The Atlantic Coastal Plain: A Map of Geological History and Human Influence
Related Articles: The Atlantic Coastal Plain: A Map of Geological History and Human Influence
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Atlantic Coastal Plain: A Map of Geological History and Human Influence. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Atlantic Coastal Plain: A Map of Geological History and Human Influence

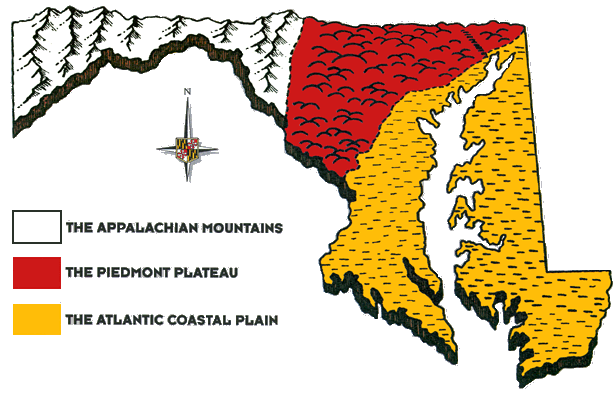
The Atlantic Coastal Plain, stretching from Cape Cod in the north to the Florida Keys in the south, is a vast expanse of low-lying land shaped by the relentless forces of nature over millions of years. This region, characterized by its flat topography, sandy soils, and rich coastal ecosystems, is a captivating tapestry of geological history and human influence. Understanding the Atlantic Coastal Plain requires a comprehensive exploration of its geological formation, its unique ecological features, and its profound impact on human settlements and economic activities.
A Journey Through Time: Geological Formation
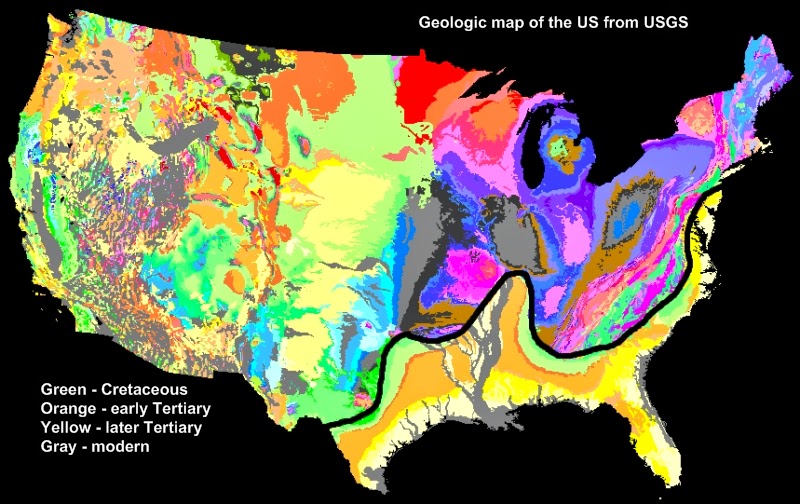
The Atlantic Coastal Plain’s genesis lies in the relentless forces of erosion and deposition, sculpted by the Atlantic Ocean over millions of years. The story begins with the breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea, which, in the Triassic period, led to the formation of the Atlantic Ocean. As the ocean basin widened, sediments eroded from the Appalachian Mountains and other ancient landmasses were transported eastward, accumulating in layers upon the continental shelf.
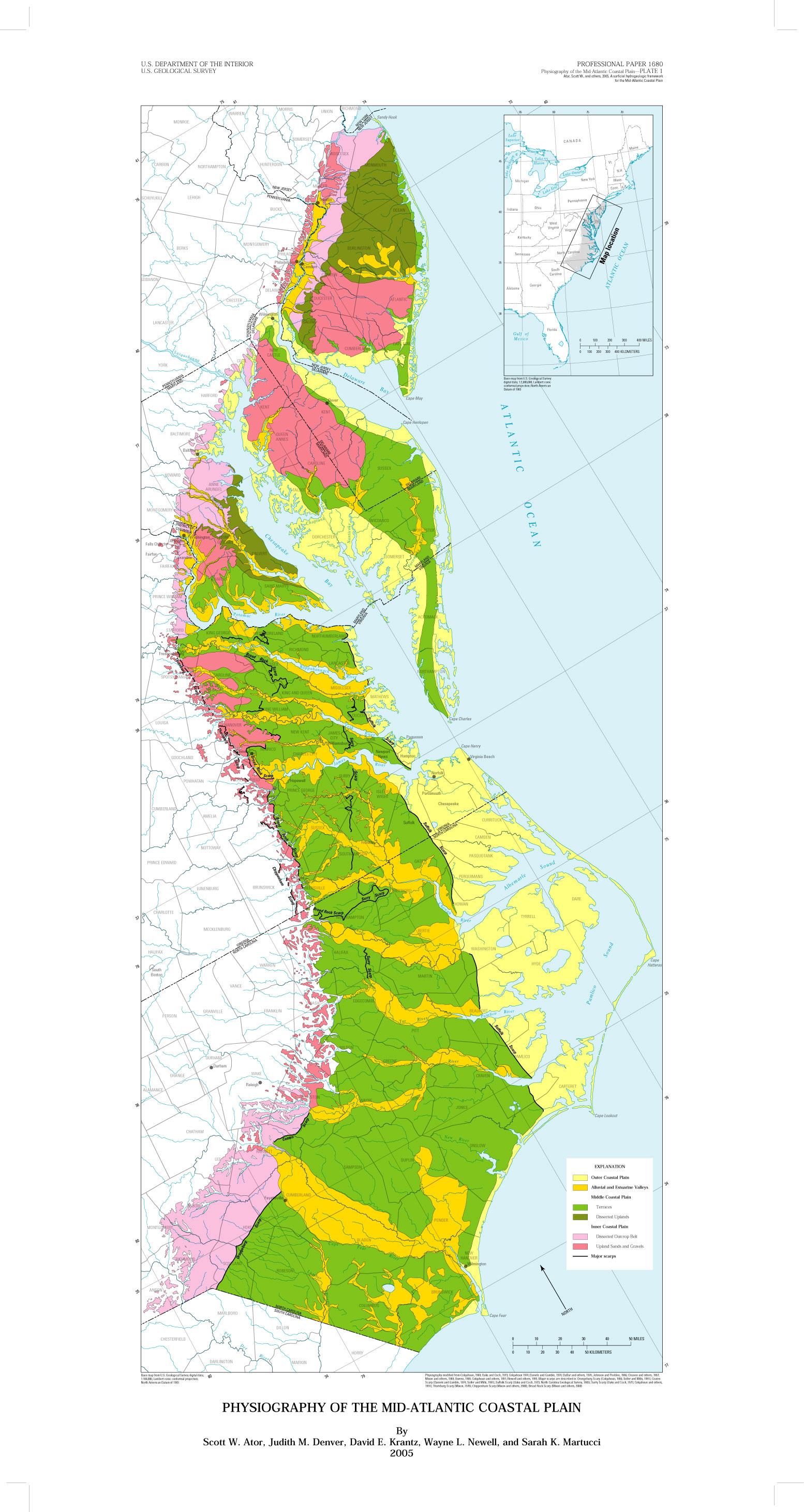
These sediments, primarily composed of sand, silt, and clay, formed a vast, shallow marine environment that eventually became the foundation for the Atlantic Coastal Plain. Over time, the weight of these sediments caused the Earth’s crust to sink, creating a broad, gently sloping plain. This process, known as subsidence, continued throughout the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras, resulting in the gradual emergence of the Coastal Plain above sea level.
The geological history of the Atlantic Coastal Plain is etched in its diverse landscapes. The oldest formations, dating back to the Triassic period, are found in the northern part of the plain, while younger sediments, from the Cretaceous and Cenozoic periods, dominate the southern region. This geological gradient is reflected in the varying soil types, elevation, and coastal features across the plain.
