Unveiling the Terrain: How Maps Depict Elevation
Related Articles: Unveiling the Terrain: How Maps Depict Elevation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Terrain: How Maps Depict Elevation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Terrain: How Maps Depict Elevation
The world is not flat. It’s a tapestry of peaks, valleys, plains, and everything in between. This undulating landscape is a vital component of our planet’s geography, influencing everything from weather patterns to human settlements. But how do we capture this three-dimensional world on a two-dimensional map? The answer lies in the art and science of representing elevation.
The Language of Elevation:
Elevation, simply put, is the vertical distance of a point on the Earth’s surface above sea level. It’s the key to understanding the topography of a region, providing insights into its physical features and the forces that have shaped it.
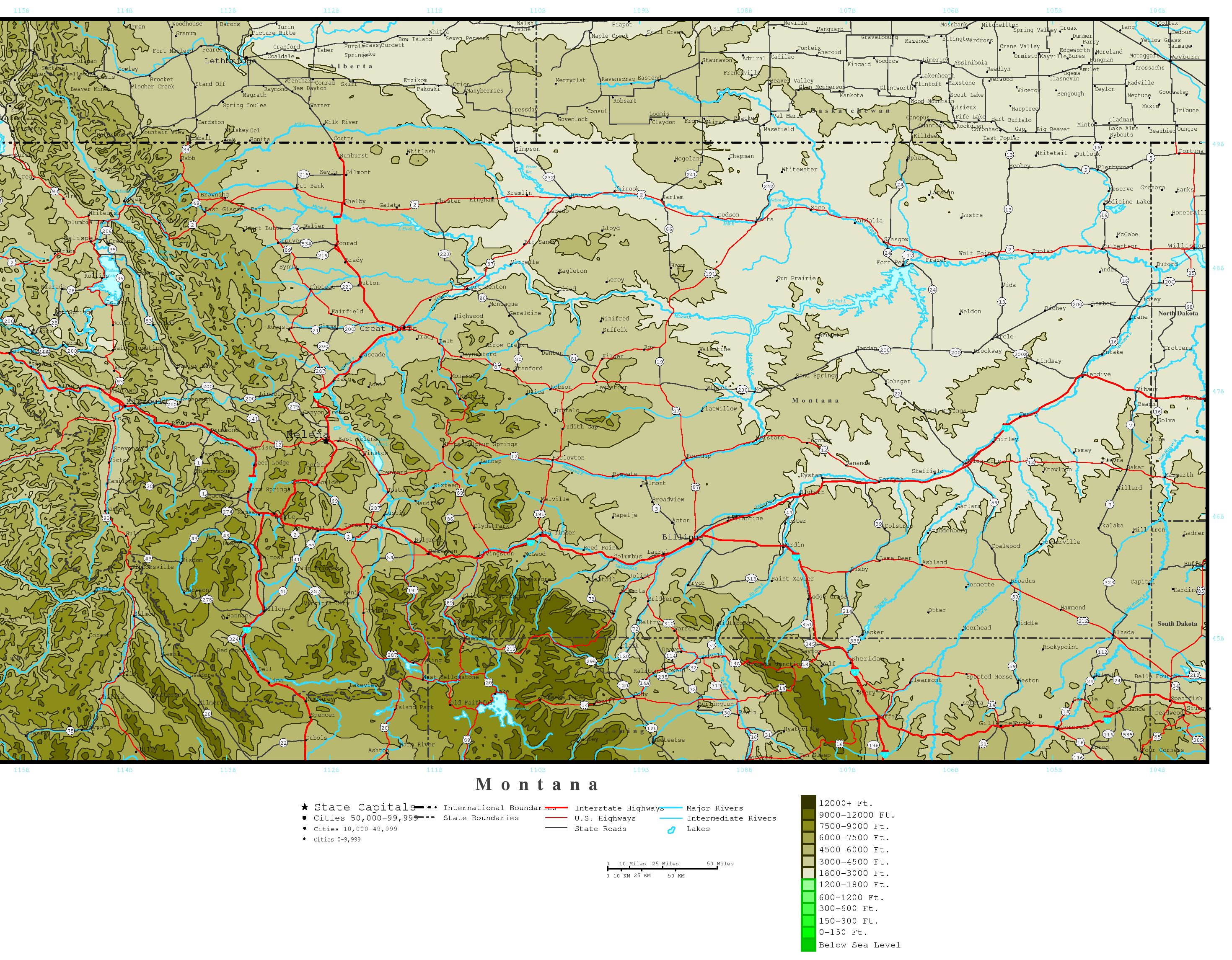
Mapping the Terrain:
Maps have long been used to depict the Earth’s surface, but representing elevation accurately requires specialized techniques. Several methods are employed to translate the complexities of terrain onto a flat surface:
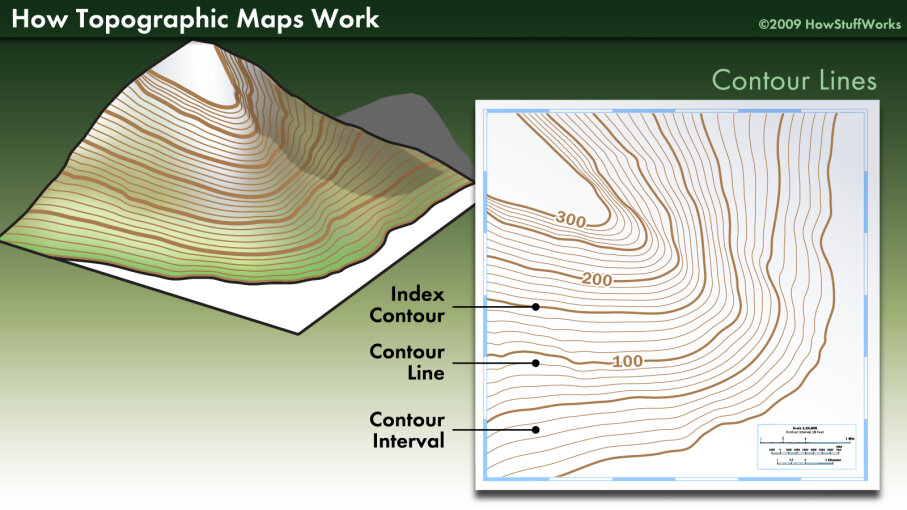
1. Contour Lines:
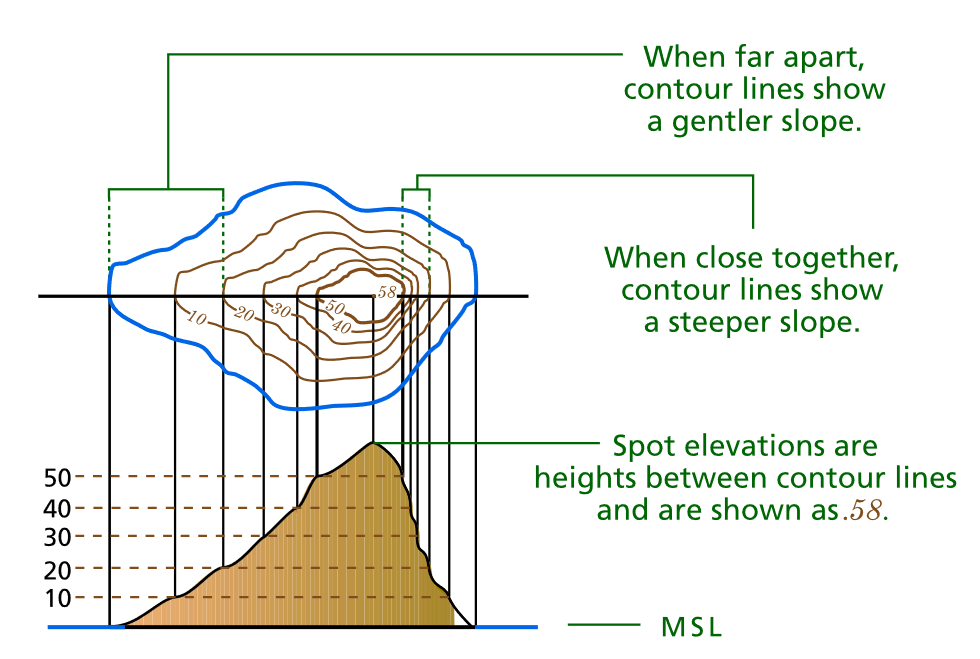
Perhaps the most common method, contour lines connect points of equal elevation. Imagine slicing a mountain with horizontal planes – each slice would represent a contour line. Closer lines indicate steeper slopes, while widely spaced lines suggest gentler terrain.
