Unveiling the Landscape of Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape of Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape of Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape of Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Maps
In the competitive landscape of modern business, understanding consumer perception is paramount. This understanding is not simply about knowing what consumers think of a product or brand; it’s about understanding how they perceive it in relation to its competitors. This is where perceptual maps come into play.
What is a Perceptual Map?
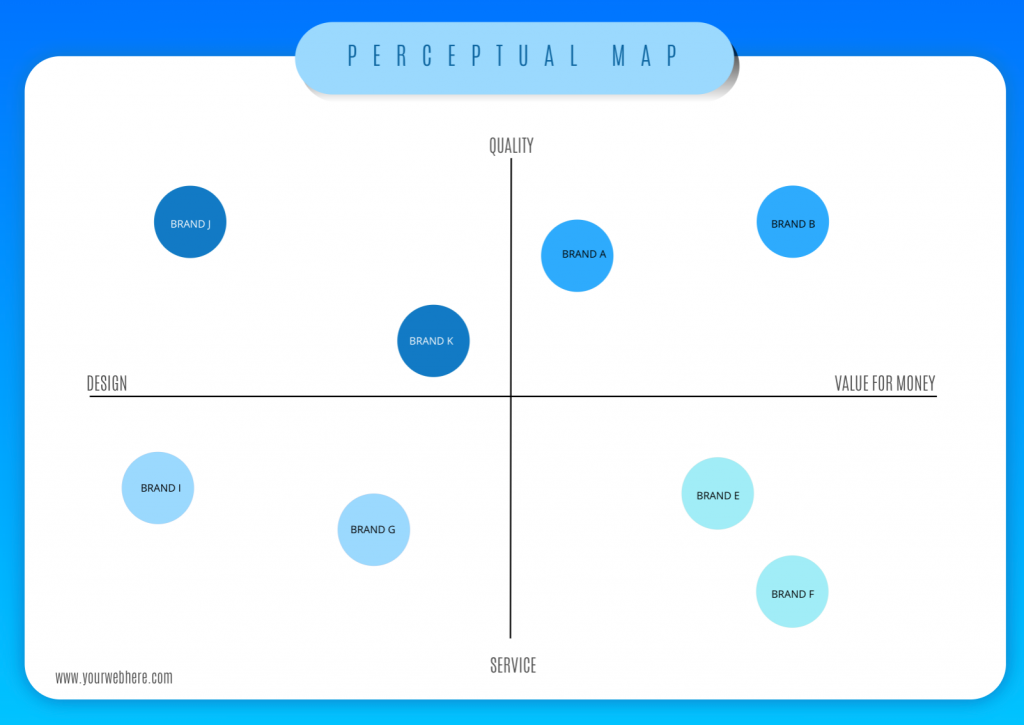
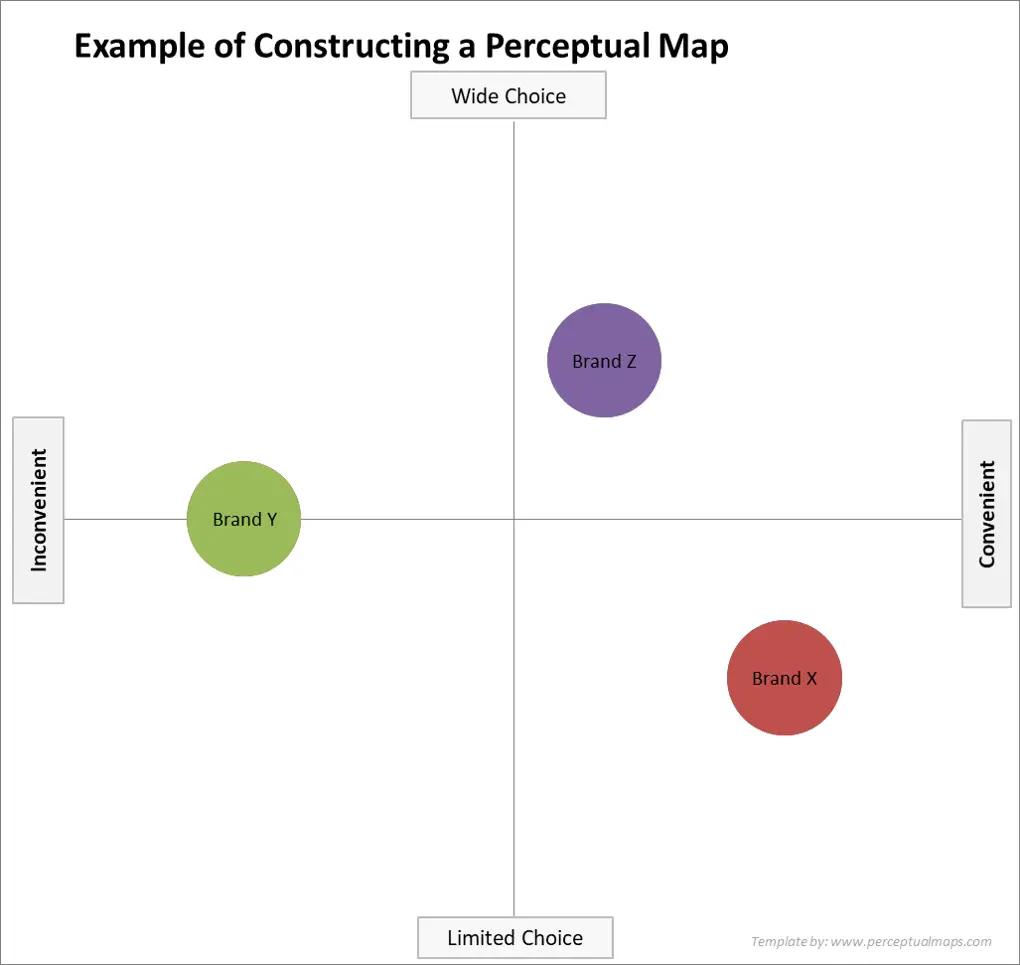
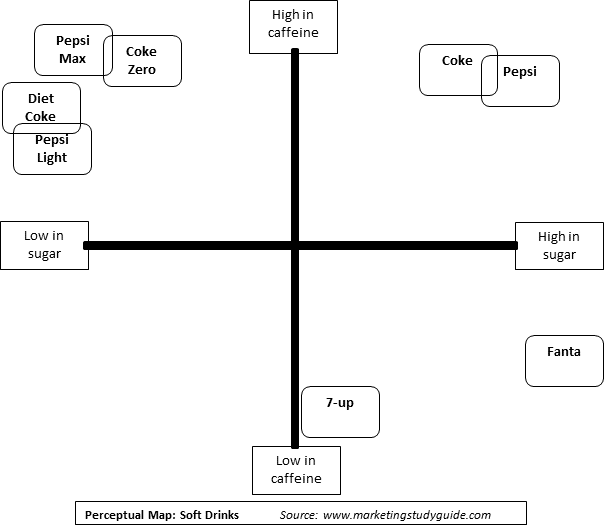
A perceptual map is a visual representation of how consumers perceive different brands or products within a particular market. It essentially plots these offerings on a two-dimensional graph, with each axis representing a key attribute or characteristic important to consumers. By visualizing this perceptual space, businesses can gain valuable insights into their positioning, identify competitive advantages, and develop effective marketing strategies.
