A Comprehensive Guide to Competitor Mapping: Understanding Your Competitive Landscape
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Competitor Mapping: Understanding Your Competitive Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Competitor Mapping: Understanding Your Competitive Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Competitor Mapping: Understanding Your Competitive Landscape

In the dynamic world of business, understanding your competitive landscape is crucial for success. A competitor map, a visual representation of your direct and indirect competitors, provides a structured framework for analyzing and strategizing against rivals. This comprehensive guide explores the nuances of competitor mapping, its benefits, and how it can be effectively implemented.
What is a Competitor Map?
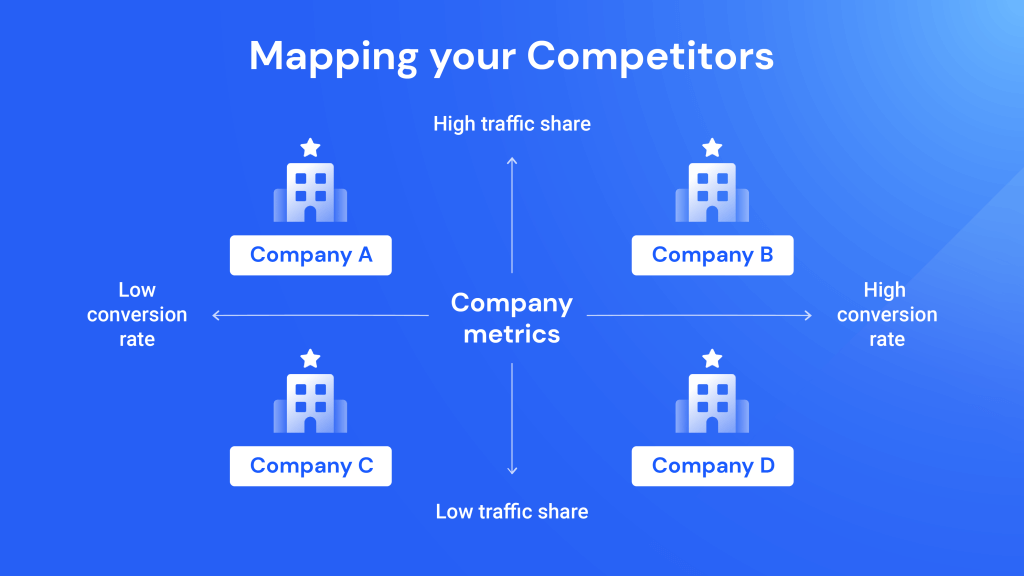
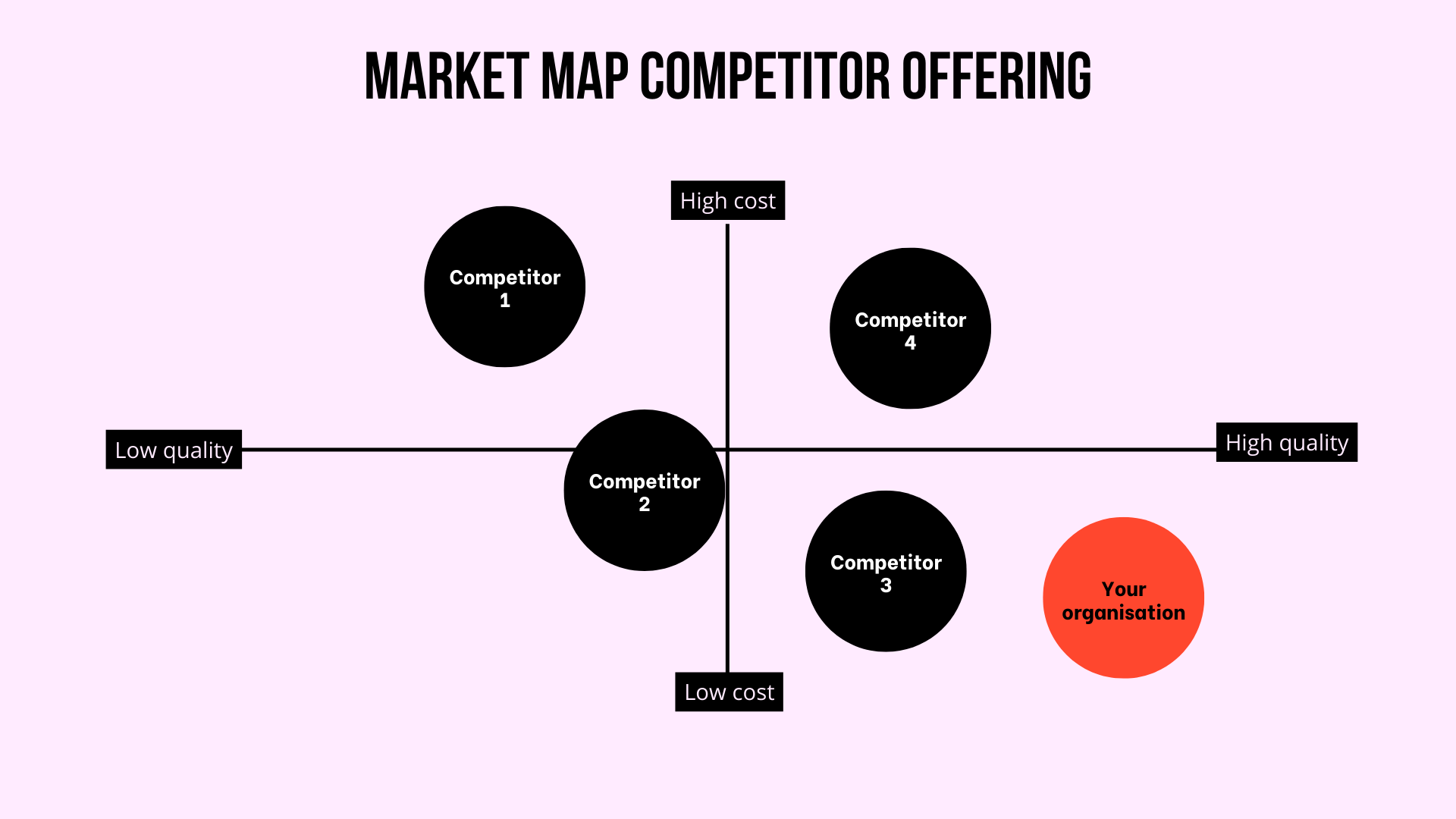
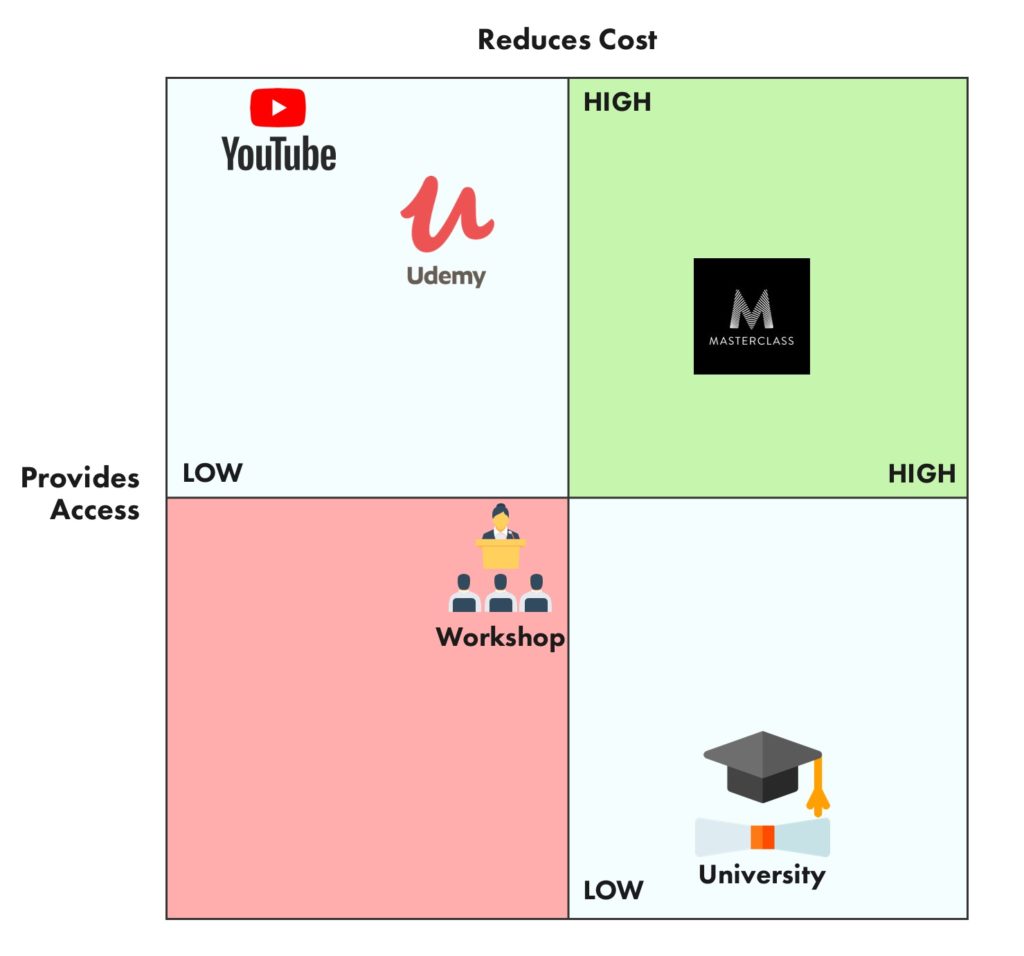
A competitor map is a visual tool that categorizes and analyzes competitors based on various factors, such as their products or services, target audience, pricing strategies, marketing channels, and competitive advantages. It helps businesses gain a clear understanding of their position within the market and identify potential threats and opportunities.