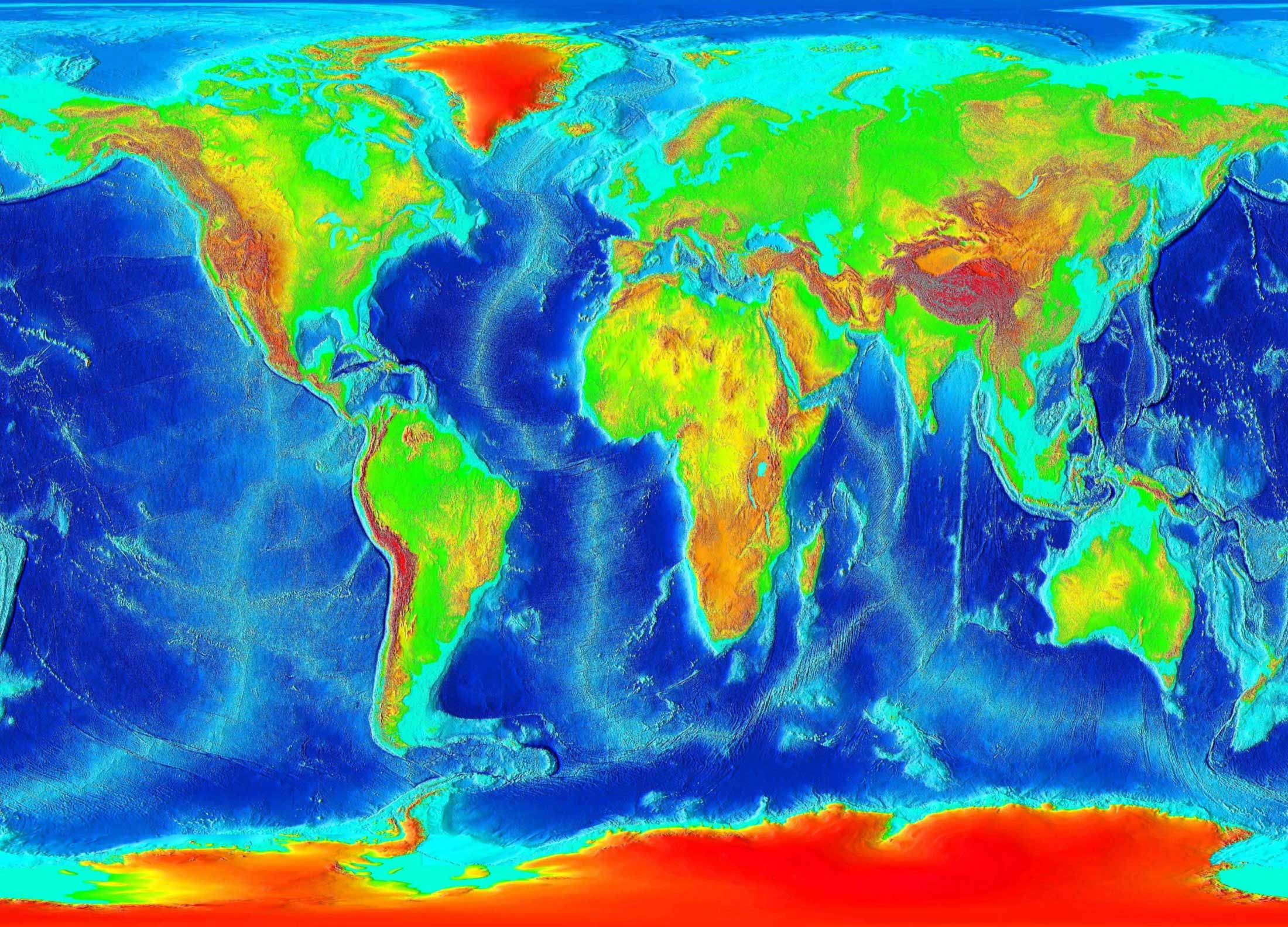
2. Hypsometric Tinting:
This technique uses color gradients to depict elevation. Different colors represent different elevation ranges, allowing for a quick visual understanding of the landscape. For example, green might represent low-lying areas, while brown indicates higher elevations.