Understanding the Building Blocks
Creating a perceptual map involves several key steps:
- Defining the Relevant Attributes: The first step is to identify the key attributes that consumers consider when making purchase decisions within the specific market. This requires thorough market research and analysis, including surveys, focus groups, and competitor analysis.
- Selecting the Axes: Based on the identified attributes, two key dimensions are chosen for the map’s axes. These dimensions should be distinct, relevant, and easily understood by consumers. For instance, in the automotive industry, axes could represent "price" and "performance," or "luxury" and "fuel efficiency."
- Positioning the Competitors: Each competitor within the market is then plotted on the map according to their perceived position along the chosen axes. This positioning is determined based on consumer perceptions, which can be gathered through market research, expert opinions, or even competitor marketing materials.
- Visualizing the Landscape: The final step involves visualizing the resulting data on a graph. This can be done using a simple scatter plot or more sophisticated visualizations depending on the complexity of the data and the desired level of detail.
Unveiling the Power of Perception
The value of perceptual maps lies in the insights they provide. By visualizing consumer perceptions, businesses can:
- Identify Gaps in the Market: Perceptual maps can highlight areas where there is less competition or where consumer needs are not being met. This can guide product development and market expansion strategies.
- Understand Competitive Positioning: By visualizing the relative positions of competitors, businesses can understand their own strengths and weaknesses in the market. This can inform pricing strategies, product positioning, and marketing campaigns.
- Develop Effective Marketing Strategies: Perceptual maps can help businesses target their marketing efforts more effectively. By understanding how consumers perceive their brand, they can craft messages and campaigns that resonate with their target audience.
- Monitor Competitive Changes: Perceptual maps can be used to track changes in consumer perceptions over time. This allows businesses to adapt their strategies in response to evolving market trends and competitor actions.
Beyond the Basics: Types of Perceptual Maps
While the basic principles remain the same, perceptual maps can take different forms depending on the specific application and desired level of detail. Some common types include:
- Perceptual Mapping of Attributes: This type focuses on mapping consumer perceptions of specific product attributes, such as quality, price, or features.
- Perceptual Mapping of Brands: This type maps consumer perceptions of different brands within a market, highlighting their relative strengths and weaknesses.
- Perceptual Mapping of Product Categories: This type maps consumer perceptions of different product categories, providing insights into the overall market structure and consumer preferences.
- Perceptual Mapping of Customer Segments: This type maps consumer perceptions of different customer segments, allowing businesses to tailor their marketing efforts to specific groups.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are some limitations of perceptual maps?
A: While powerful tools, perceptual maps are not without limitations. They are based on consumer perceptions, which can be subjective and prone to bias. Additionally, the choice of attributes and axes can influence the map’s outcome, making it essential to carefully consider these elements.
Q: How can I create a perceptual map for my business?
A: Creating a perceptual map requires a combination of market research, data analysis, and visualization skills. You can either conduct your own research or engage with market research firms specializing in perceptual mapping.
Q: How can I use a perceptual map to improve my marketing strategy?
A: Perceptual maps can guide your marketing strategy by identifying target audiences, positioning your brand effectively, and crafting messages that resonate with consumers. By understanding where your brand stands in the perceptual landscape, you can develop more effective marketing campaigns.
Tips for Effective Perceptual Map Development:
- Involve stakeholders: Collaborate with marketing, sales, and product development teams to ensure the map reflects the organization’s overall goals.
- Use clear and concise language: Ensure the attributes and axes are easily understood by consumers and stakeholders.
- Test and refine: Conduct pilot studies and gather feedback to ensure the map accurately reflects consumer perceptions.
- Stay updated: Regularly update the map to reflect changes in consumer preferences and competitive landscape.
Conclusion: Navigating the Perceptual Landscape
Perceptual maps offer a powerful framework for understanding consumer perceptions and navigating the competitive landscape. By visualizing how consumers perceive different brands and products, businesses can gain valuable insights into their positioning, identify opportunities, and develop effective marketing strategies. As the business world continues to evolve, understanding the power of perception will be crucial for success.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape of Perception: A Comprehensive Guide to Perceptual Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!