Types of Competitor Maps:
Several types of competitor maps exist, each offering a unique perspective on the competitive landscape:
- Direct Competitors: These companies offer similar products or services to your own, targeting the same customer base.
- Indirect Competitors: These companies offer alternative solutions to the same customer needs, but their products or services are not directly comparable to yours.
- Aspirational Competitors: These are companies that you admire and aspire to emulate, often larger and more established players in the market.
- Emerging Competitors: These are new players who are entering the market and may pose a future threat to your business.
Key Elements of a Competitor Map:
A comprehensive competitor map should include the following key elements:
- Competitor Identification: Clearly define and list all relevant competitors, including both direct and indirect players.
- Product/Service Offering: Analyze the products and services offered by each competitor, highlighting their key features and differentiators.
- Target Audience: Identify the customer segments targeted by each competitor and their respective demographics, psychographics, and needs.
- Pricing Strategies: Examine the pricing strategies employed by each competitor, including their pricing models, discounts, and promotions.
- Marketing Channels: Analyze the marketing channels used by each competitor, including their online presence, advertising campaigns, and public relations activities.
- Competitive Advantages: Identify the unique strengths and competitive advantages of each competitor, such as brand recognition, product innovation, or customer service excellence.
- Weaknesses: Analyze the weaknesses of each competitor, such as poor product quality, limited distribution channels, or outdated marketing strategies.
Benefits of Competitor Mapping:
A well-constructed competitor map offers numerous benefits for businesses:
- Market Understanding: Gain a deeper understanding of your market, including the key players, their strengths and weaknesses, and the competitive landscape.
- Strategic Planning: Identify opportunities and threats posed by competitors, inform strategic planning decisions, and guide product development, marketing, and pricing strategies.
- Competitive Advantage: Develop strategies to differentiate your business from competitors and gain a competitive advantage by leveraging your unique strengths.
