Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Forecast Rain Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Forecast Rain Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Forecast Rain Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Forecast Rain Maps
Weather forecasting has come a long way from the days of simple barometers and cloud observations. Today, we have access to sophisticated tools that allow us to predict the likelihood and intensity of precipitation with remarkable accuracy. One such tool is the forecast rain map, a visual representation of predicted rainfall across a specific geographical area. This article delves into the intricacies of these maps, exploring their creation, interpretation, and the invaluable benefits they offer to various sectors.
The Genesis of a Forecast Rain Map:
The foundation of a forecast rain map lies in the complex interplay of meteorological data and advanced computer models. Meteorologists gather data from a multitude of sources, including:
- Weather Satellites: These orbiting instruments provide continuous snapshots of cloud cover, precipitation patterns, and atmospheric conditions.
- Weather Balloons: Twice daily, weather balloons are launched around the globe, carrying sensors that measure temperature, humidity, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure at various altitudes.
- Surface Observations: Ground-based stations collect data on temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and other variables, providing crucial information about local conditions.
- Radar Systems: These powerful instruments emit radio waves that bounce off precipitation, allowing meteorologists to track the movement and intensity of storms in real-time.
This wealth of data is then fed into sophisticated numerical weather prediction (NWP) models. These models utilize complex mathematical equations to simulate the behavior of the atmosphere, taking into account various factors like temperature, humidity, wind patterns, and terrain. By processing this data, the models generate predictions of future weather conditions, including the likelihood and intensity of precipitation.
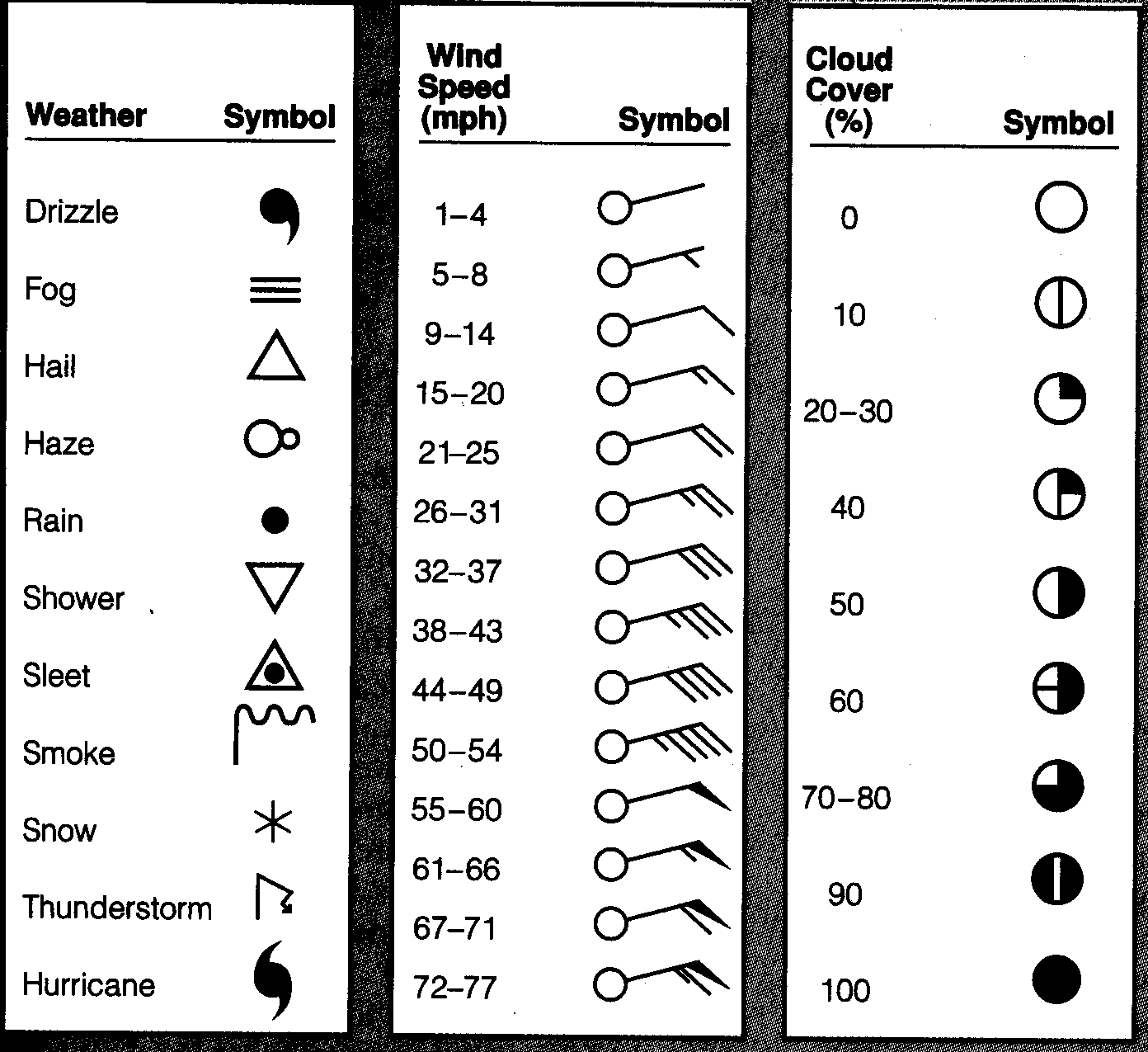
Decoding the Colors and Symbols:
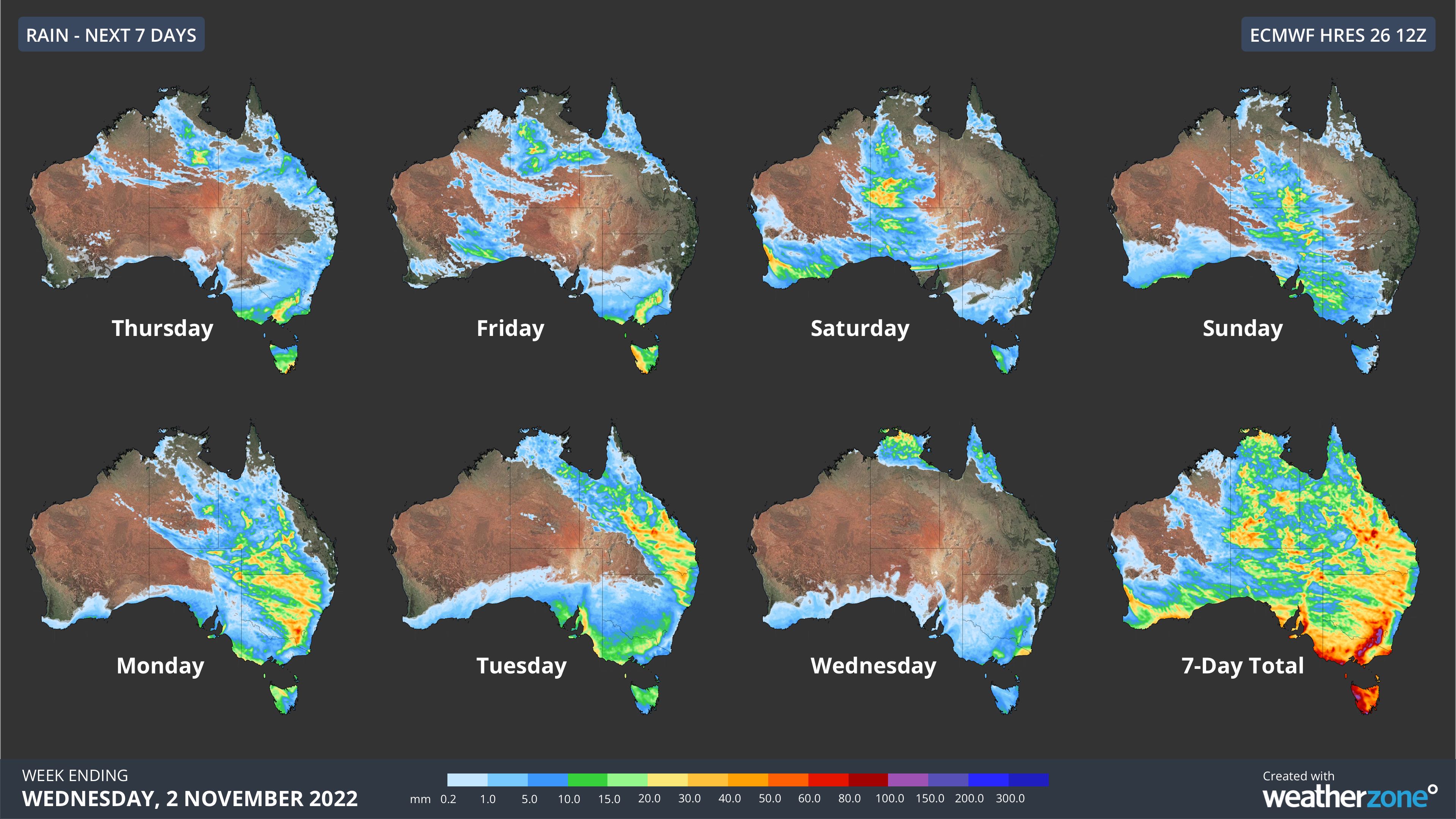
Forecast rain maps are typically presented as colorful grids superimposed on a geographical map. Each color represents a different level of predicted rainfall, ranging from light showers to heavy downpours. The specific color scheme and intensity levels may vary depending on the source of the forecast, but generally, darker shades indicate heavier precipitation.
