboration by providing a shared platform for data exploration, analysis, and communication, fostering a common understanding and promoting data-driven decision-making.
The Benefits of a Map Hub
The advantages of implementing a map hub extend far beyond mere data visualization. These platforms offer a range of benefits across various domains:
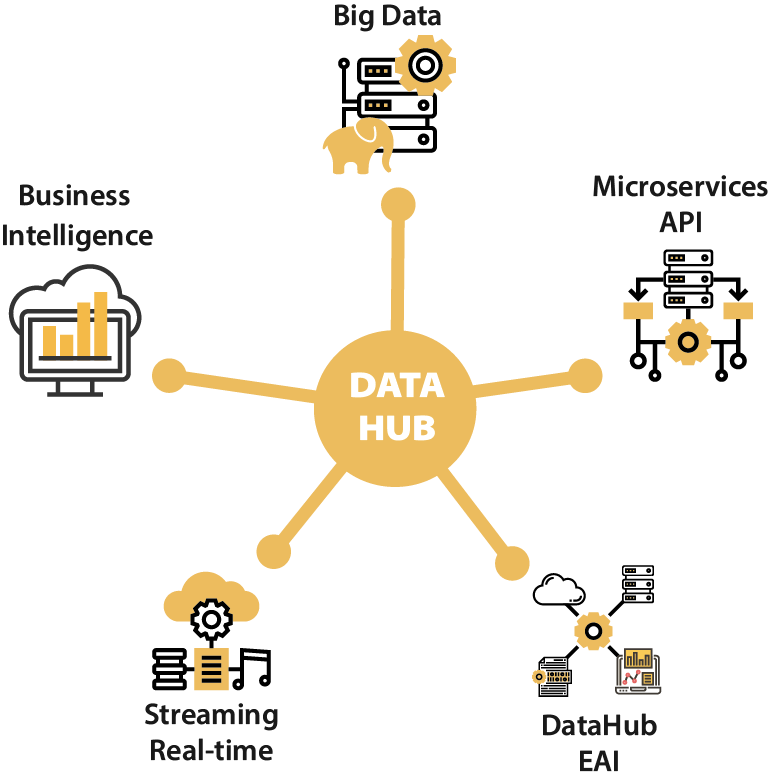
- Business Intelligence: By visualizing sales data, customer demographics, and market trends on a map, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their market, identify growth opportunities, and optimize resource allocation.
- Urban Planning: Map hubs empower urban planners to analyze population density, transportation networks, infrastructure needs, and environmental factors, informing decisions regarding zoning, development, and public services.
- Environmental Monitoring: Environmental agencies can use map hubs to track deforestation, pollution levels, and climate change impacts, enabling them to develop effective conservation strategies and mitigate environmental risks.
- Disaster Response: In emergency situations, map hubs can be used to visualize evacuation routes, identify vulnerable populations, and coordinate relief efforts, aiding in rapid response and minimizing damage.
- Healthcare: Map hubs can help track disease outbreaks, analyze healthcare resource distribution, and identify areas with high patient demand, enabling healthcare organizations to optimize resource allocation and improve patient care.
Key Features of a Map Hub
A comprehensive map hub typically incorporates a range of features to support diverse data analysis needs:
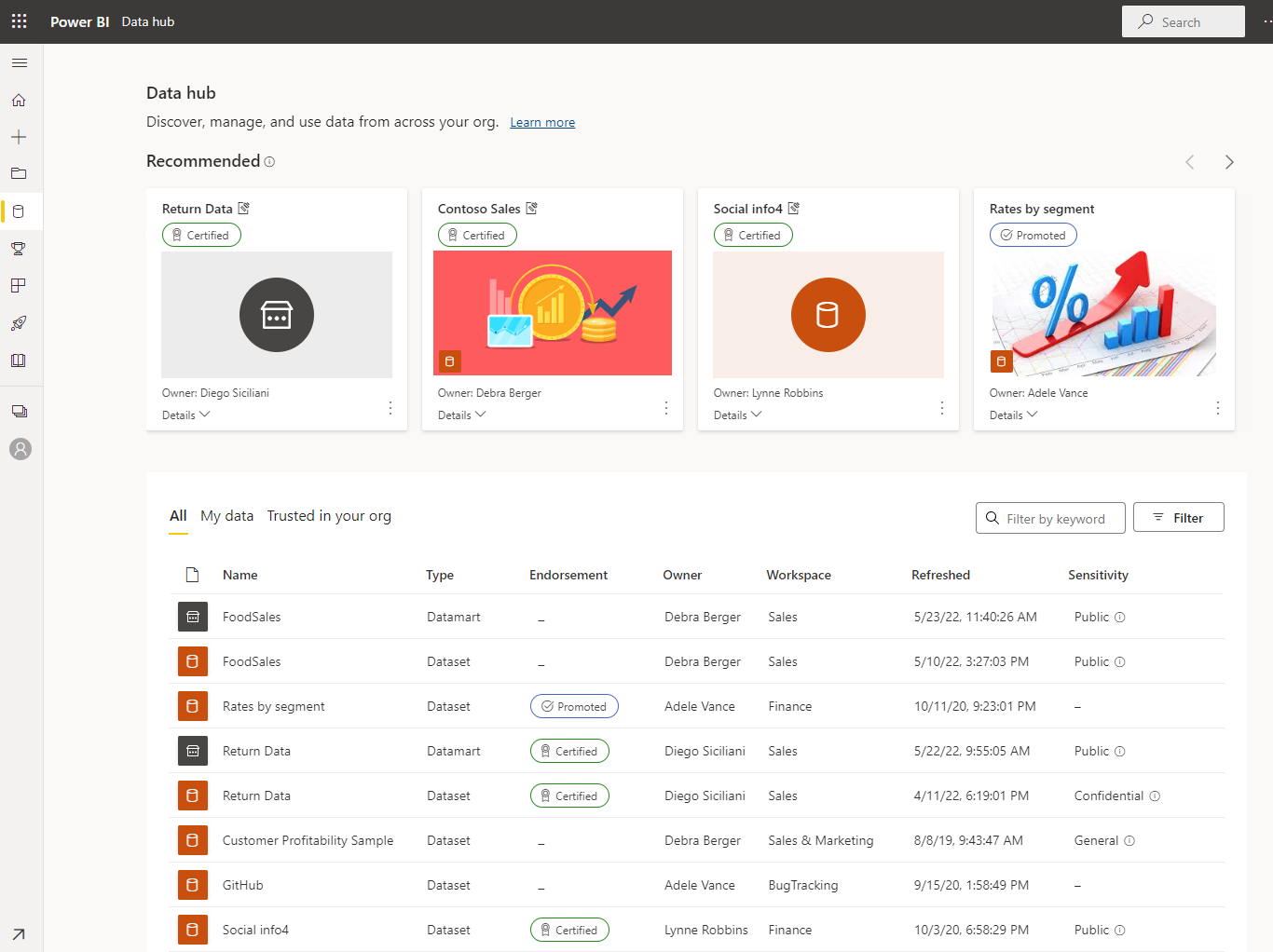
- Data Integration: The ability to ingest data from various sources, including databases, spreadsheets, APIs, and spatial data formats, ensuring a unified and comprehensive data pool.
- Mapping Tools: A suite of mapping tools for creating thematic maps, choropleth maps, heatmaps, and other visualizations, allowing users to represent data effectively and communicate insights clearly.
- Analytical Capabilities: Functions for performing spatial analysis, such as proximity analysis, buffer analysis, and overlay analysis, enabling users to extract meaningful insights from the data.
- Collaboration Features: Tools for sharing maps, collaborating on data analysis, and communicating insights with colleagues, fostering a collaborative data exploration environment.
- Customization Options: The ability to customize maps with unique styles, legends, and labels, tailoring the visualization to specific needs and audiences.
FAQs about Map Hubs
Q: What types of data can be visualized in a map hub?