- Customer Insights: Gain insights into the needs and preferences of your target audience by analyzing the customer segments targeted by competitors.
- Innovation: Encourage innovation and product development by identifying competitor gaps and exploring new market opportunities.
Creating a Competitor Map:
Building an effective competitor map requires a systematic approach:
- Identify Your Competitors: Conduct thorough market research to identify all relevant competitors, both direct and indirect.
- Gather Information: Collect data on each competitor, including their products, services, target audience, pricing, marketing channels, competitive advantages, and weaknesses.
- Categorize Competitors: Classify competitors based on their product/service offerings, target audience, and competitive strategies.
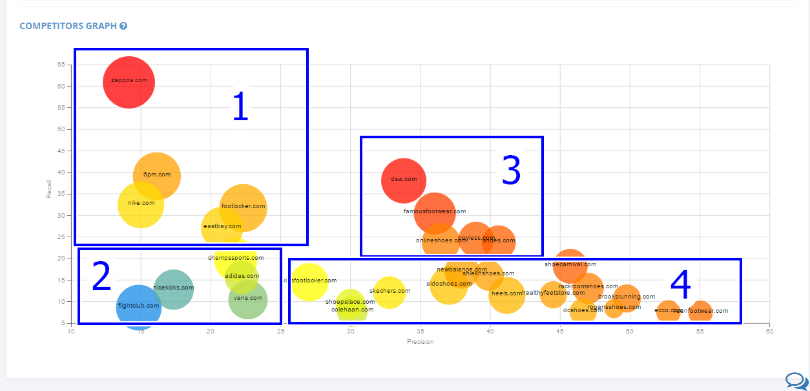
- Visualize the Map: Create a visual representation of your competitor map, using a table, chart, or other suitable format.
- Analyze and Interpret: Analyze the data gathered and interpret the competitive landscape, identifying key trends, opportunities, and threats.
Frequently Asked Questions about Competitor Mapping:
Q: How often should a competitor map be updated?
A: Competitor maps should be updated regularly, ideally on a quarterly or semi-annual basis, to reflect changes in the market and competitor activities.
Q: What are the best tools for creating competitor maps?
A: Various tools can be used for creating competitor maps, including spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel, visual mapping tools like Lucidchart or Miro, and dedicated market research platforms.
Q: How can I gather information about my competitors?
A: You can gather information about your competitors through various sources, including:
- Industry reports: Market research firms and industry publications often provide detailed reports on specific industries and competitors.
- Competitor websites: Analyze competitor websites, including their product pages, marketing materials, and blog posts.
- Social media: Monitor competitor activity on social media platforms, including their content, engagement, and advertising campaigns.
- Customer feedback: Gather feedback from customers about their experiences with competitors and their perceived strengths and weaknesses.
Tips for Creating a Successful Competitor Map:
- Focus on Key Competitors: Prioritize your analysis on the most relevant competitors, those who directly impact your business and pose the most significant threats.
- Use a Consistent Framework: Ensure consistency in the data gathered and the framework used for analyzing competitors.
- Be Objective: Avoid bias and strive for objectivity when assessing competitors’ strengths and weaknesses.
- Stay Up-to-Date: Regularly update your competitor map to reflect changes in the market and competitor activities.
- Use the Map to Inform Strategic Decisions: Leverage the insights gained from your competitor map to inform strategic planning and decision-making.
Conclusion:
Competitor mapping is a powerful tool for businesses seeking to gain a competitive advantage. By understanding the competitive landscape, businesses can identify opportunities and threats, develop effective strategies, and position themselves for success. A well-constructed competitor map provides valuable insights into the market, customer needs, and competitor strategies, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and stay ahead of the competition.

![How to Create a Competitive Analysis (With Examples) [2022] • Asana](https://assets.asana.biz/m/72a66e680f4c6a26/original/inline-project-planning-competitive-analysis-example-2-2x.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Competitor Mapping: Understanding Your Competitive Landscape. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!