In addition to colors, forecast rain maps may incorporate various symbols to represent other weather phenomena. For instance, a lightning bolt might indicate the potential for thunderstorms, while a snowflake might signify the possibility of snow or sleet.
Benefits of Forecast Rain Maps:
The impact of forecast rain maps extends far beyond the realm of personal weather planning. These maps play a critical role in various sectors, enabling informed decision-making and mitigating potential risks:
- Agriculture: Farmers rely heavily on accurate precipitation forecasts to optimize irrigation schedules, protect crops from excessive rainfall, and plan for harvesting.
- Transportation: Forecast rain maps help transportation authorities anticipate road closures, delays, and potential flooding, allowing them to implement measures like traffic diversions and safety warnings.
- Emergency Management: In disaster-prone areas, accurate rain forecasts are crucial for predicting the likelihood of floods, landslides, and other weather-related emergencies. This information allows emergency responders to prepare resources and issue timely evacuation warnings.
- Construction: Construction projects are often sensitive to weather conditions. Rain forecasts help project managers schedule work around potential delays, preventing costly disruptions and ensuring project deadlines are met.
- Energy Production: Hydroelectric power plants rely on rainfall for generating electricity. Forecast rain maps help operators anticipate water flow and adjust power generation accordingly.
FAQs About Forecast Rain Maps:
Q: How accurate are forecast rain maps?
A: The accuracy of rain forecasts varies depending on factors like the complexity of the weather system, the available data, and the time horizon of the forecast. While short-term forecasts (1-3 days) tend to be more accurate, longer-term forecasts (3-7 days) can be less precise.
Q: How often are rain forecasts updated?
A: Forecast rain maps are typically updated multiple times a day, with some services providing hourly updates. The frequency of updates depends on the specific forecasting agency and the availability of new data.
Q: What are the limitations of forecast rain maps?
A: While forecast rain maps are powerful tools, they are not infallible. They can be influenced by the inherent complexities of atmospheric dynamics and the limitations of data collection and processing. Additionally, local topography and microclimates can influence rainfall patterns, leading to variations between predicted and actual precipitation.
Tips for Utilizing Forecast Rain Maps Effectively:
- Consider the source: Different forecasting agencies use different models and data sources, leading to variations in their predictions. It is advisable to consult multiple sources for a comprehensive understanding of the forecast.
- Pay attention to the time horizon: Short-term forecasts are generally more reliable than long-term forecasts.
- Be aware of local conditions: Topography, proximity to bodies of water, and urban heat island effects can all influence local rainfall patterns.
- Interpret the maps with caution: Rain forecasts are not guarantees, and localized variations can occur.
Conclusion:
Forecast rain maps are invaluable tools for understanding and predicting precipitation patterns, enabling informed decision-making across various sectors. By utilizing these maps responsibly and recognizing their limitations, individuals and organizations can effectively prepare for and mitigate the potential impacts of rainfall, ensuring safety, efficiency, and success in their endeavors. As weather forecasting technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even more precise and reliable rain maps, further enhancing our ability to navigate the unpredictable forces of nature.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Secrets of the Sky: Understanding Forecast Rain Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