A: Map hubs can accommodate diverse data types, including demographic data, sales data, customer information, environmental data, transportation data, and more. The key is that the data has a spatial component, meaning it can be linked to a geographical location.
Q: What are the common applications of map hubs?
A: Map hubs find applications in various industries and sectors, including business intelligence, urban planning, environmental monitoring, disaster response, healthcare, and education.
Q: How secure are map hubs?
A: The security of a map hub depends on the specific platform and its implementation. Reputable map hub providers prioritize data security, employing encryption, access controls, and other measures to safeguard sensitive information.
Q: What are the costs associated with implementing a map hub?
A: The cost of implementing a map hub varies depending on the chosen platform, the scale of the project, and the complexity of the data integration process. Some platforms offer free or affordable options, while others require a subscription or custom development.
Tips for Effective Map Hub Implementation
- Define Clear Objectives: Before implementing a map hub, clearly define the goals and objectives you want to achieve. This will guide the data selection, visualization strategies, and overall design of the platform.
- Choose the Right Platform: Evaluate different map hub platforms based on their features, functionality, pricing, and compatibility with your data sources and existing infrastructure.
- Ensure Data Quality: The accuracy and reliability of your data are crucial for meaningful insights. Implement data cleaning and validation processes to ensure data integrity.
- Develop a User-Friendly Interface: Design a user interface that is intuitive and easy to navigate, enabling users to easily explore data, create maps, and analyze information.
- Promote Collaboration and Communication: Encourage collaboration by providing tools for sharing maps, data, and insights. Foster open communication to ensure that users understand the data and its implications.
Conclusion
Map hubs are powerful tools for navigating the complex landscape of data, transforming raw information into actionable insights. By providing a central platform for data visualization, analysis, and collaboration, map hubs empower organizations to make informed decisions, solve complex challenges, and unlock the full potential of their data assets. As data continues to grow exponentially, the importance of map hubs will only increase, enabling us to navigate the information age with clarity and purpose.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of the Map Hub: Navigating Data, Connecting Insights. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!