A Mosaic of Ecosystems: Biodiversity and Coastal Dynamics
The Atlantic Coastal Plain is a haven for biodiversity, hosting a rich tapestry of ecosystems that thrive in its unique environment. The region’s flat topography and proximity to the ocean have fostered a mosaic of habitats, including:
- Coastal Forests: The Atlantic Coastal Plain is home to vast forests of pine, oak, and cypress, adapted to the region’s sandy soils and high rainfall. These forests provide essential habitat for a diverse array of wildlife, including deer, squirrels, and numerous bird species.
- Wetlands: The Coastal Plain is dotted with extensive wetlands, including marshes, swamps, and bogs. These waterlogged areas play a crucial role in regulating water flow, filtering pollutants, and providing critical breeding grounds for fish, amphibians, and birds.
- Beaches and Dunes: The Atlantic coastline is defined by its iconic beaches and sand dunes, which serve as natural barriers against storms and coastal erosion. These dynamic landscapes are constantly reshaped by waves, tides, and wind, creating a constantly evolving environment.
- Estuaries: The Coastal Plain is home to numerous estuaries, where freshwater rivers meet the saltwater ocean. These transitional zones are rich in nutrients and support a diverse array of marine life, making them vital for commercial fisheries and recreational activities.
The Atlantic Coastal Plain’s ecosystems are constantly in flux, influenced by a complex interplay of natural processes and human activities. Sea level rise, coastal erosion, and the impact of climate change are altering the region’s delicate balance, posing challenges to its biodiversity and human populations.
Human Impact: A Legacy of Settlement and Economic Development
The Atlantic Coastal Plain has long been a focal point for human settlement and economic activity. Its fertile soils, abundant water resources, and access to transportation routes have attracted generations of settlers, shaping the region’s cultural landscape and economic development.
- Agriculture: The Coastal Plain’s fertile soils have made it a major agricultural region, producing a wide variety of crops, including corn, soybeans, cotton, and tobacco. The region’s agricultural heritage has contributed significantly to its economic prosperity and cultural identity.