3. Relief Shading:
This method uses shading to create the illusion of light and shadow, mimicking the way sunlight interacts with the terrain. Lighter areas represent elevated regions, while darker areas represent valleys or depressions.
4. 3D Models and Digital Elevation Models (DEMs):
With the advent of digital technology, elevation data can be transformed into three-dimensional models, offering a more realistic and interactive representation of the terrain. These models are often used for navigation, planning, and environmental studies.
The Importance of Elevation Maps:
Elevation maps are not merely visual representations; they are powerful tools with diverse applications:
- Navigation and Planning: Hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts rely on elevation maps to plan their routes, assess difficulty levels, and identify potential hazards.
- Engineering and Construction: Civil engineers use elevation data to design roads, bridges, and buildings, ensuring stability and minimizing environmental impact.
- Agriculture and Resource Management: Elevation maps help farmers understand soil types, irrigation needs, and potential risks associated with flooding or drought.
- Environmental Studies: Scientists utilize elevation data to analyze climate change impacts, predict landslides, and study wildlife habitat patterns.
- Disaster Relief: Elevation data is crucial for emergency responders during natural disasters, enabling them to assess flood risks, plan evacuation routes, and manage rescue operations.
FAQs: Unveiling the Mysteries of Elevation Maps:
1. What is the difference between elevation and altitude?
While often used interchangeably, elevation refers to the vertical distance above sea level, while altitude refers to the height above a specific reference point, which can be sea level, ground level, or even the starting point of a flight.
2. How are elevation maps created?
Elevation data is collected through various methods, including:
- Surveys: Traditional land surveys use instruments like levels and theodolites to measure distances and angles, calculating elevation based on reference points.
- Aerial Photography and Remote Sensing: Specialized cameras and sensors mounted on aircraft or satellites capture images of the Earth’s surface, which are processed to generate elevation data.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses laser pulses to measure distances and create highly accurate 3D models of the terrain.
3. What is the significance of contour lines?
Contour lines are crucial because they:
- Depict the shape of the terrain: Closely spaced lines indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced lines suggest gentle terrain.
- Reveal the presence of features: Closed contour lines represent hills, while lines that converge indicate valleys.
- Provide elevation information: Each contour line represents a specific elevation, allowing for precise measurements.
4. Can I create my own elevation map?
Yes, several free and paid software tools allow you to create your own elevation maps. Some popular options include:
- QGIS: A free and open-source geographic information system (GIS) software.
- ArcGIS: A professional-grade GIS software used for advanced mapping and analysis.
- Google Earth: A user-friendly platform that allows users to create and share custom maps.
Tips for Reading Elevation Maps:
- Understand the contour interval: The contour interval indicates the difference in elevation between each contour line.
- Look for changes in contour line spacing: Closely spaced lines indicate steep slopes, while widely spaced lines suggest gentler terrain.
- Identify key features: Closed contour lines represent hills, while converging lines indicate valleys.
- Use the map legend: The legend explains the symbols and colors used on the map, including elevation ranges and other features.
Conclusion:
Elevation maps are essential tools for understanding the Earth’s surface and its diverse topography. They play a crucial role in various fields, from navigation and planning to environmental studies and disaster relief. By mastering the art of reading and interpreting elevation maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate complexities of our planet and its ever-changing landscape. From the towering peaks to the deepest valleys, these maps reveal the hidden stories of our world, inviting us to explore, understand, and appreciate the beauty of our planet’s varied terrain.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Terrain: How Maps Depict Elevation. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!