- Forestry: The Coastal Plain’s vast forests are a valuable resource for timber production, providing materials for construction, furniture, and paper. Sustainable forestry practices are essential for maintaining the region’s ecological integrity and economic vitality.
- Tourism: The Atlantic Coastal Plain’s stunning beaches, scenic landscapes, and rich history have made it a major tourist destination. The region’s tourism industry provides employment opportunities and supports local economies.
- Urbanization: The Coastal Plain’s strategic location and access to transportation have fostered significant urbanization, with major cities like New York, Philadelphia, and Baltimore emerging as centers of commerce, finance, and culture.
The Atlantic Coastal Plain’s human impact is a complex and evolving story, characterized by both opportunities and challenges. Balancing economic development with environmental conservation is crucial for ensuring the region’s long-term sustainability.
Navigating the Future: Challenges and Opportunities
The Atlantic Coastal Plain faces a number of challenges, including:
- Sea Level Rise: The region is particularly vulnerable to sea level rise, which threatens coastal communities, infrastructure, and ecosystems. Adapting to rising sea levels will require innovative solutions and collaboration between government, industry, and communities.
- Coastal Erosion: Erosion is a natural process along the Atlantic Coast, but it is being exacerbated by sea level rise, storms, and human development. Protecting coastal communities and ecosystems will require strategic planning and investment in erosion control measures.
- Pollution: The Coastal Plain’s rivers, estuaries, and coastal waters are vulnerable to pollution from industrial activity, agriculture, and urban runoff. Addressing pollution requires a comprehensive approach that involves reducing sources of pollution and improving water quality management.
- Climate Change: The Atlantic Coastal Plain is experiencing the impacts of climate change, including increased frequency and intensity of storms, changes in precipitation patterns, and rising temperatures. Adapting to these changes will require innovative solutions and investment in climate resilience.
Despite these challenges, the Atlantic Coastal Plain also presents a number of opportunities for sustainable development:
- Renewable Energy: The region’s abundant wind and solar resources offer potential for developing renewable energy sources, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and contributing to a cleaner energy future.
- Ecotourism: The Coastal Plain’s diverse ecosystems and natural beauty offer opportunities for developing ecotourism, providing economic benefits while promoting environmental conservation.
- Green Infrastructure: Investing in green infrastructure, such as wetlands restoration and urban forestry, can improve water quality, reduce flooding, and create healthier communities.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing sustainable agricultural practices, such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage, can improve soil health, reduce water pollution, and enhance biodiversity.
Navigating the future of the Atlantic Coastal Plain requires a commitment to sustainable development, balancing economic growth with environmental protection. By working together, communities, governments, and businesses can address the region’s challenges and capitalize on its opportunities, ensuring a prosperous and sustainable future for generations to come.
FAQs
1. What are the defining characteristics of the Atlantic Coastal Plain?
The Atlantic Coastal Plain is characterized by its flat topography, sandy soils, and rich coastal ecosystems. It is formed by layers of sediment deposited over millions of years, creating a broad, gently sloping plain.
2. What is the significance of the Atlantic Coastal Plain in terms of human settlement and economic activity?
The Atlantic Coastal Plain has been a focal point for human settlement due to its fertile soils, abundant water resources, and access to transportation routes. It has been a major agricultural region, a source of timber, a tourist destination, and a hub for urbanization.
3. What are the major challenges facing the Atlantic Coastal Plain?
The Atlantic Coastal Plain faces challenges such as sea level rise, coastal erosion, pollution, and climate change. These challenges threaten coastal communities, infrastructure, and ecosystems.
4. What are some of the opportunities for sustainable development in the Atlantic Coastal Plain?
The Atlantic Coastal Plain presents opportunities for sustainable development in renewable energy, ecotourism, green infrastructure, and sustainable agriculture.
5. What are some tips for understanding and appreciating the Atlantic Coastal Plain?
To understand and appreciate the Atlantic Coastal Plain, it is helpful to:
- Explore the region’s diverse ecosystems: Visit coastal forests, wetlands, beaches, and estuaries to experience the region’s unique biodiversity.
- Learn about the region’s geological history: Visit geological formations and museums to understand the forces that shaped the Coastal Plain.
- Engage with local communities: Talk to residents, visit local businesses, and participate in community events to gain insight into the region’s culture and history.
- Support sustainable practices: Choose eco-friendly accommodations, support local businesses that prioritize environmental sustainability, and advocate for policies that protect the region’s natural resources.
Conclusion
The Atlantic Coastal Plain, a testament to the Earth’s geological history and human ingenuity, is a region of profound beauty and significance. Understanding its geological formation, appreciating its diverse ecosystems, and recognizing the challenges and opportunities it faces is essential for ensuring a sustainable future for this vital region. By working together, we can protect its natural resources, foster economic growth, and preserve its unique cultural heritage for generations to come.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Atlantic Coastal Plain: A Map of Geological History and Human Influence. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!